Cells movement across membranes pt 2
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
0 likes•2,548 views
Spring 2021
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Characteristics of Life

Museum of Science and Industry, Chicago: Science Teacher PD Course "All About You" > "Characteristics of Life" Lesson
Recommended
Characteristics of Life

Museum of Science and Industry, Chicago: Science Teacher PD Course "All About You" > "Characteristics of Life" Lesson
Cell- the unit of life (Introduction)

This presentation provides the overview of the CELL for senior secondary classes
Cilia and flagella ppt by ramana babu

molecular iology,and other then cell biology.....cilia and flagella
Cell d pharma 1st year Human anatomy and physiology

D pharma
Human anatomy ad physiology
Cell chapter
1.4 Notes

Guided notes covering material from Topic 1.4 of the updated IB Biology syllabus for 2016 exams. Notes sequence and prompts are based on the Oxford IB Biology textbook by Allott and Mindorff.
More Related Content
What's hot
Cell- the unit of life (Introduction)

This presentation provides the overview of the CELL for senior secondary classes
Cilia and flagella ppt by ramana babu

molecular iology,and other then cell biology.....cilia and flagella
Cell d pharma 1st year Human anatomy and physiology

D pharma
Human anatomy ad physiology
Cell chapter
What's hot (19)
Cell d pharma 1st year Human anatomy and physiology

Cell d pharma 1st year Human anatomy and physiology
Similar to Cells movement across membranes pt 2
1.4 Notes

Guided notes covering material from Topic 1.4 of the updated IB Biology syllabus for 2016 exams. Notes sequence and prompts are based on the Oxford IB Biology textbook by Allott and Mindorff.
BIOLOGY FORM 4 CHAPTER 3 - MOVEMENT OF SUBSTANCES ACROSS THE PLASMA MEMBRANE

BIOLOGY FORM 4 CHAPTER 3 - MOVEMENT OF SUBSTANCES ACROSS THE PLASMA MEMBRANE
Chapter 5 notes cell membranes and signalling

AP biology cell membranes, transport and cell signaling mechanisms
1.Define the term selectivity permeable2. A. Name 3 types of p.pdf

1.Define the term selectivity permeable
2. A. Name 3 types of passive transport
B. Does passive transport require cellular energy (e.g ATP) in order to occur
3.Define diffusion
4. A.Why does cell require substances to diffuse across the plasma membrane?
B. Give 2 examples of substances that must diffuse across the plasma membrane.
5. A. Name 5 factors that can affect diffusion across the plasma membrane
B. Which molecule would cross the cell membrane more easily- O2 (molecular oxygen) or
sodium ions? Why? Pre-Lab: Read the Introduction to this lab below. Complete the Pre-Lab
Questions to be turned in at the beginning of your next lab. Living organisms and cells are
constantly exchanging materials with their surroundings in order to stay alive. We take in food
molecules for energy and building materials for our tissues and organs and eliminate waste. We
take in oxygen when we breathe in and eliminate the waste product carbon dioxide when we
breathe out. The cells of our body are surrounded by bodily fluids, which are mostly water but
also contain many different molecules. So, the cell, like our bodies, must control or regulate what
goes in and out. Cells do that by controlling what crosses the cell or plasma membrane. In other
words, the plasma membrane is selectively permeable. Once the plasma membrane, they must
move through the cytoplasm rapidly enough to allow the cell to function. There are a number of
different ways that molecules can cross the selectively permeable plasma membrane, based on
the size and the chemical nature of the molecules. Some molecules move by a process called
passive transport. Remember that all molecules are constantly moving and the direction of this
movement is random; this molecular movement is referred to as Brownian motion. In passive
transport, molecules move from high concentration to low concentration
Solution
1. Selective permeable mean that a membrane allows only specific molecules to pass through it
and do not let others to pass. This can be through active or passive transport.
2. A. Passive transport includes transfer of molecules through the cell membrane without the
need of energy. This includes : Osmosis, Diffusion and Facilitated diffusion.
B. Passive transport does not require energy as it is down the concentration gradient..
Mechanism of transport of small molecules across membrane.pptx

