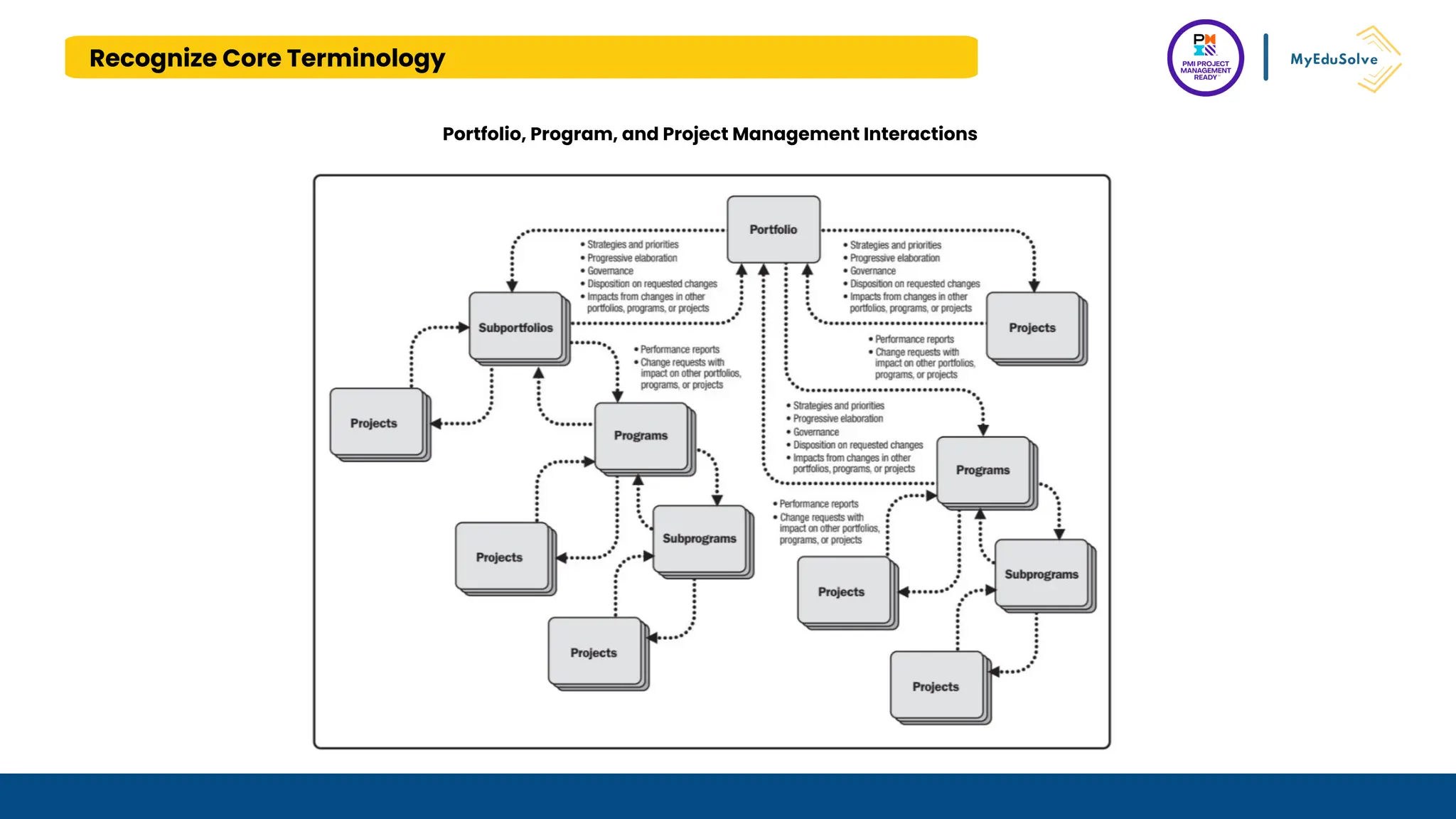
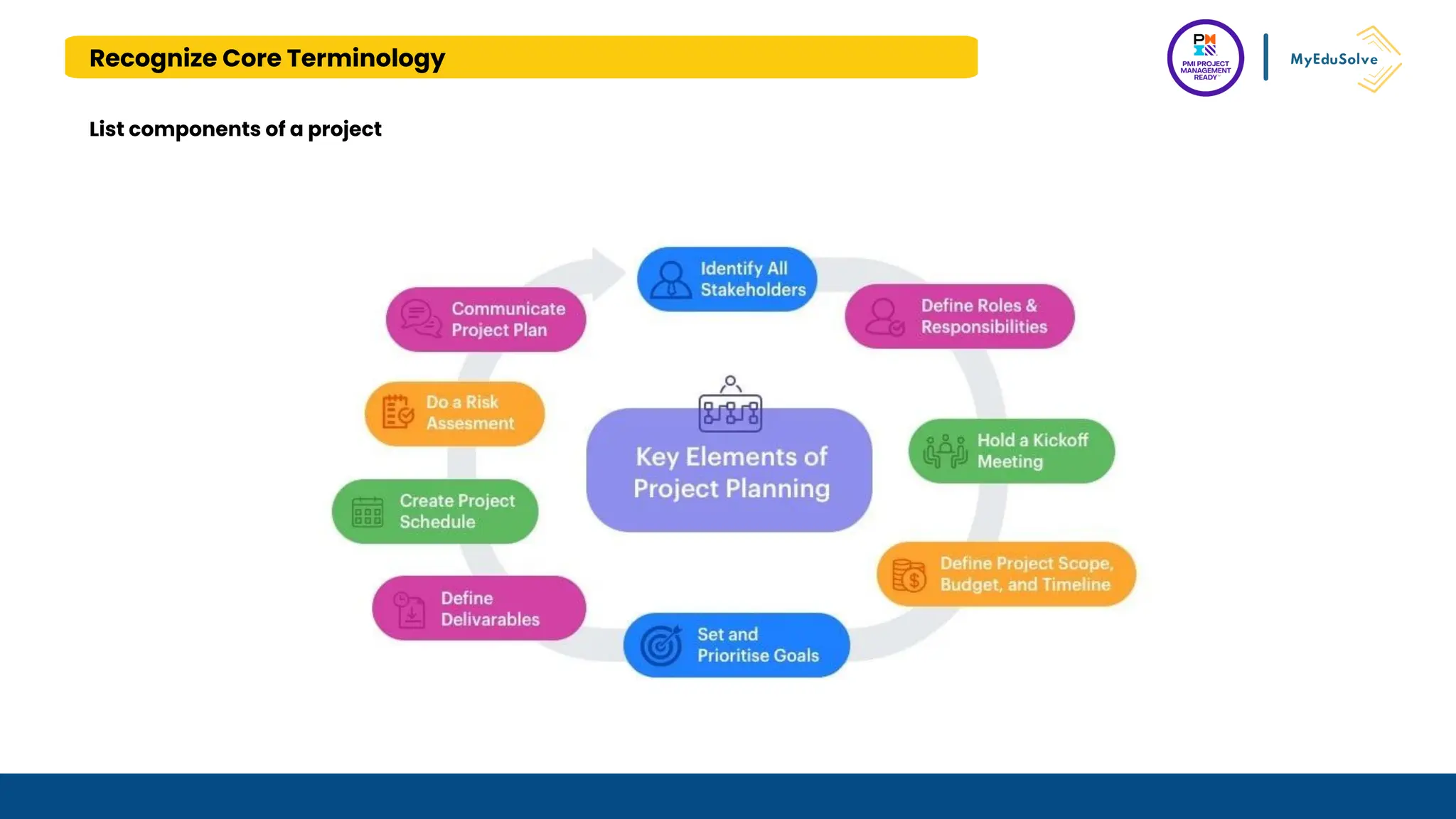
