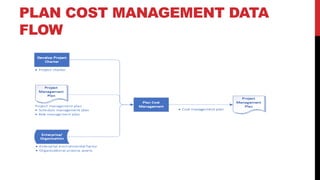
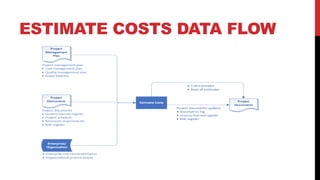
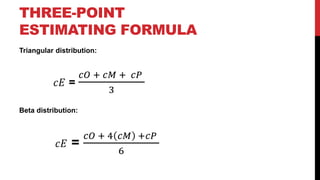
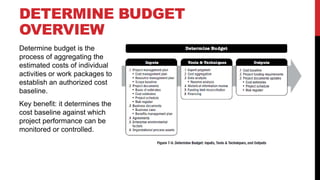
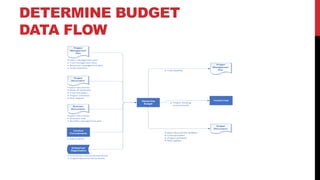
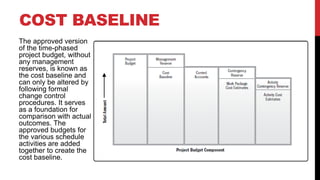
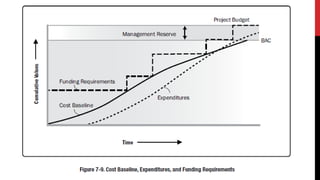
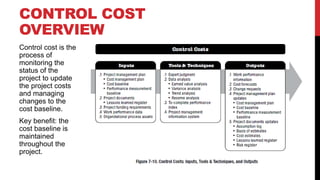
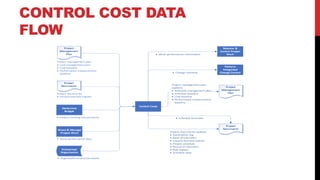
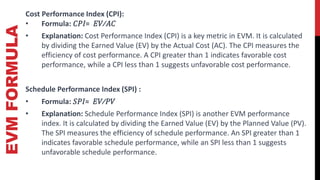
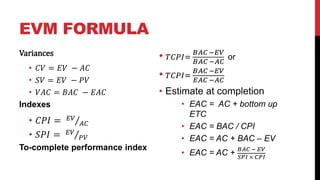
This document provides an overview of project cost management processes including plan cost management, estimate costs, determine budget, and control costs. Key concepts such as earned value management, cost estimating techniques like three-point estimating, and terms like cost baseline and management reserve are defined. The document also discusses trends in project cost management like expanding earned value management to include earned schedule. Sample formulas for calculating earned value metrics like cost variance, schedule variance, and estimate at completion are provided.