Some molecules can easily diffuse through the plasma membrane while others cannot , so they require certain mechanisms for their transport which will be discussed in the following sections.
In this chapter, we consider how cell membranes control the traffic of inorganic ions and small, water-soluble molecules into and out of the cell and its membrane-enclosed organelles.
IB Cell Membrane & Transport Review (1.3-1.4)

Review worksheet covering IB Biology content in Membrane Structure and Cell Transport (Topics 1.3-1.4)
Answer the following questions about molecule movement across a membr.pdf

Answer the following questions about molecule movement across a membrane. a. How is
osmosis similar to simple diffusion of CO_2 across a membrane? How is it different? If an
aquaporin is involved, how does this change your answer? b. Compare and contrast carrier
proteins and channel proteins. Include information about both structure and mechanism of
transport. c. Compare and contrast indirect and direct active transport. Give a specific example
for each type of transport.
Solution
5a: Osmosis is the movement of water molecules down the concentration gradiant through a
semipermeable membrane. Both osmosis and simple diffusion of CO2 across a membrane occur
down the concentration gradiant and are passive transport. However, osmosis transports
hydrophilic water molecules while simple diffusion transports hydrophobic non polar CO2
molecules. If an aquaporin is involved, the proces would be called as facililated diffusion which
refers to transport of polar, charged, hydrophilic molecules down the concentration gradiant with
the help of membrane transport proteins.
5b: Carrier proteins are the transporter proteins that are actually the integral membrane proteins
serving in transport of ions across the membrane. These proteins have ion binding sites and
exhibit changes in shape to transport the ions. Channel proteins are the integral membrane
proteins that form the hydrophilic channels for transport of polar, charged and hydrophilic
substances across the membrane. They do not undergo the shape change.
5c: Direct active transport couples the exergonic chemical reaction for increasing the solute/ion
concentration on one side of the membrane. The indirect active transport includes coupling of
favorable downhill movement of one solute to the unfavorable uphill movement of other
substance. For ex: sodium potassium pump couples ATP hydrolysis with uphill movement of
sodium (direct active transport). Downhill movement of sodium coupled with uphill movement
of glucose (indirect active transport)..
Cellular transport

This presentation include different kind of transport mechanism of different material inside the cell and outside the cell including Passive transport and Active transport mechenism.
Similar to Cells movement across membranes pt 2 (20)
BIOLOGY FORM 4 CHAPTER 3 - MOVEMENT OF SUBSTANCES ACROSS THE PLASMA MEMBRANE

BIOLOGY FORM 4 CHAPTER 3 - MOVEMENT OF SUBSTANCES ACROSS THE PLASMA MEMBRANE
1.Define the term selectivity permeable2. A. Name 3 types of p.pdf

1.Define the term selectivity permeable2. A. Name 3 types of p.pdf
Mechanism of transport of small molecules across membrane.pptx

Mechanism of transport of small molecules across membrane.pptx
Answer the following questions about molecule movement across a membr.pdf

Answer the following questions about molecule movement across a membr.pdf
More from C Ebeling (20)
Recently uploaded
Operation Blue Star - Saka Neela Tara

Operation “Blue Star” is the only event in the history of Independent India where the state went into war with its own people. Even after about 40 years it is not clear if it was culmination of states anger over people of the region, a political game of power or start of dictatorial chapter in the democratic setup.
The people of Punjab felt alienated from main stream due to denial of their just demands during a long democratic struggle since independence. As it happen all over the word, it led to militant struggle with great loss of lives of military, police and civilian personnel. Killing of Indira Gandhi and massacre of innocent Sikhs in Delhi and other India cities was also associated with this movement.
Chapter 3 - Islamic Banking Products and Services.pptx

Chapter 3 - Islamic Banking Products and Services.pptxMohd Adib Abd Muin, Senior Lecturer at Universiti Utara Malaysia
This slide is prepared for master's students (MIFB & MIBS) UUM. May it be useful to all.Acetabularia Information For Class 9 .docx

Acetabularia acetabulum is a single-celled green alga that in its vegetative state is morphologically differentiated into a basal rhizoid and an axially elongated stalk, which bears whorls of branching hairs. The single diploid nucleus resides in the rhizoid.
Digital Artifact 2 - Investigating Pavilion Designs

Digital Artifact 2 - Pavilions
NGV Architecture Commission Competition
MPavilion Commission Competition
Other Pavilion Designs
TESDA TM1 REVIEWER FOR NATIONAL ASSESSMENT WRITTEN AND ORAL QUESTIONS WITH A...