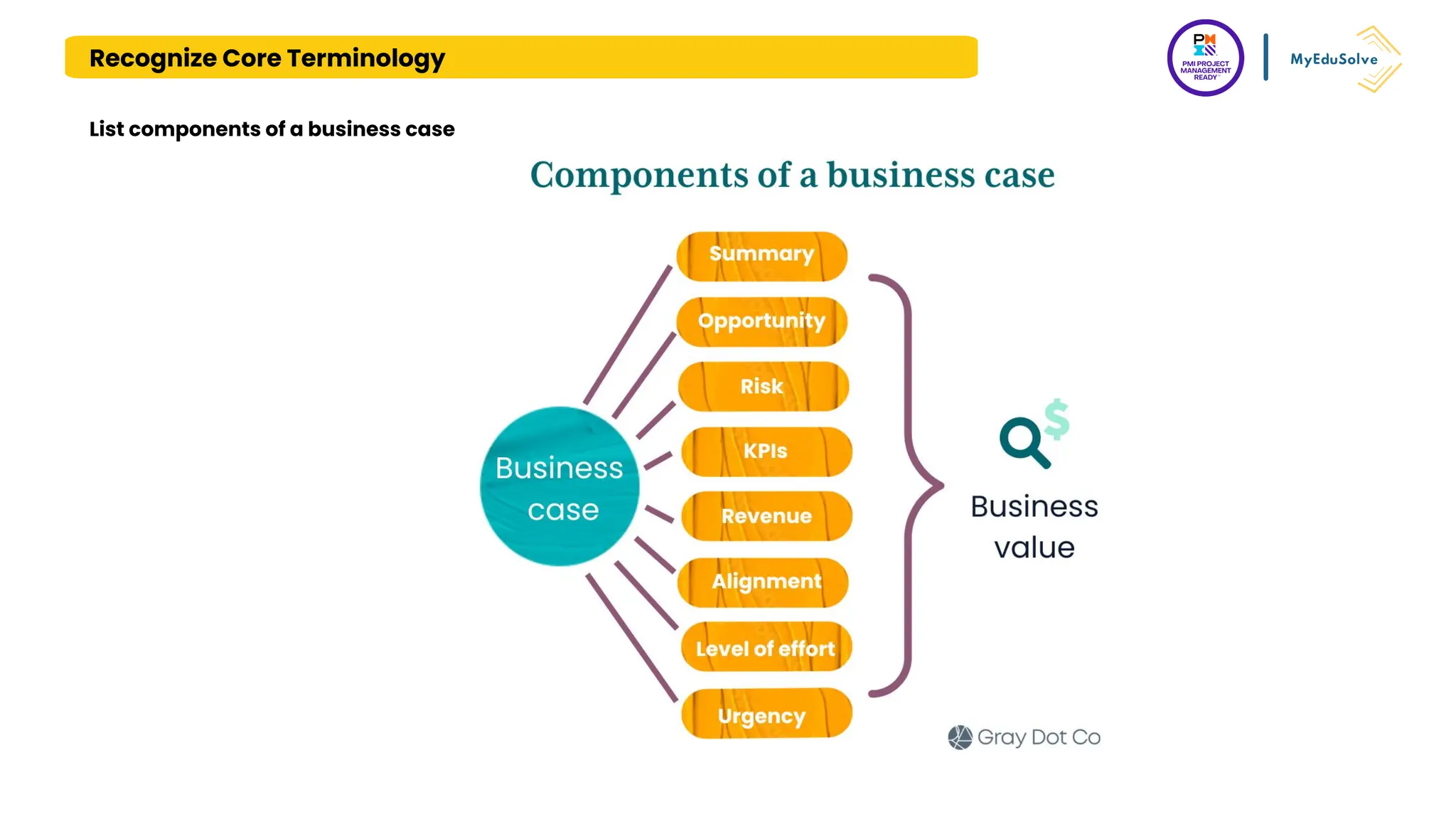
