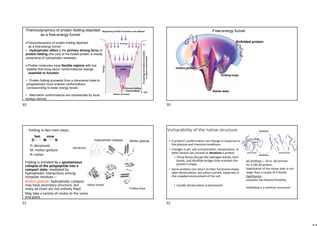
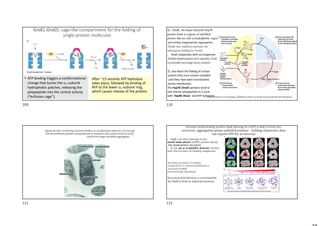
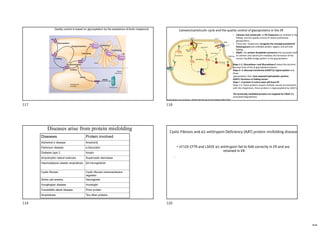
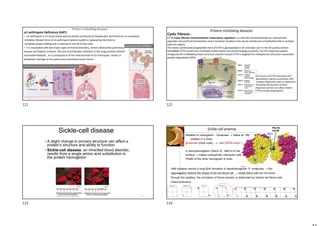
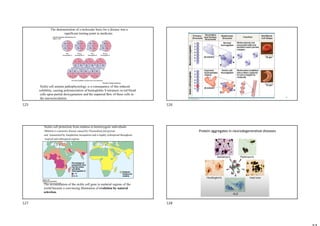
The document provides information on protein structure and function including:
- Proteins have a variety of functions including catalysis, structure, transport, signaling, and storage.
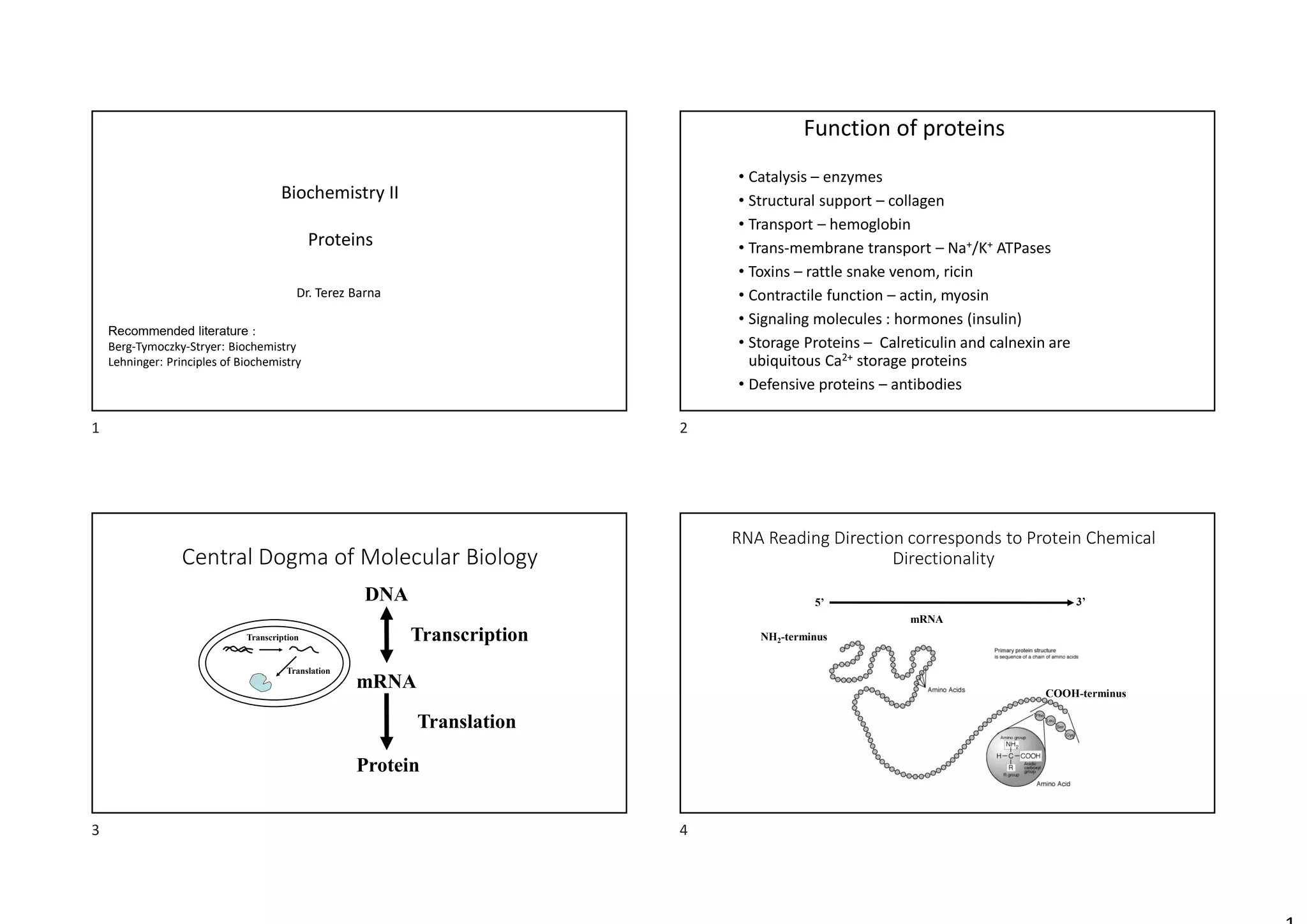
- The central dogma of molecular biology describes how DNA is transcribed into mRNA and then translated into proteins.
