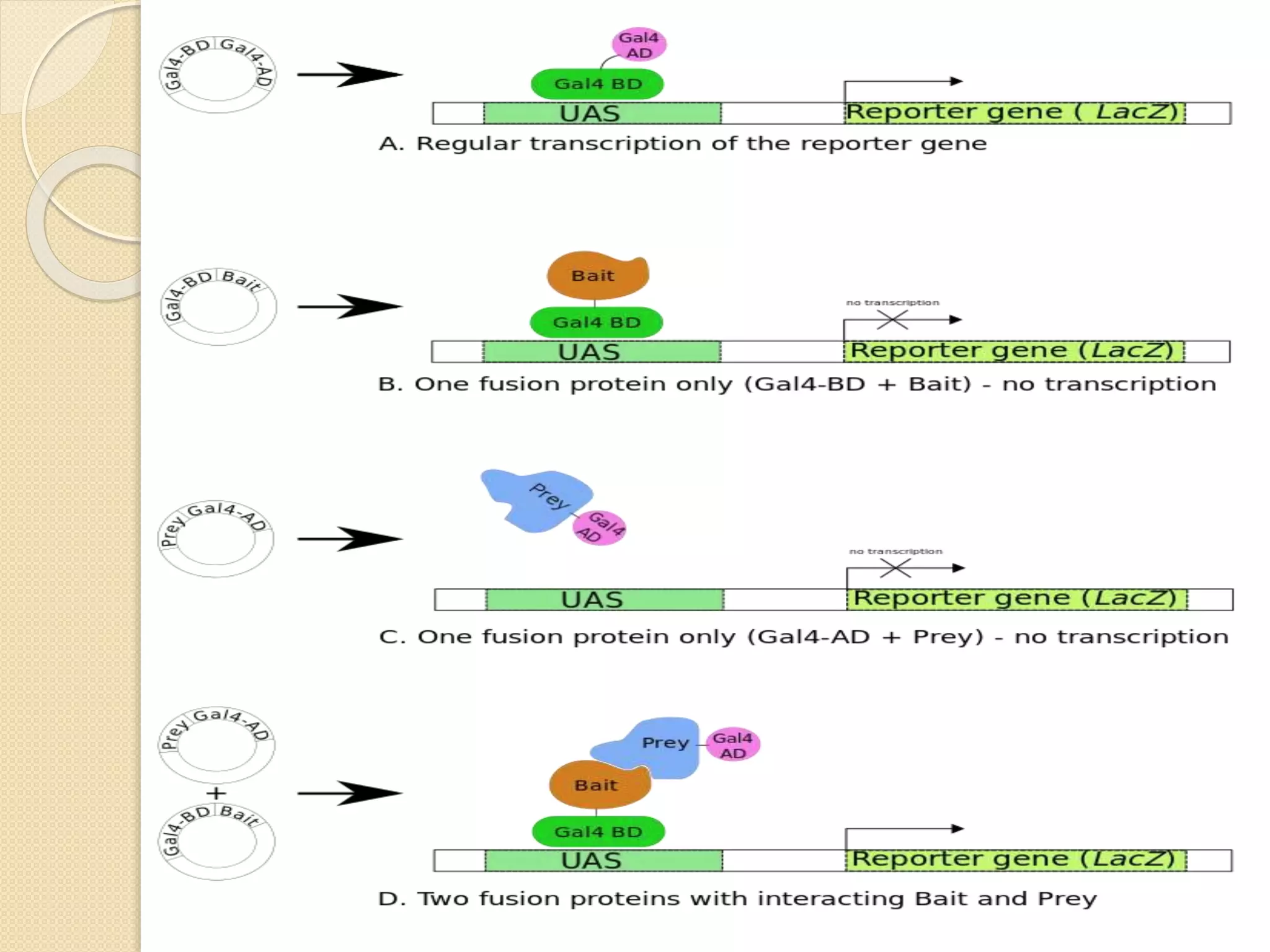
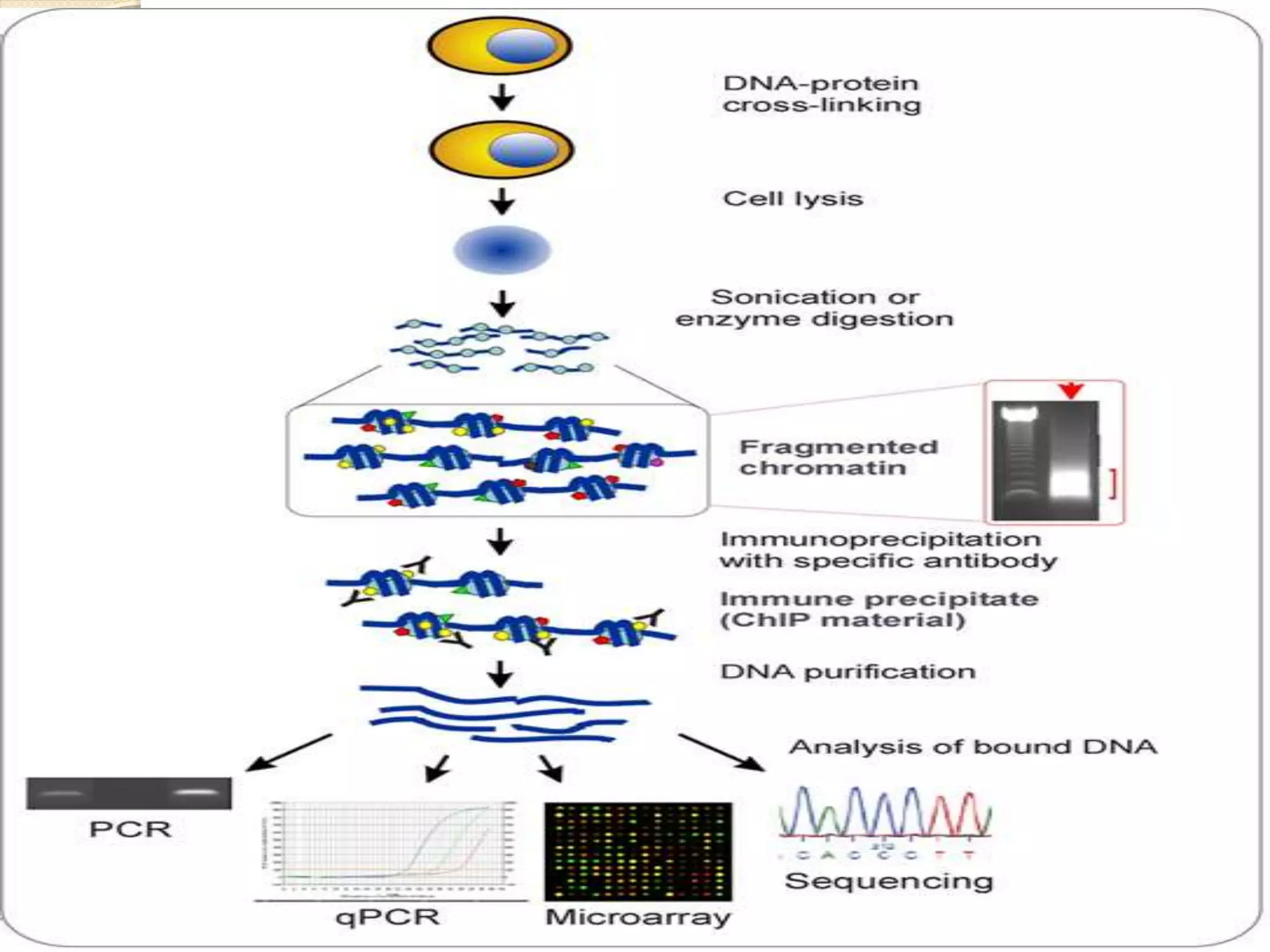
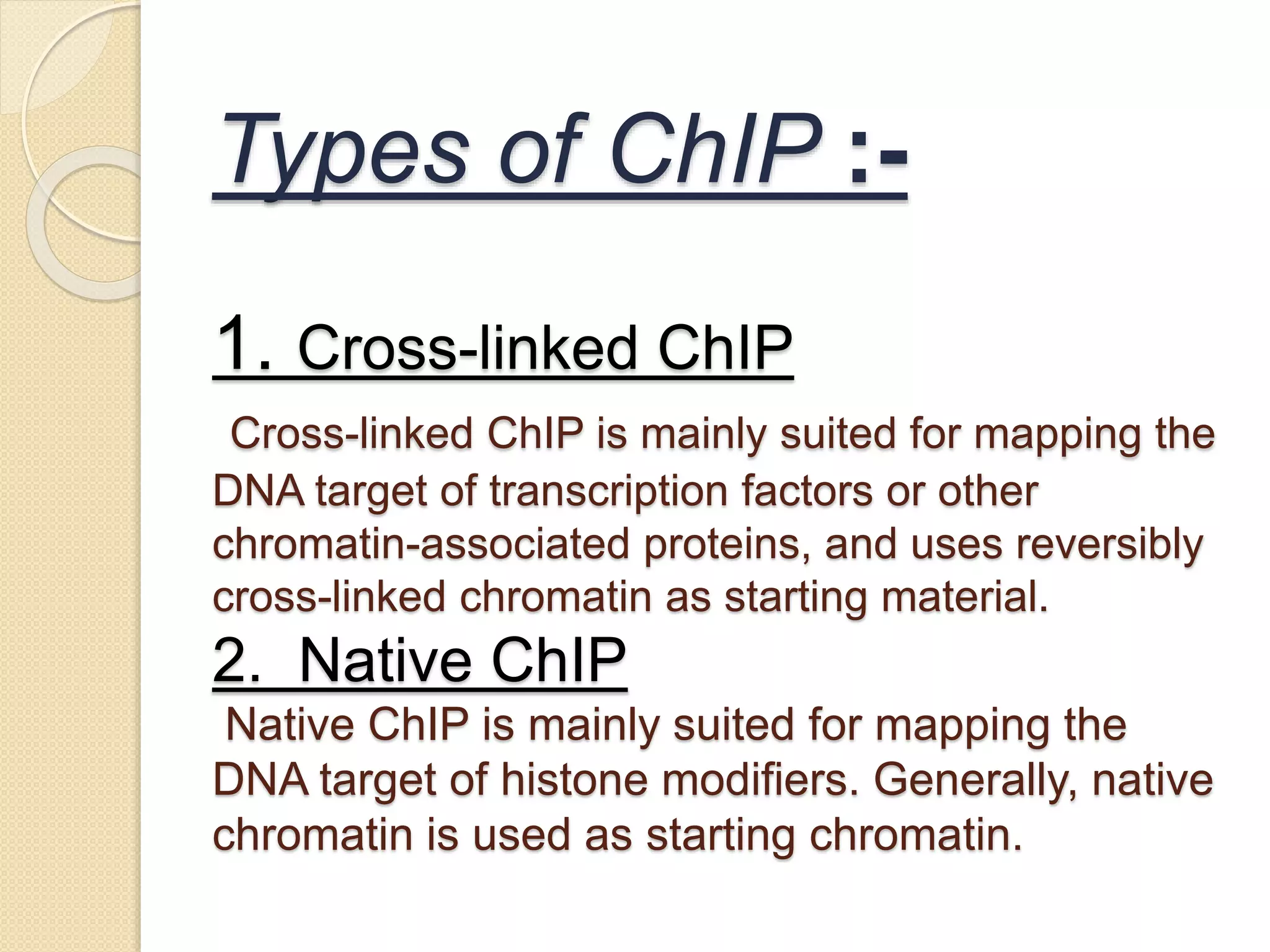
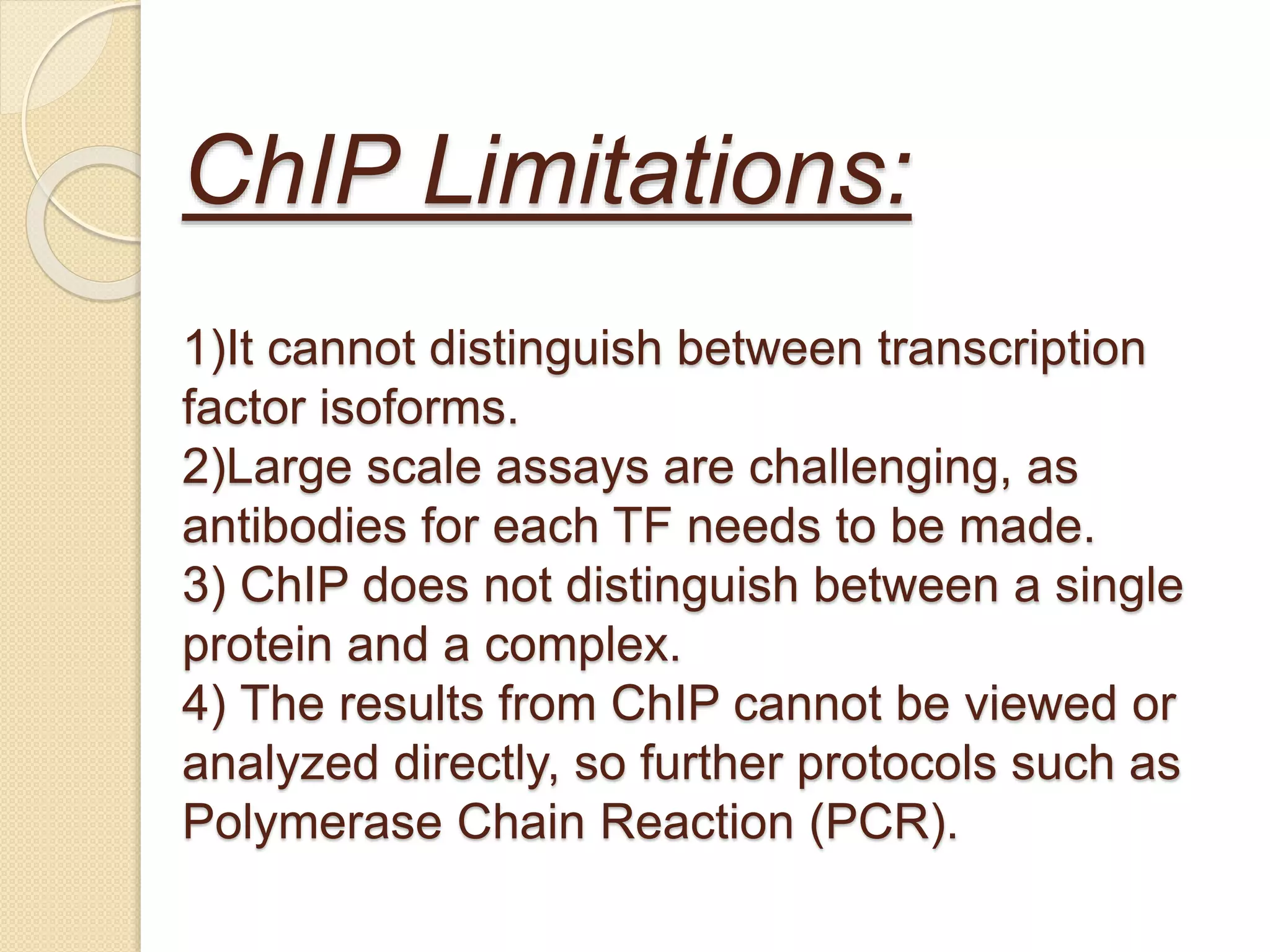
The yeast two hybrid (Y2H) system, developed in 1989, is a technique for studying protein-protein interactions by utilizing specific protein domains to link transcription factors and activate reporter genes. While it offers advantages like simplicity and partner identification, it has limitations such as potential absence of interactions in yeast and possible interference from fusion proteins. Conversely, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) is a method to analyze protein-DNA interactions but faces challenges like distinguishing protein isoforms and difficulty with large-scale assays.