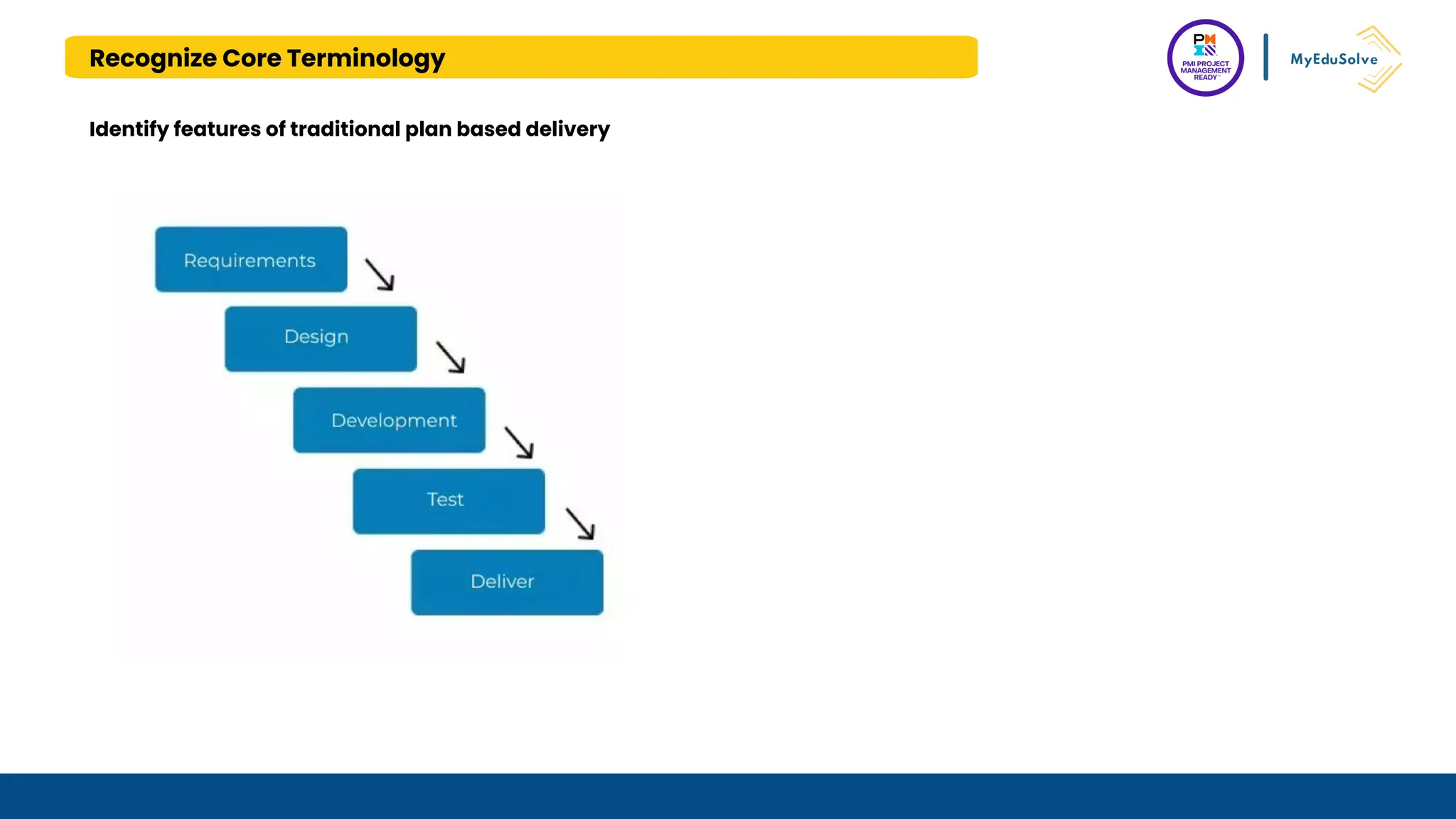
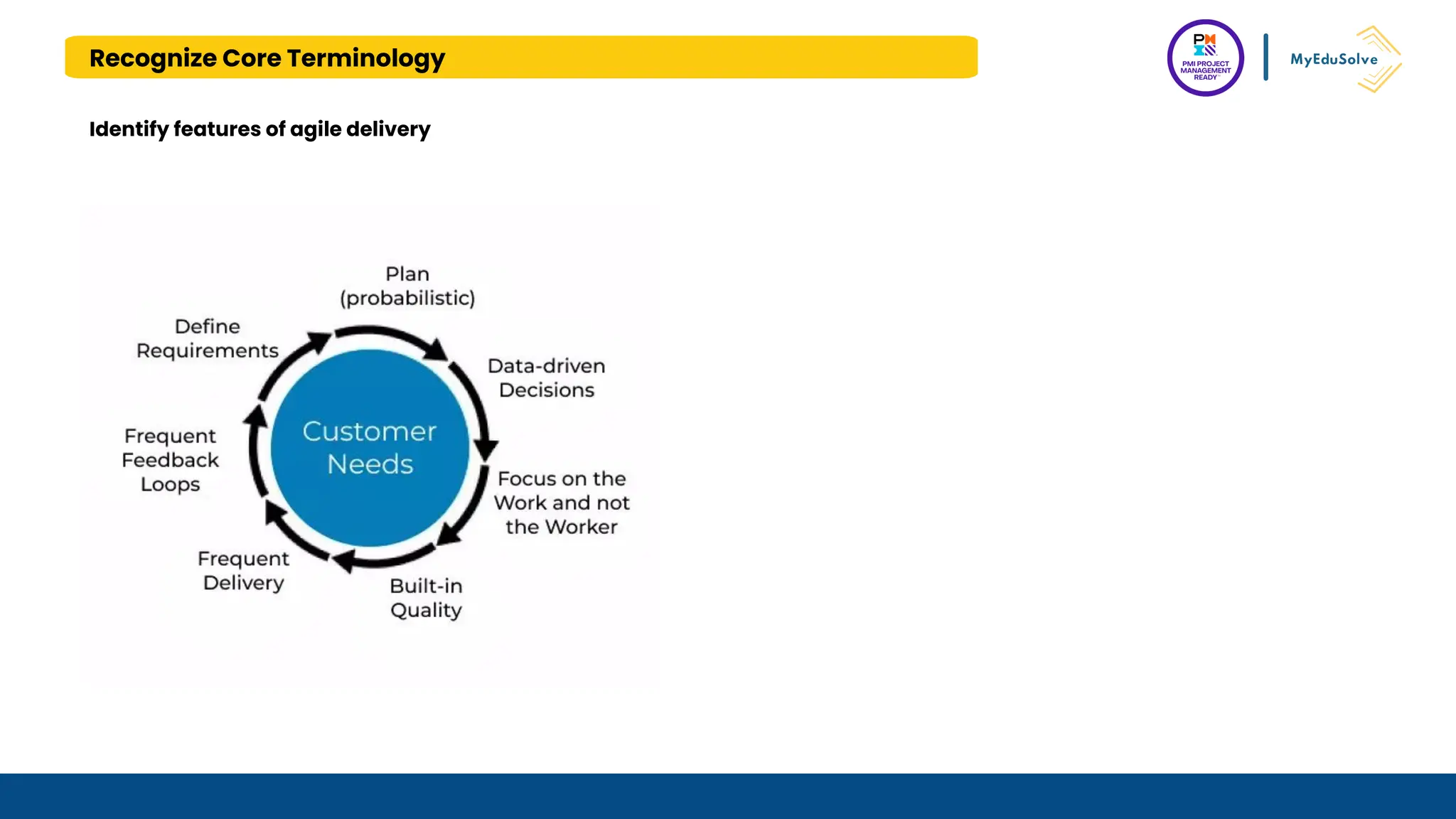
