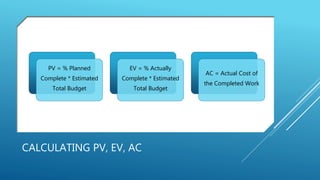
The document outlines the processes involved in project cost management, including planning, estimating, budgeting, and controlling costs to ensure that projects stay within budget. It details techniques for estimating project costs, creating a cost baseline, and using earned value management to track performance against budget. Key concepts include cost management plans, contingency reserves, and various estimating techniques to manage expenses effectively.