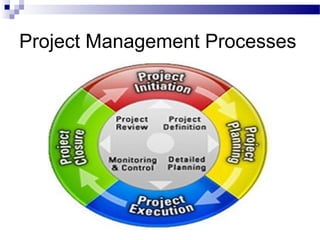
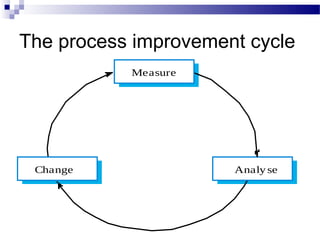
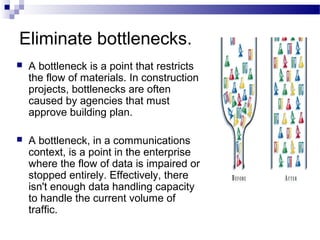
The document discusses improving project management processes. It describes projects, project management, and processes. There are nine key project management processes: scope, schedule, budget, quality, team, stakeholder, information, risk, and contract management. These processes can be improved through measurement, analysis, and change. Process improvement focuses on reducing defects, costs, and schedules. Continuous improvement is important to keep up with competition.