TESDA TM1 REVIEWER FOR NATIONAL ASSESSMENT WRITTEN AND ORAL QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS.
Honest Reviews of Tim Han LMA Course Program.pptx

Personal development courses are widely available today, with each one promising life-changing outcomes. Tim Han’s Life Mastery Achievers (LMA) Course has drawn a lot of interest. In addition to offering my frank assessment of Success Insider’s LMA Course, this piece examines the course’s effects via a variety of Tim Han LMA course reviews and Success Insider comments.
Introduction to AI for Nonprofits with Tapp Network

Dive into the world of AI! Experts Jon Hill and Tareq Monaur will guide you through AI's role in enhancing nonprofit websites and basic marketing strategies, making it easy to understand and apply.
How libraries can support authors with open access requirements for UKRI fund...

How libraries can support authors with open access requirements for UKRI funded books
Wednesday 22 May 2024, 14:00-15:00.
Unit 8 - Information and Communication Technology (Paper I).pdf

This slides describes the basic concepts of ICT, basics of Email, Emerging Technology and Digital Initiatives in Education. This presentations aligns with the UGC Paper I syllabus.
Normal Labour/ Stages of Labour/ Mechanism of Labour

Normal labor is also termed spontaneous labor, defined as the natural physiological process through which the fetus, placenta, and membranes are expelled from the uterus through the birth canal at term (37 to 42 weeks
"Protectable subject matters, Protection in biotechnology, Protection of othe...

Protectable subject matters, Protection in biotechnology, Protection of other biological materials, Ownership and period of protection
Unit 2- Research Aptitude (UGC NET Paper I).pdf

This slide describes the research aptitude of unit 2 in the UGC NET paper I.
Overview on Edible Vaccine: Pros & Cons with Mechanism

This ppt include the description of the edible vaccine i.e. a new concept over the traditional vaccine administered by injection.
Chapter -12, Antibiotics (One Page Notes).pdf

This is a notes for the D.Pharm students and related to the antibiotic drugs.
The Challenger.pdf DNHS Official Publication

Read| The latest issue of The Challenger is here! We are thrilled to announce that our school paper has qualified for the NATIONAL SCHOOLS PRESS CONFERENCE (NSPC) 2024. Thank you for your unwavering support and trust. Dive into the stories that made us stand out!
Recently uploaded (20)
Chapter 3 - Islamic Banking Products and Services.pptx

Chapter 3 - Islamic Banking Products and Services.pptx
Digital Artifact 2 - Investigating Pavilion Designs

Digital Artifact 2 - Investigating Pavilion Designs
TESDA TM1 REVIEWER FOR NATIONAL ASSESSMENT WRITTEN AND ORAL QUESTIONS WITH A...

TESDA TM1 REVIEWER FOR NATIONAL ASSESSMENT WRITTEN AND ORAL QUESTIONS WITH A...
Introduction to AI for Nonprofits with Tapp Network

Introduction to AI for Nonprofits with Tapp Network
How libraries can support authors with open access requirements for UKRI fund...

How libraries can support authors with open access requirements for UKRI fund...
Unit 8 - Information and Communication Technology (Paper I).pdf

Unit 8 - Information and Communication Technology (Paper I).pdf
Normal Labour/ Stages of Labour/ Mechanism of Labour

Normal Labour/ Stages of Labour/ Mechanism of Labour
"Protectable subject matters, Protection in biotechnology, Protection of othe...

