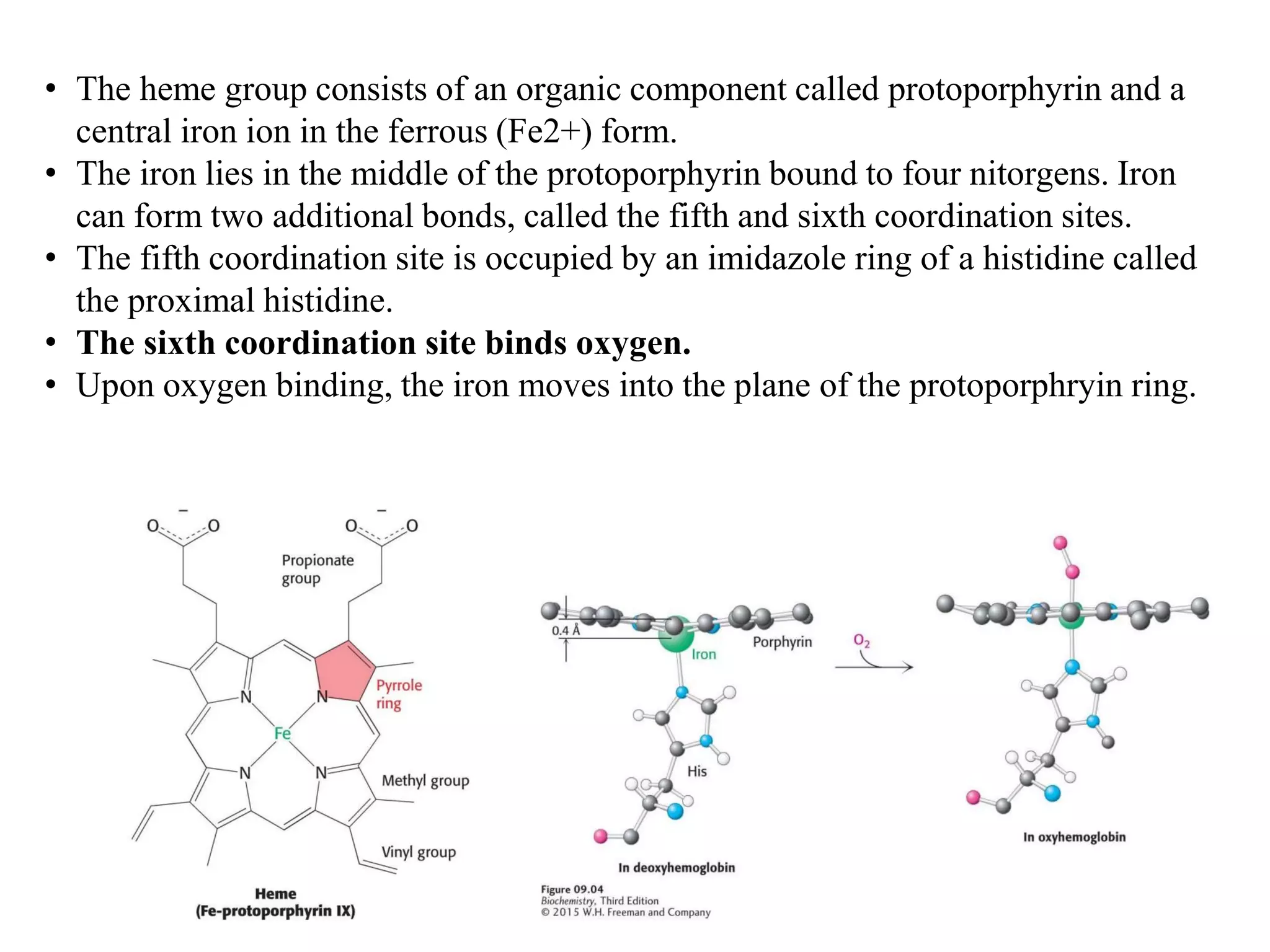
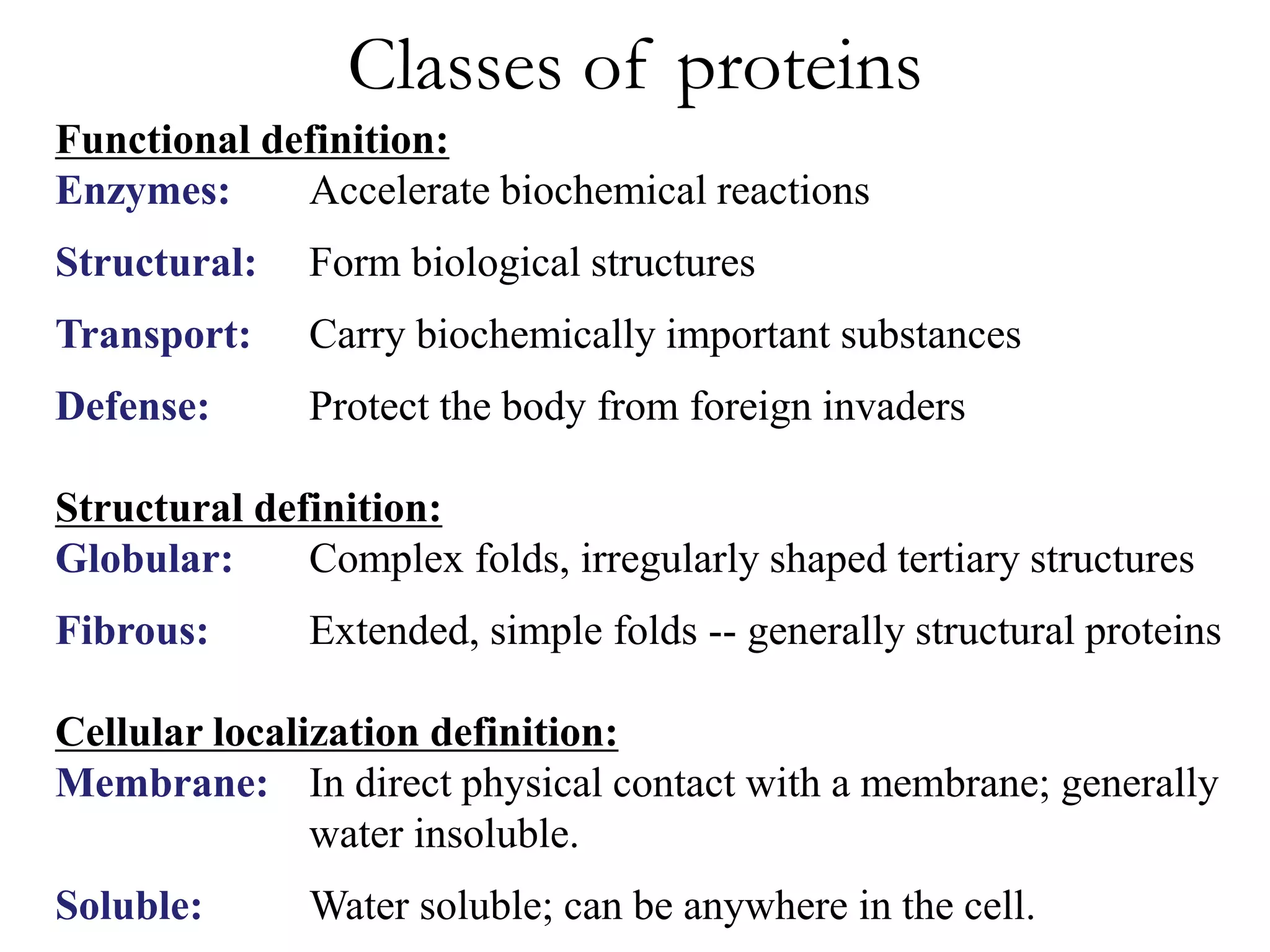
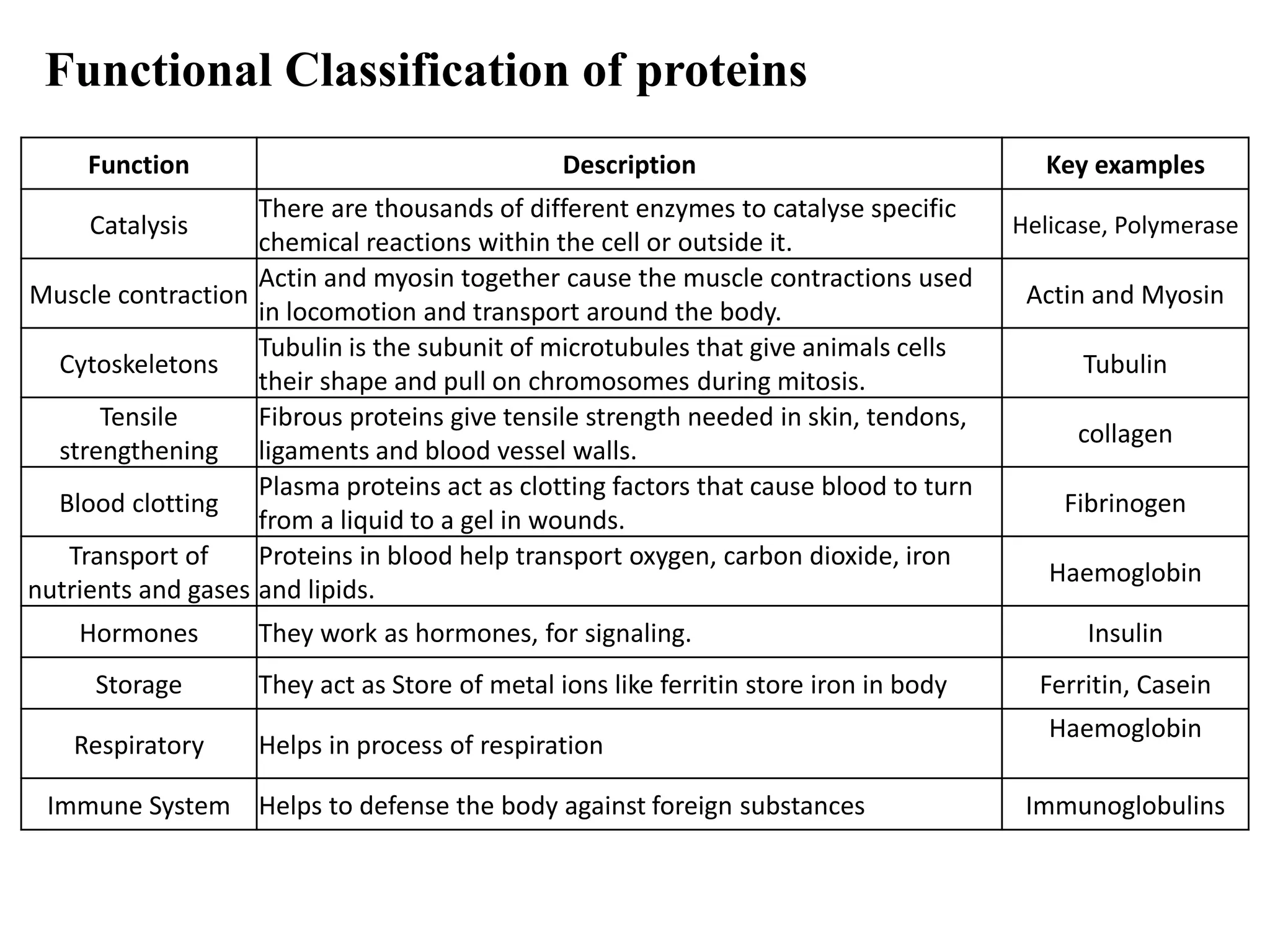
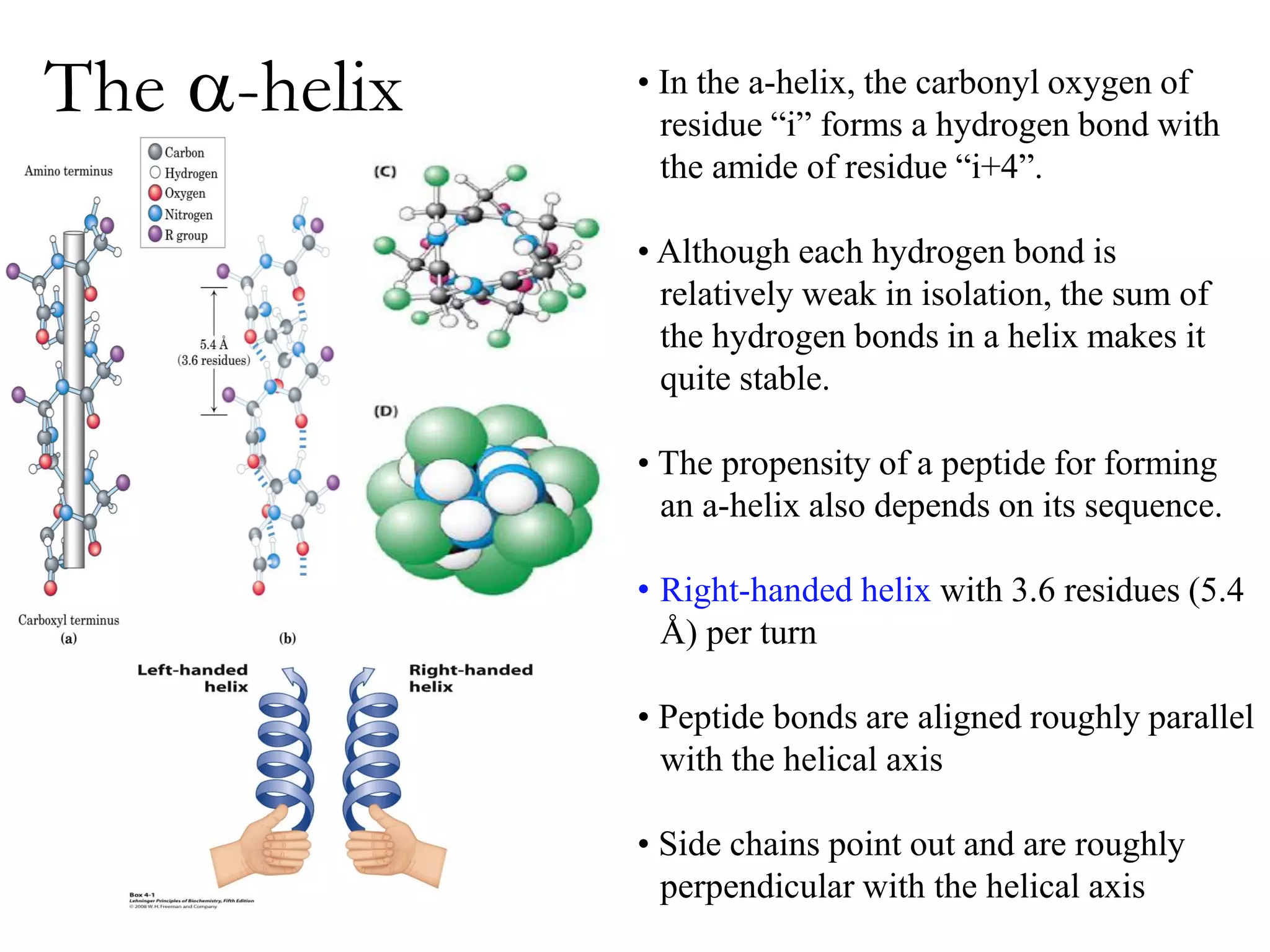
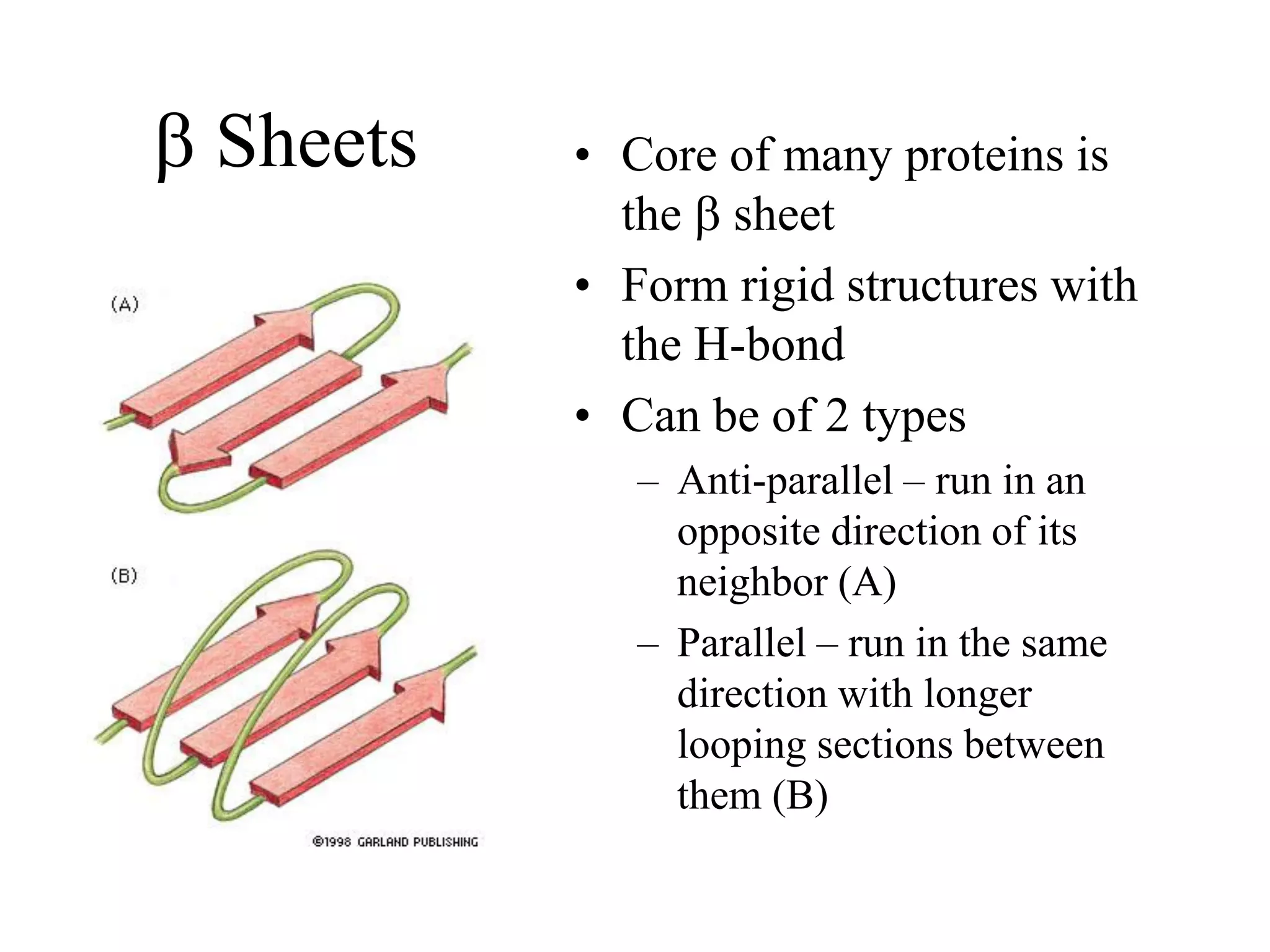
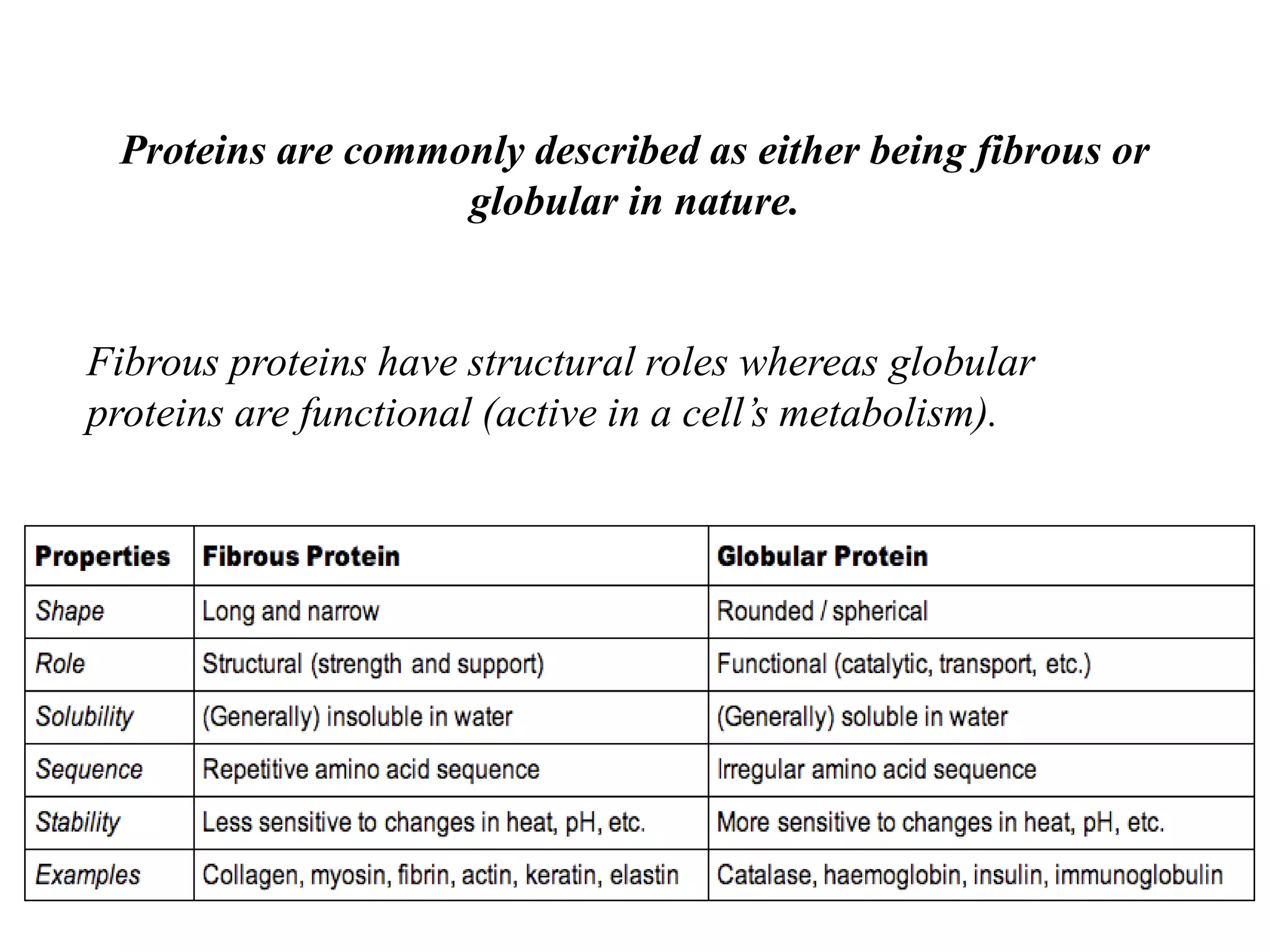
Proteins have four levels of structure: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. The primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids. Regular patterns of hydrogen bonding in the primary structure give rise to secondary structures like alpha helices and beta sheets. The overall three-dimensional folded structure of a protein is its tertiary structure, stabilized by interactions between R groups. Quaternary structure involves the assembly of multiple protein subunits. Common protein structures were discussed including fibrous proteins, globular proteins, and structural elements like helices and sheets.





















![Hemoglobin function
a2,b2 dimer which are structurally similar to myoglobin
•Transports oxygen from lungs to tissues.
•O2 diffusion alone is too poor for transport in larger animals.
•Solubility of O2 is low in plasma i.e. 10-4 M.
•But bound to hemoglobin, [O2] = 0.01 M or that of air
•Two alternative O2 transporters are;
•Hemocyanin, a Cu containing protein.
•Hemoerythrin , a non-heme containing protein.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/proteinfinal1-230304151151-82a8d102/75/protein-25-2048.jpg)