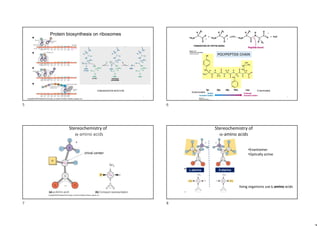
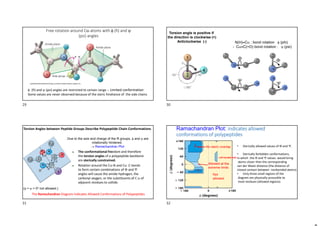
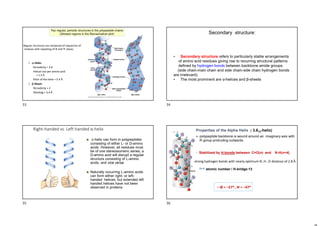
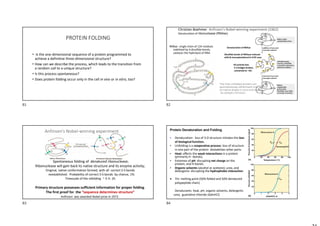
- Protein structure is determined by each protein's unique amino acid sequence and how they fold into secondary structures like alpha helices and beta sheets.
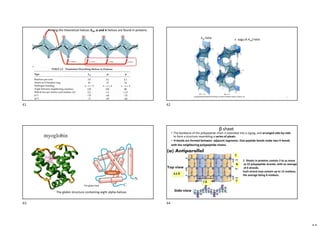
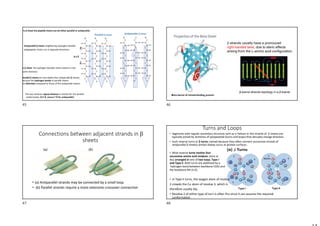
- The alpha helix and beta sheet are the most common secondary structures, stabilized by hydrogen bonds between amino acids in the backbone.











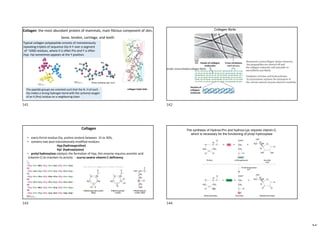
![Permanent Waving
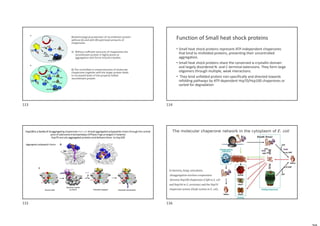
• Keratin is rich in Cys residues, which form disulfide bonds that crosslink adjacent
polypeptide chains.
• The keratins are classified as “hard” or “soft” according to whether they have a high
or low sulfur content (hard keratins: hair, horn, and nail).
• The disulfide bonds can be reductively cleaved by disulfide interchange with mercaptans .
Hair so treated can be curled and set in a “permanent wave” by applying an oxidizing agent
that reestablishes the disulfide bonds in the new “curled” conformation.
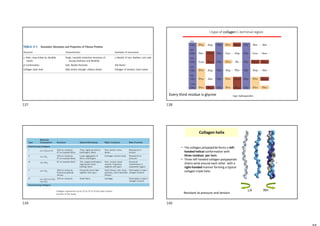
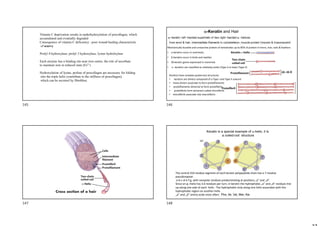
• Extended -conformation, forces involved:
H-bonds between different sheets, made
by: insects and spiders
• Silk does not stretch because it is already
highly extended
• Rich in Ala and Gly, allowing close packing
Ser Ala Ala
. / / / /
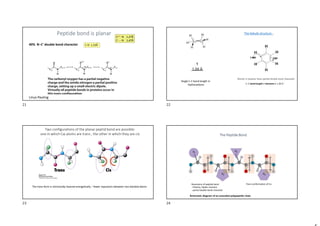
. Gly Gly Gly
600-times repeat
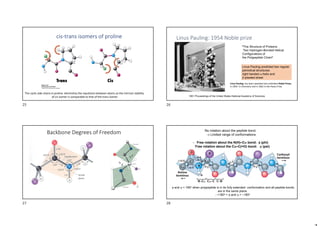
•It forms antiparalel -sheet
•The insertion of Val and Tyr in the -sheet
causes flexibility of the structure
[ ]
Silk Fibroin
149 150](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/proteinstructure2022-221130172539-677f0b10/85/Protein_structure_2022-pdf-38-320.jpg)