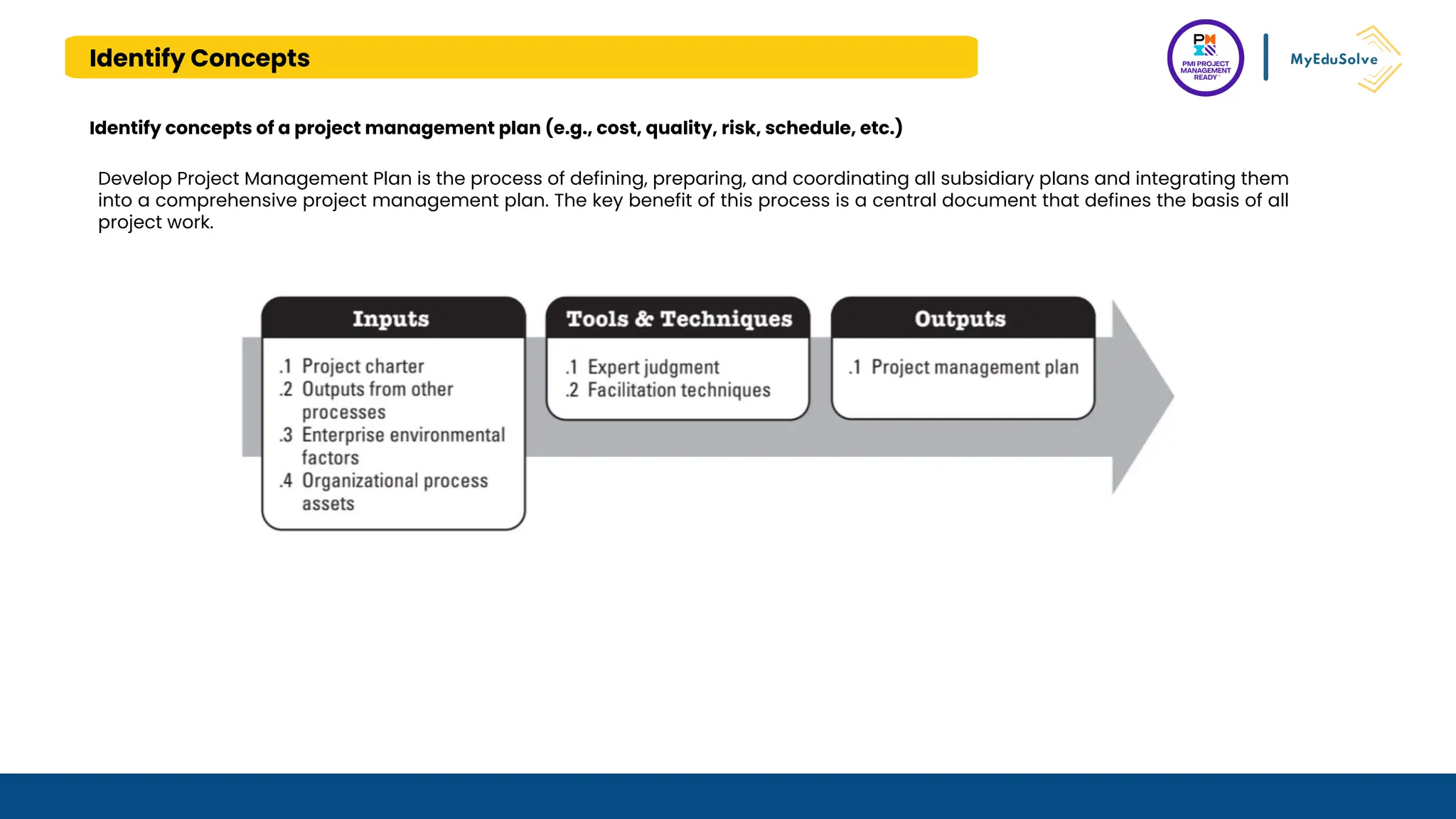
