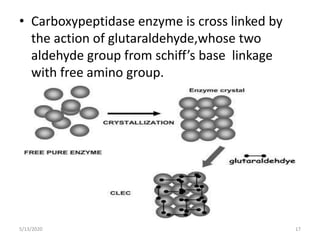
1. Immobilization of enzymes refers to confining enzymes to an inert support to make them more stable and reusable for industrial applications.
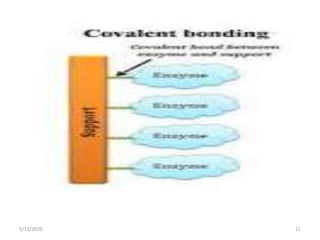
2. Common immobilization methods include adsorption, ionic bonding, covalent bonding, entrapment, microencapsulation, and cross-linking.
3. Immobilized enzymes have advantages like stability, reusability, and being suitable for industrial processes, but their activity may be reduced compared to free enzymes.