1. Prosthetic valve obstruction can be life-threatening, with morbidity and mortality rates ranging from 0.1-6% per patient year depending on the valve type and position.
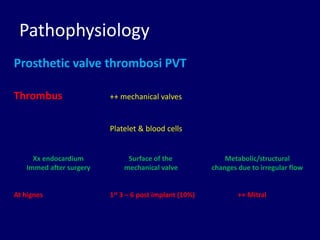
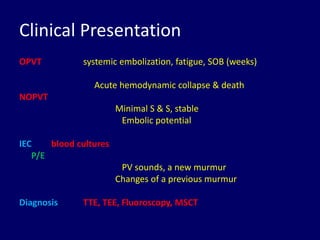
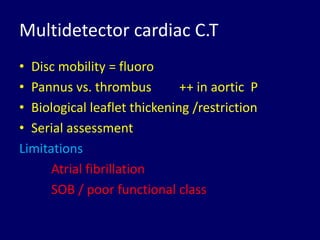
2. Thrombus, pannus, and vegetation are common causes of prosthetic valve obstruction. Predictors include valve type, anticoagulation status, valve position, atrial fibrillation, and ventricular dysfunction.
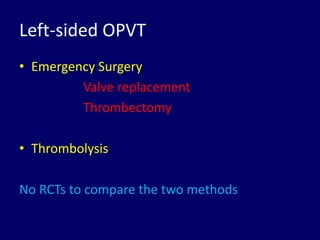
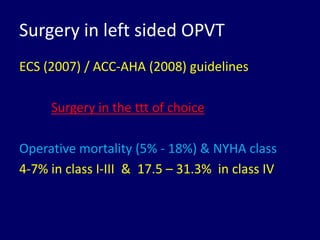
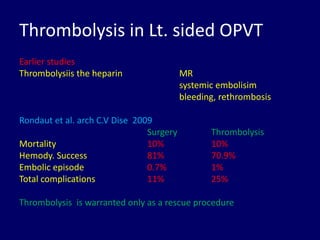
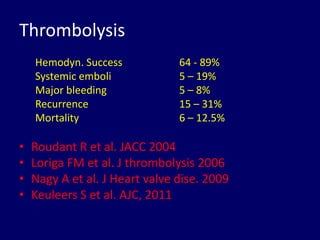
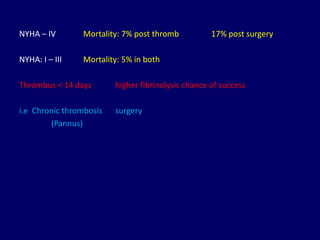
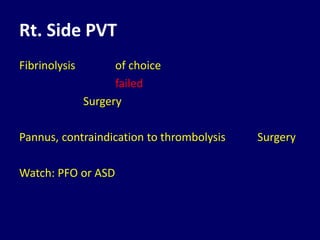
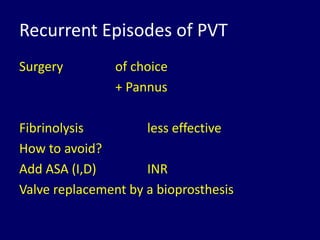
3. Treatment depends on the location and size of obstruction, functional status, and surgical risk. For left-sided obstruction, surgery is generally preferred but thrombolysis may be considered for lower risk patients with smaller thrombi.