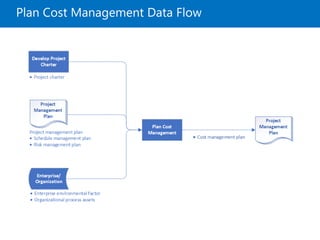
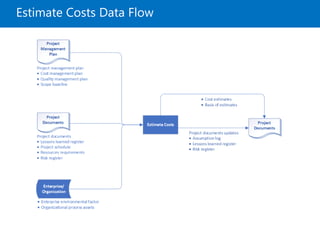
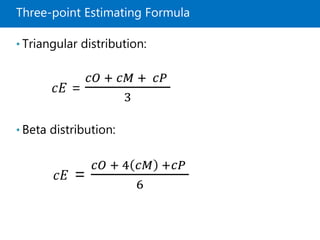
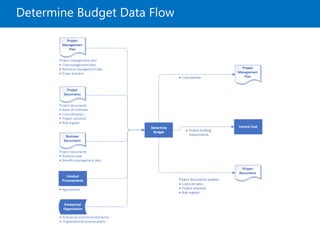
The document covers project cost management, emphasizing key processes such as planning, estimating, budgeting, and controlling costs to ensure projects are completed within approved budgets. It includes definitions and trends related to cost management, different types of costs, and tools and techniques for estimating and controlling costs. Key concepts like earned value management and life cycle costing, as well as the importance of adaptive practices in project environments, are highlighted.




























![References
• [PMBOK6] – The PMBOK 6th edition from pmi.org
• [RITA9] – Rita Mulcahy’s PMP Exam Prep 9th
edition from RMC Publications™](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmp07-cost-180417011543/85/Project-Cost-Management-PMBOK6-39-320.jpg)