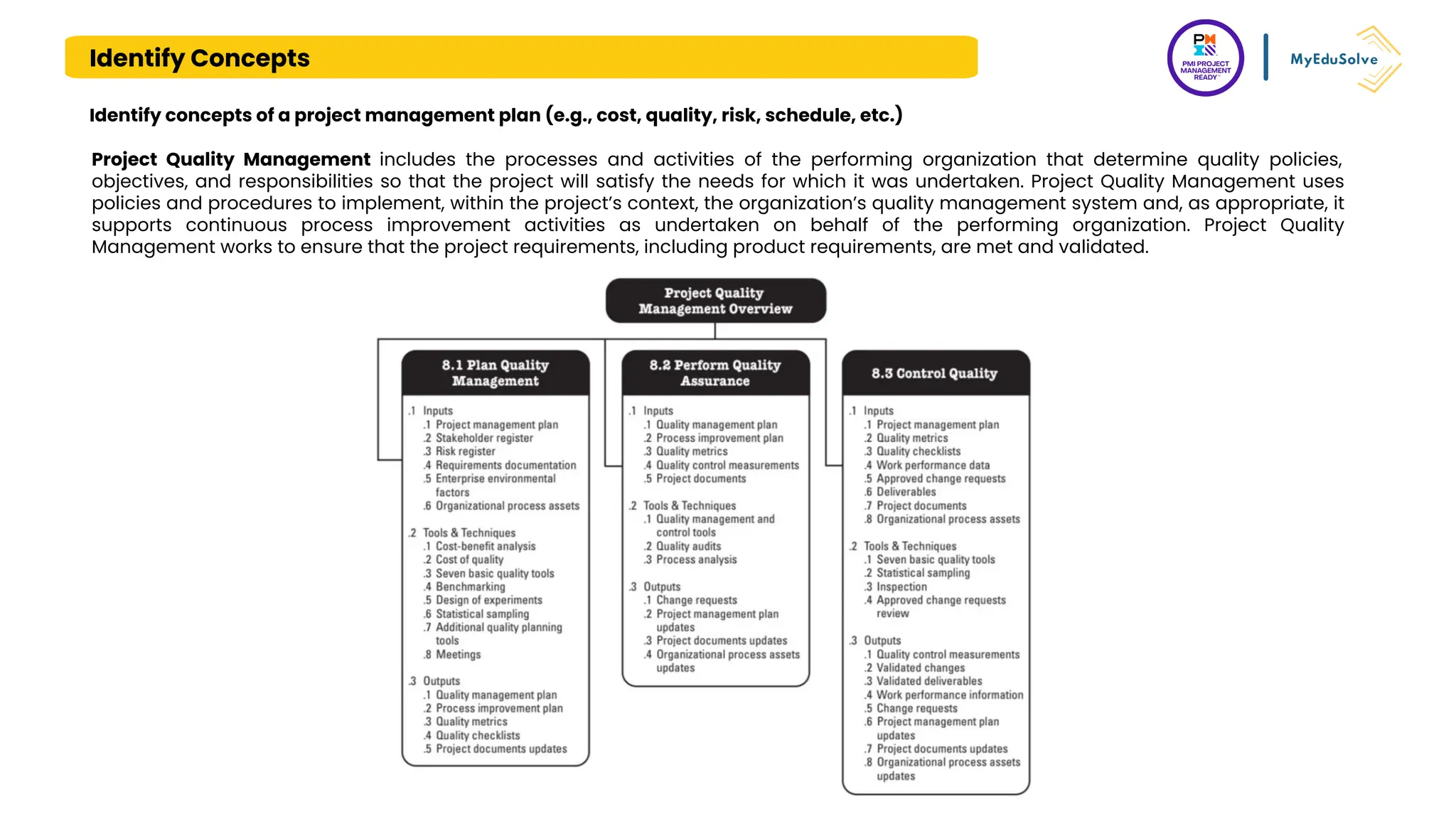
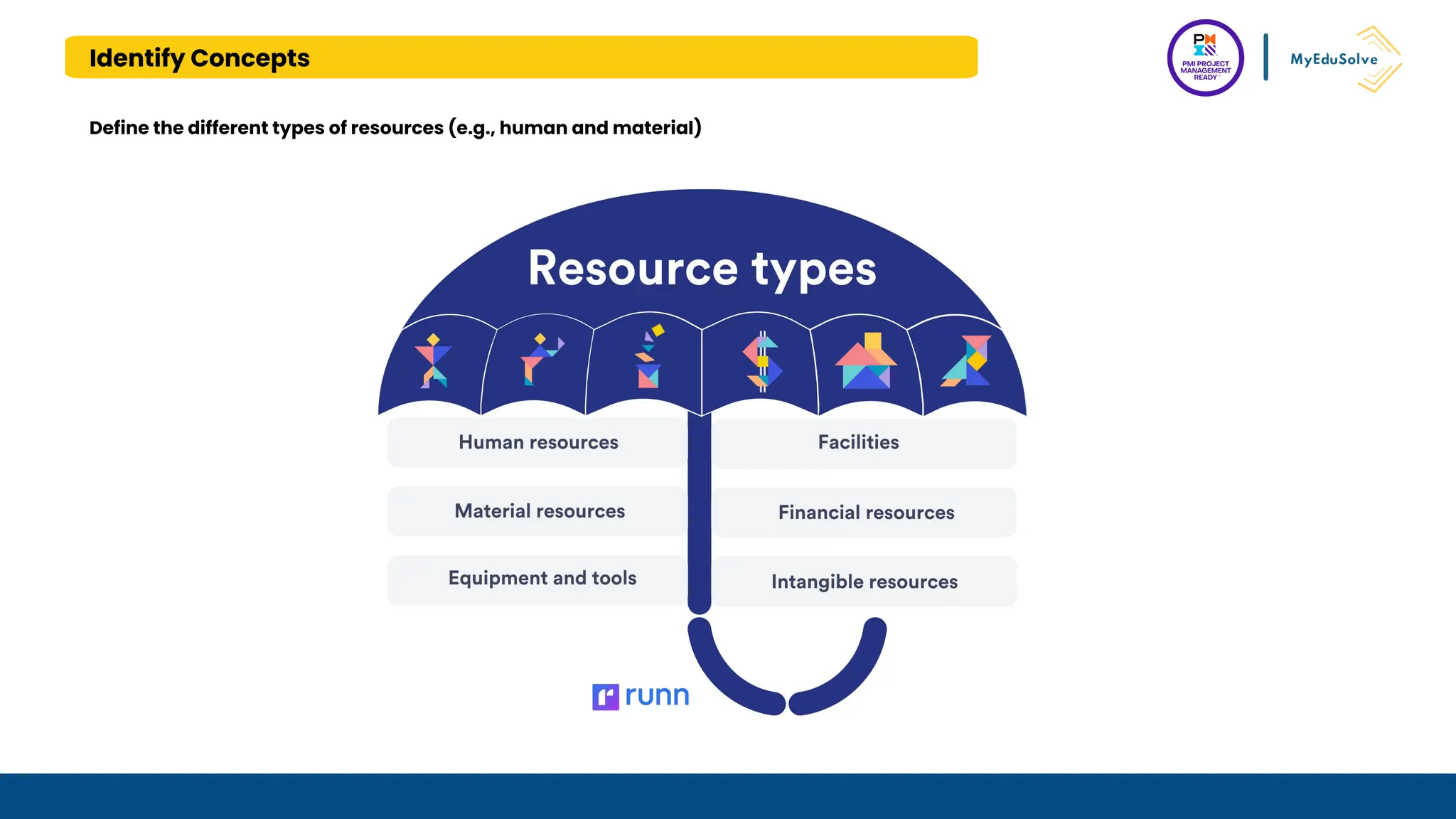