"Protectable subject matters, Protection in biotechnology, Protection of othe...
Multithreading_in_C++ - std::thread, race condition

Multithreading_in_C++ - std::thread, race condition
Overview on Edible Vaccine: Pros & Cons with Mechanism

Overview on Edible Vaccine: Pros & Cons with Mechanism
Cells movement across membranes pt 2
- 1. Cells - Movement across membranes BIOL 1306 Ebeling
- 2. Learning Objectives 1.Describe the properties of a cell. 2.Identify the components common to all cells. 3.Compare and contrast the cells that characterize the three domains of life. 4.Explain how the chemical structure of phospholipids enables them to form a bilayer in water. 5.Explain why a biological membrane has selective permeability. 6.Identify different functions of membrane proteins. 7.Compare and contrast the ways that molecules move across membranes. 8.Explain the relationship between diffusion and concentration gradients. 9.Explain how processes of passive transport work including Osmosis and Diffusion 10.Explain how mechanisms of active transport work including the Sodium-Potassium Pump 11.Explain how larger objects/molecules cross membranes including: Exocytosis and Endocytosis 12.Predict when each of these transport mechanisms might be in use 13.Identify the functions of the organelles in eukaryotic cells. 14.Describe how organelles interact in carrying out a cell’s function. 15.Compare and contrast the structure and function of cytoskeletal proteins 16.Compare and contrast different cell junctions in animal cells. 17.Explain the function of plasmodesmata in plant cells.
- 3. Phospholipids act as semipermeable membranes
- 5. Section 4.5 This image is a concentration gradient of black pixels, with high concentration at the top and low concentration at the bottom. At the top, the black pixels are abundant and close together. High concentration of black pixels Low concentration of black pixels At the bottom, the black pixels are sparse. “Gradient” Describes a Difference Between Neighboring Regions
- 6. Section 4.5 The balls within this box have the same concentration gradient as the black pixels did. High concentration of balls Low concentration of balls This arrow points down the concentration gradient since it starts at high concentration and ends at low concentration of balls. Concentration Gradients Have a Tendency to Dissipate
- 7. Movement across membranes • Passive Transport – does not require input of energy – leads to equilibrium – Simple diffusion – Facilitated diffusion – Osmosis • Active Transport – requires energy input – can concentrate substances
- 9. Section 4.5 In simple diffusion, particles move from high concentration to low concentration—that is, they move down their concentration gradient. Low concentration areas High concentration areas Figure 4.15 Passive Transport Does Not Require Energy
- 11. Section 4.5 Facilitated diffusion is passive transport that requires membrane proteins. Table 4.2 Passive Transport Does Not Require Energy
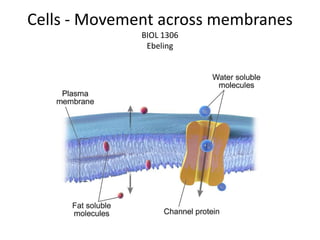
- 12. Membrane Proteins Transport Ions and Polar Molecules Section 4.5 The hydrophobic tails of phospholipids repel hydrophilic substances. Therefore, ions (such as Cl- and Na+) and polar substances must pass through a protein channel to cross the membrane. Table 4.2 Return to AP
- 13. Section 4.5 Osmosis, the diffusion of water down its concentration gradient, is also a type of passive transport. Figure 4.16 Passive Transport Does Not Require Energy
- 14. Section 4.5 Water moves toward high solute concentrations as it moves down its concentration gradient. Figure 4.17 Passive Transport Does Not Require Energy All blood cells: © Dr. David M. Phillips/Visuals Unlimited
- 18. Turgor Pressure
- 19. Active Transport
- 20. Active Transport Requires Energy Section 4.5 In active transport, the cell uses energy and a transport protein to move a substance against its concentration gradient. Table 4.2
- 22. For example, the sodium- potassium pump uses ATP to transport Na+ and K+ across the membrane. Figure 4.19 Section 4.5 Active Transport Requires Energy
- 23. Endocytosis
- 26. Membrane Transport Summary Is the substance nonpolar? Yes No Is the substance moving down its concentration gradient? Yes No Is the substance very large? No Yes Is the substance entering or leaving the cell? Exocytosis Facilitated diffusion Simple diffusion Active transport Entering Endocytosis Leaving Section 4.5