The document discusses various aspects of protein structure, including:
1) Proteins have primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels of structure that determine their shape and function.
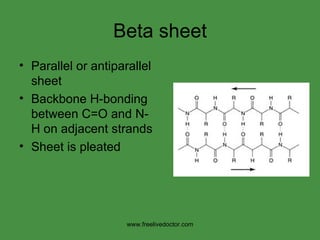
2) Secondary structures like alpha helices and beta sheets involve hydrogen bonding between amino acids in the protein chain.
3) Tertiary structure refers to a protein's final 3D shape after folding. Quaternary structure involves interactions between protein subunits.
4) Techniques like X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy can be used to determine protein structures at high resolutions.