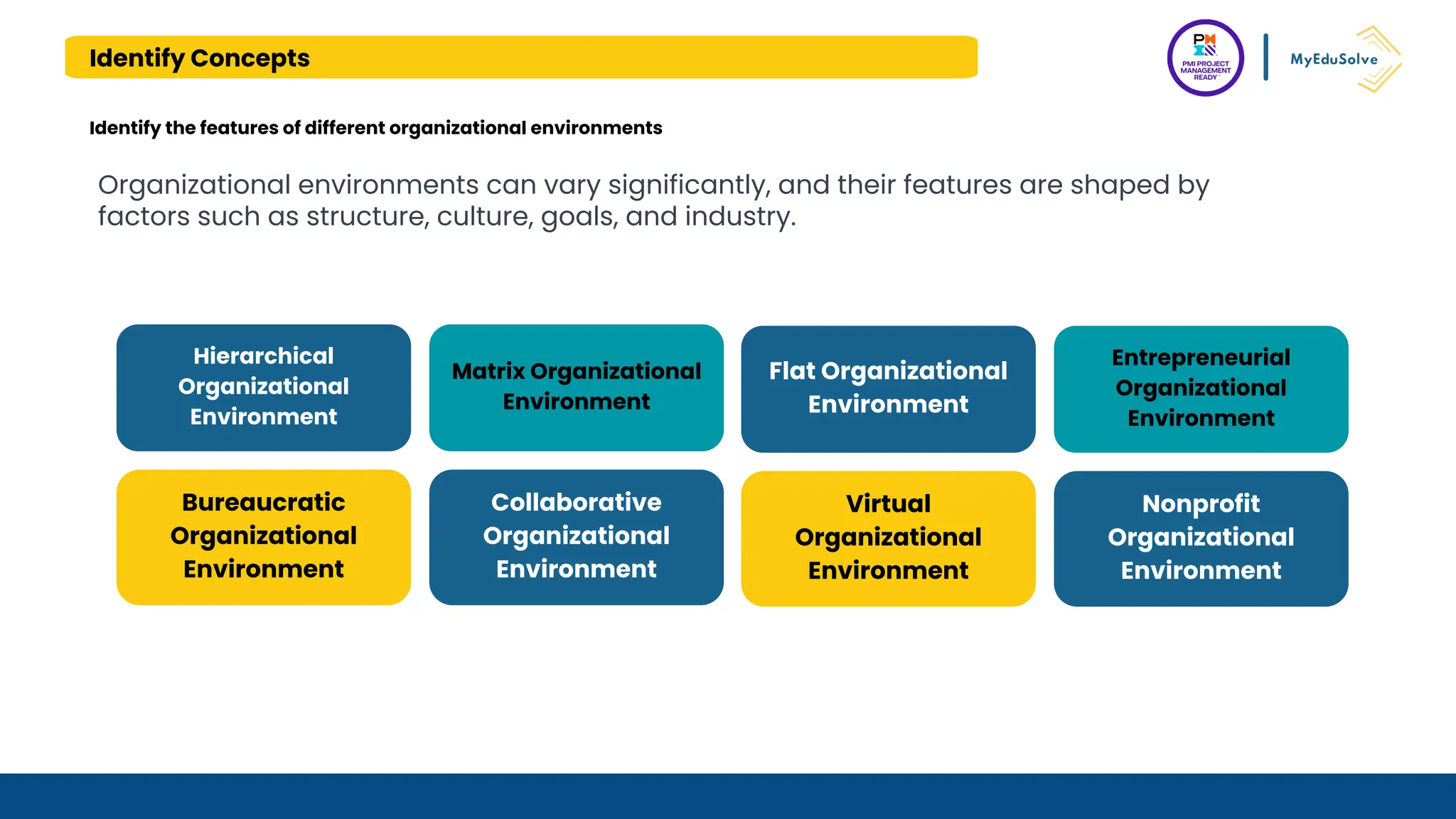
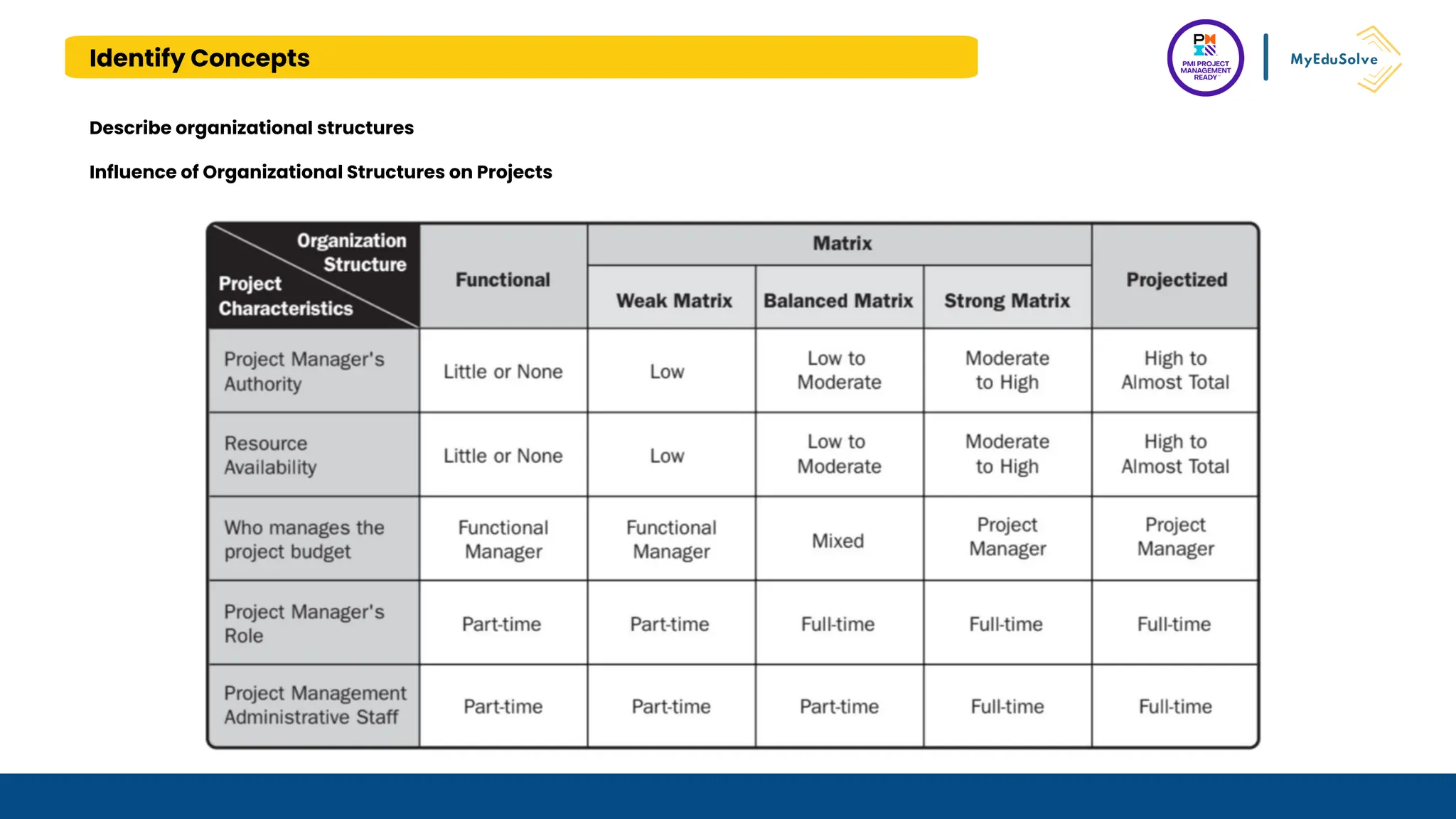
