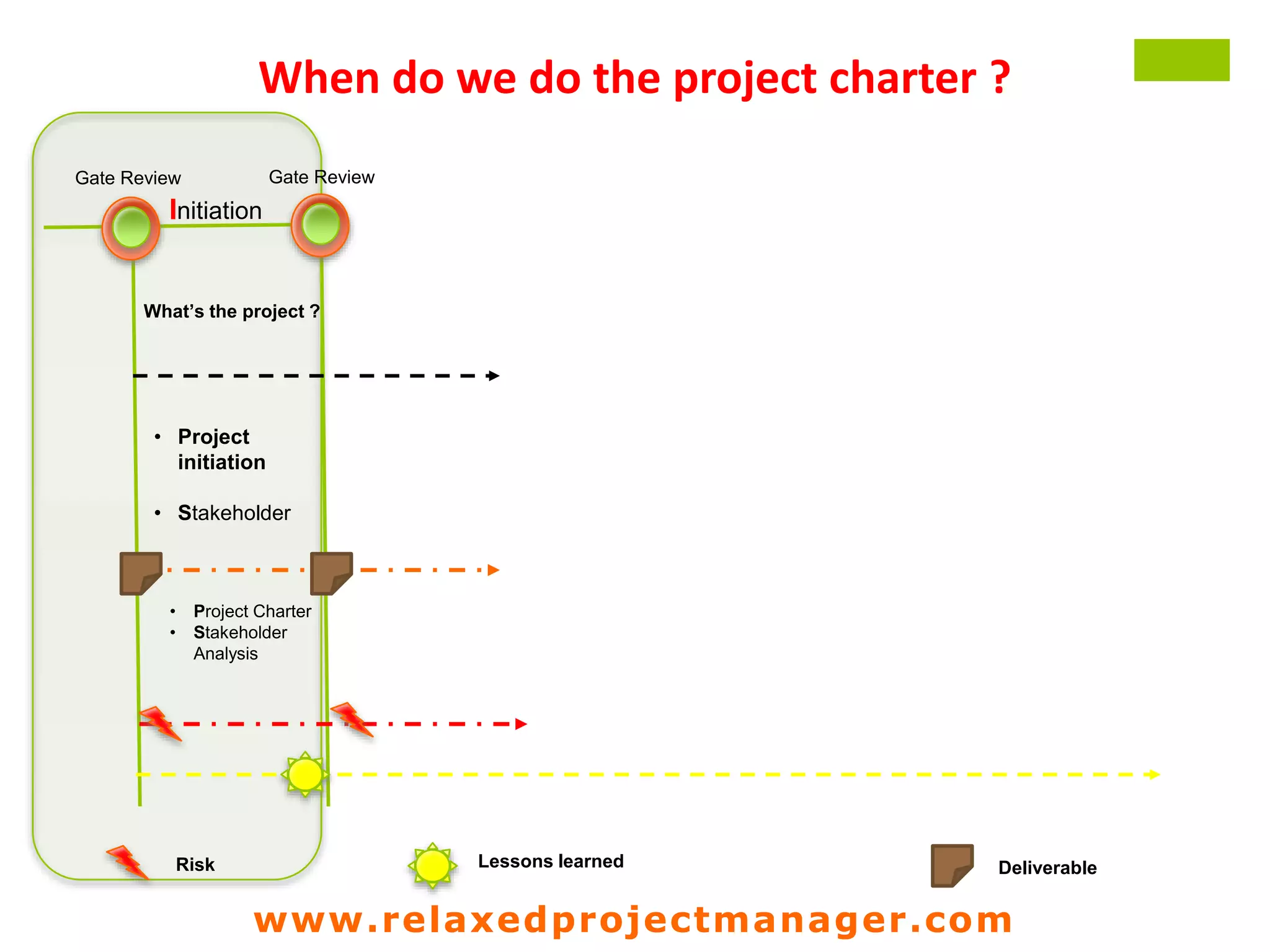
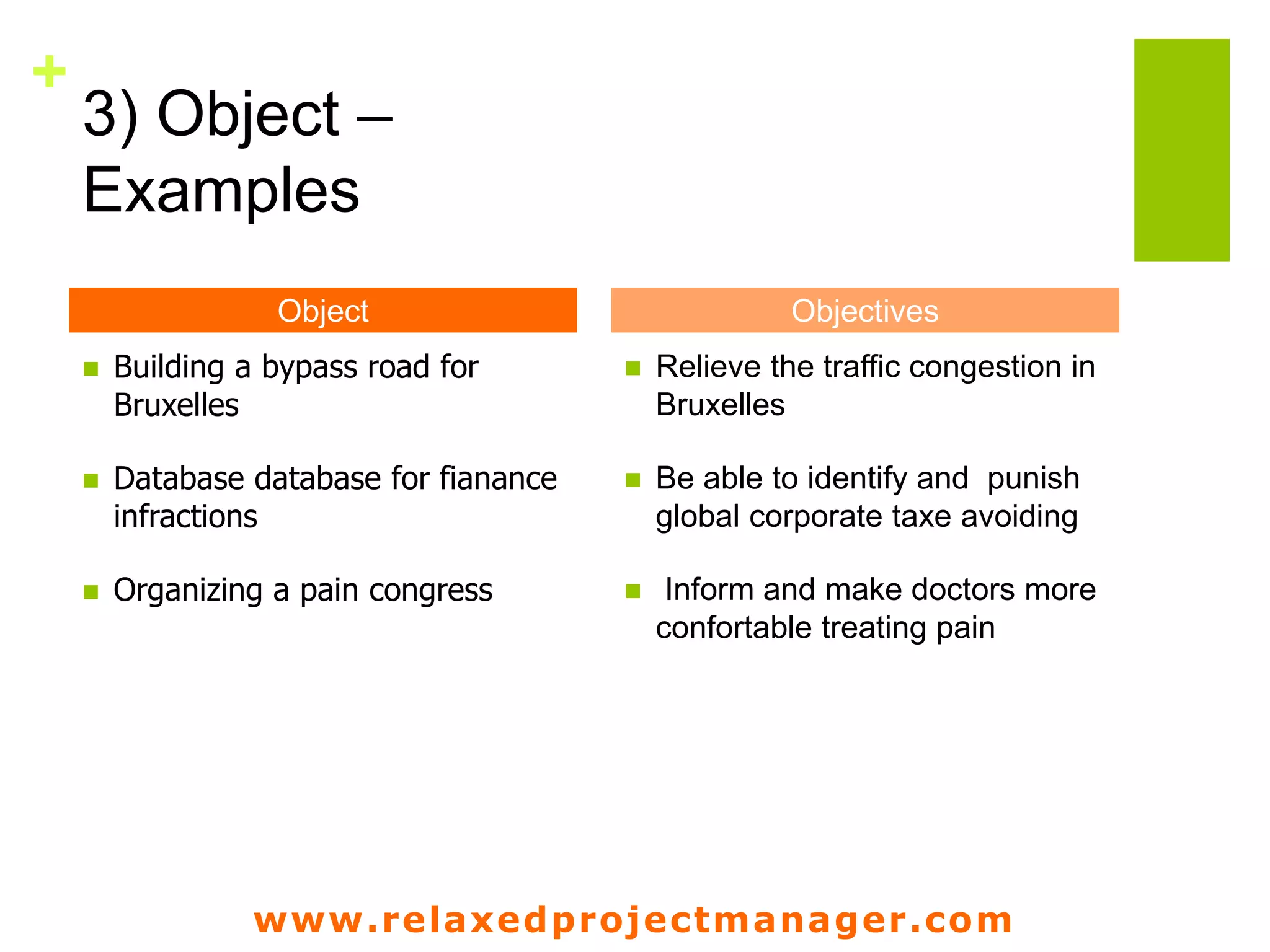
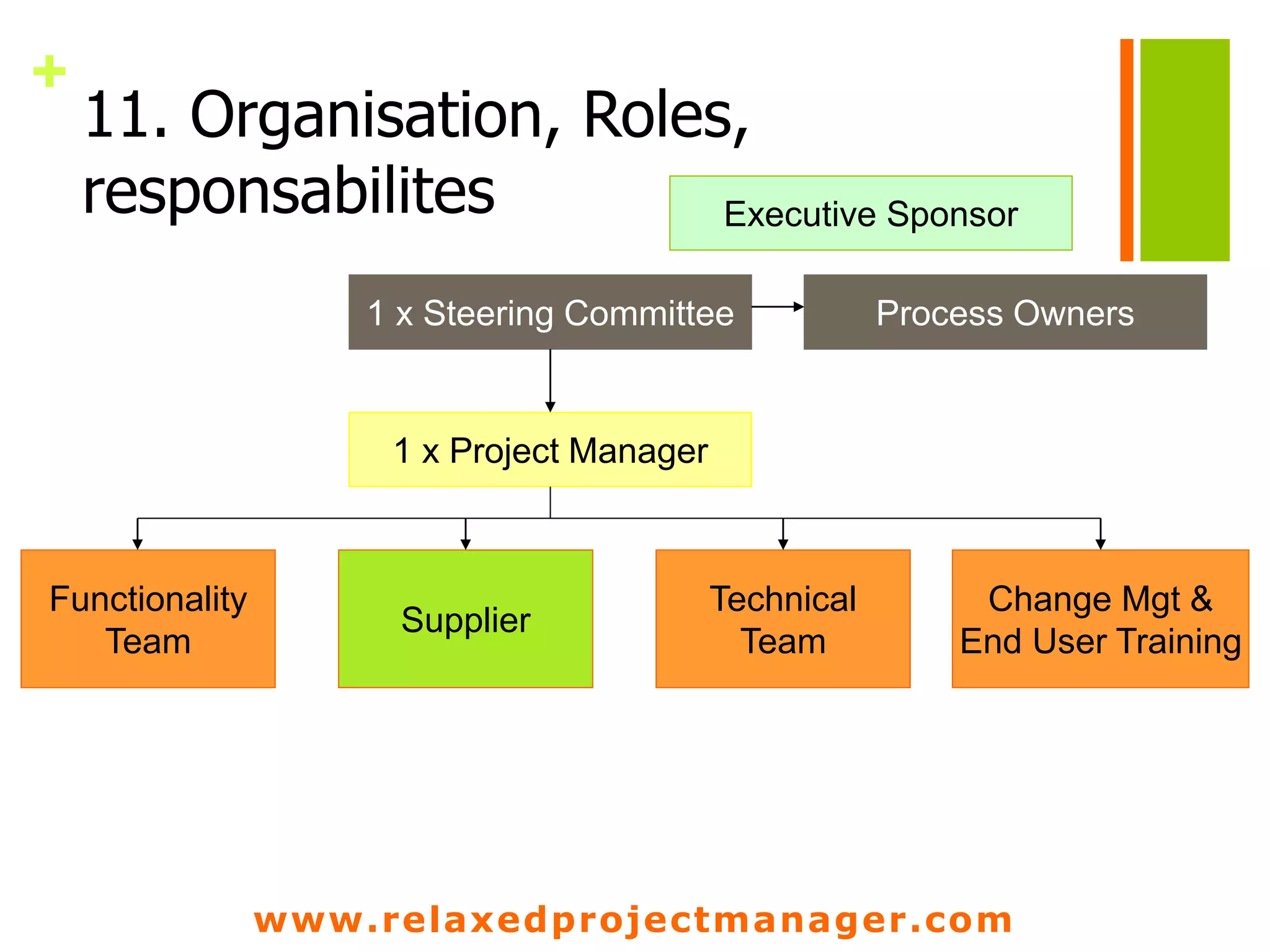
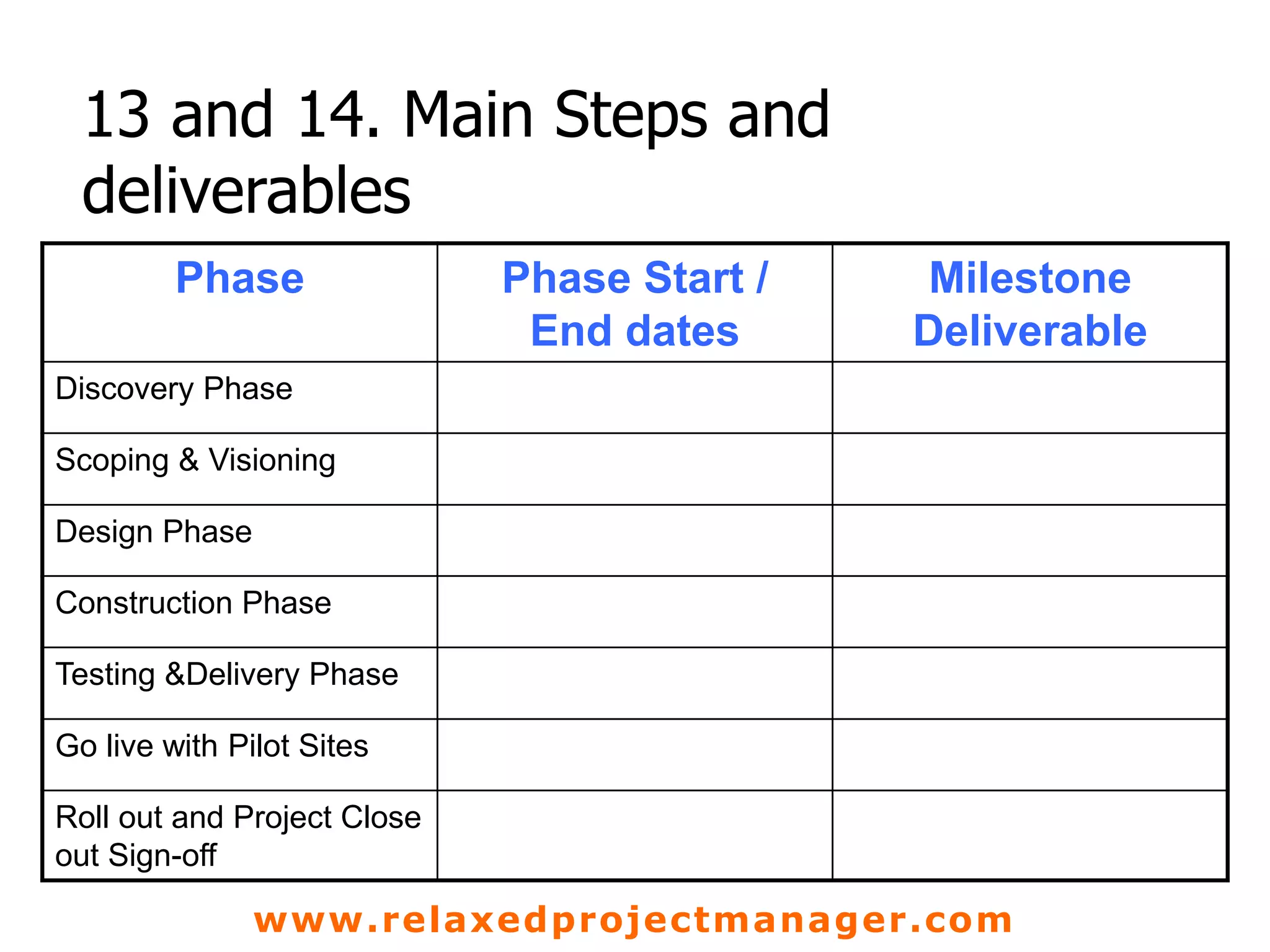
The document discusses key elements to include in a project charter such as the project description, objectives, scope, assumptions, constraints, roles and responsibilities, stakeholders, steps, deliverables, and risks. It emphasizes that the charter is an agreement between the project manager and sponsor that defines the project goals, deliverables, schedule, and resources. It should provide a clear and shared understanding of the project for all involved parties.