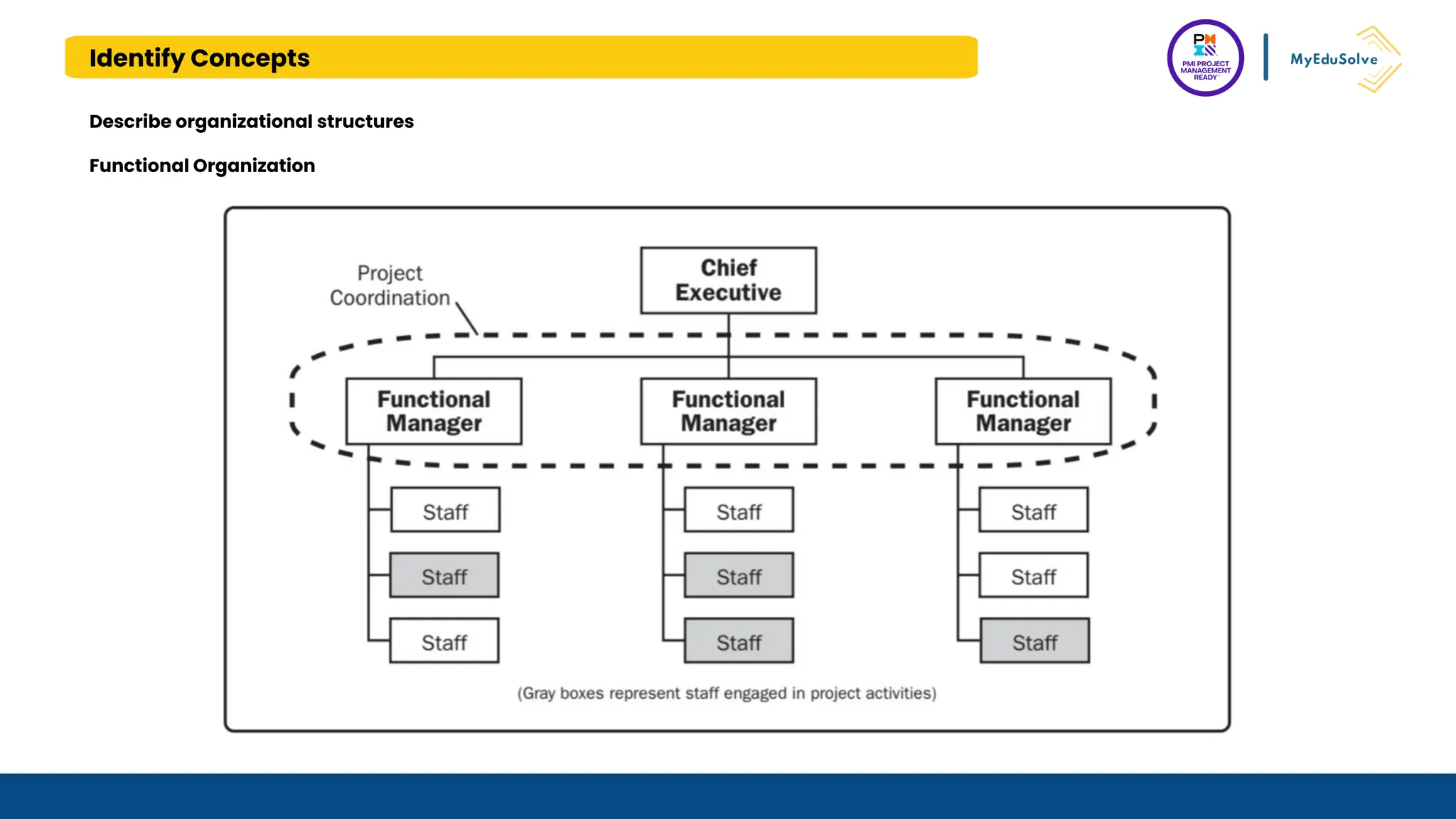
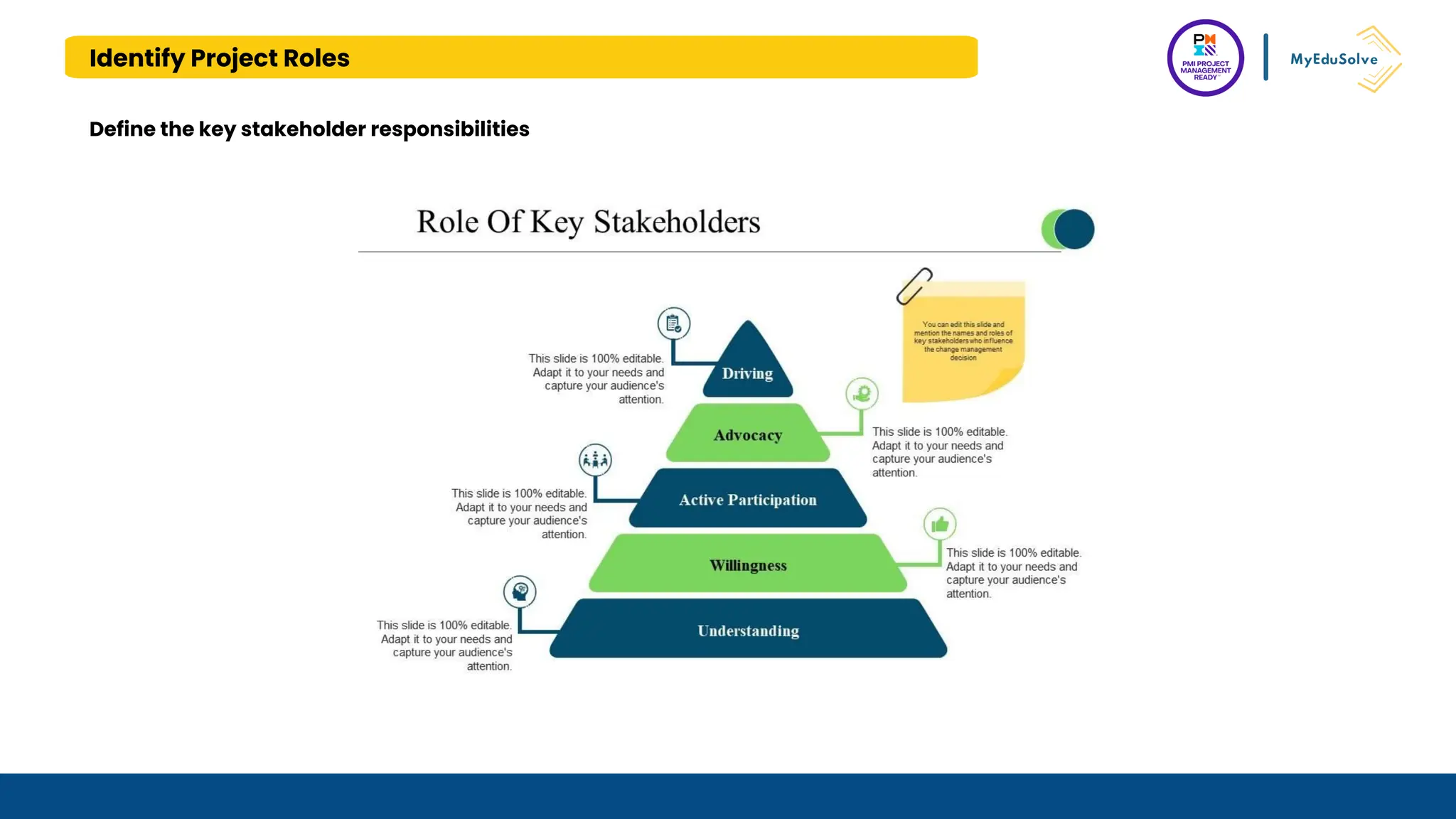
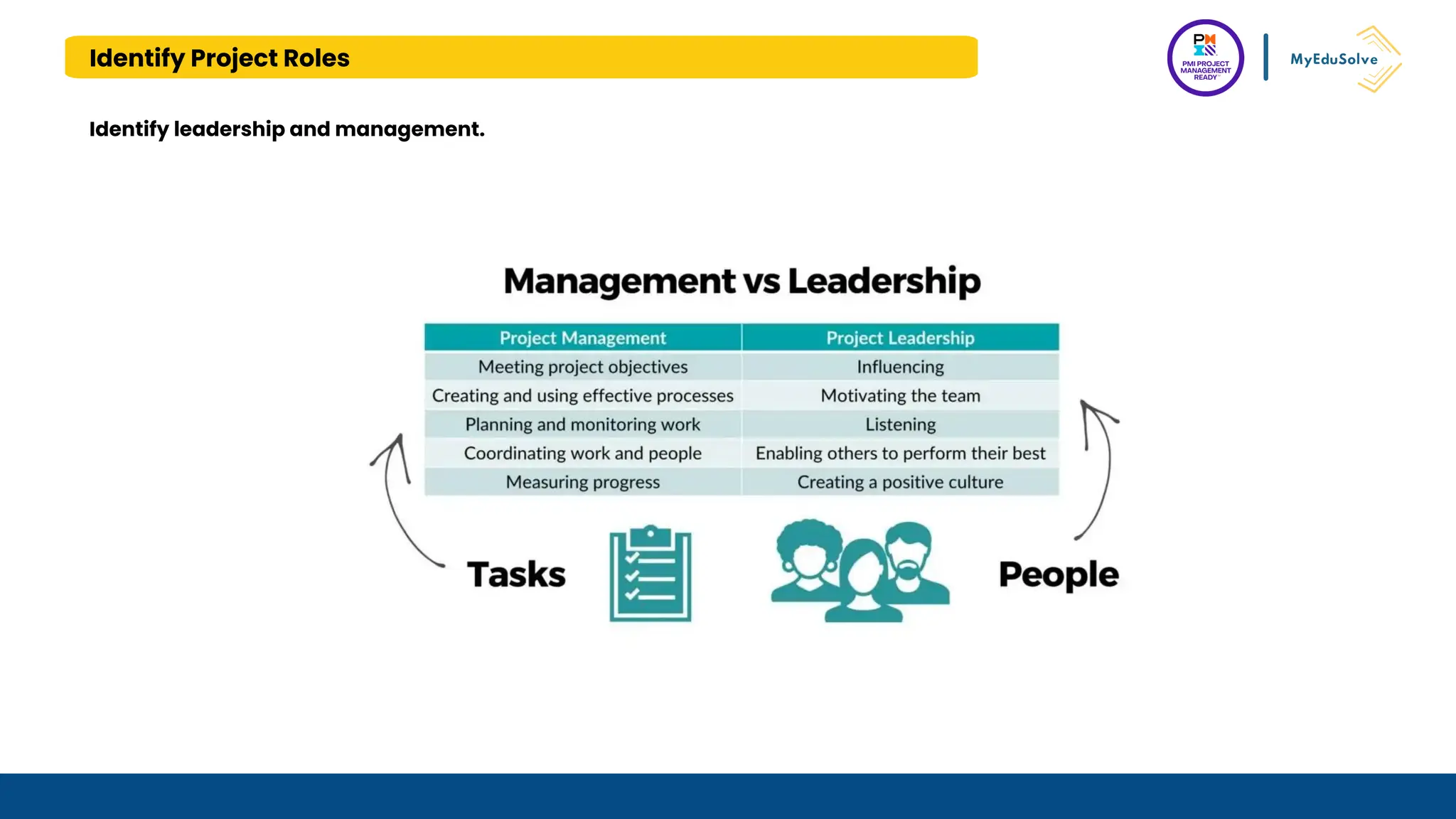
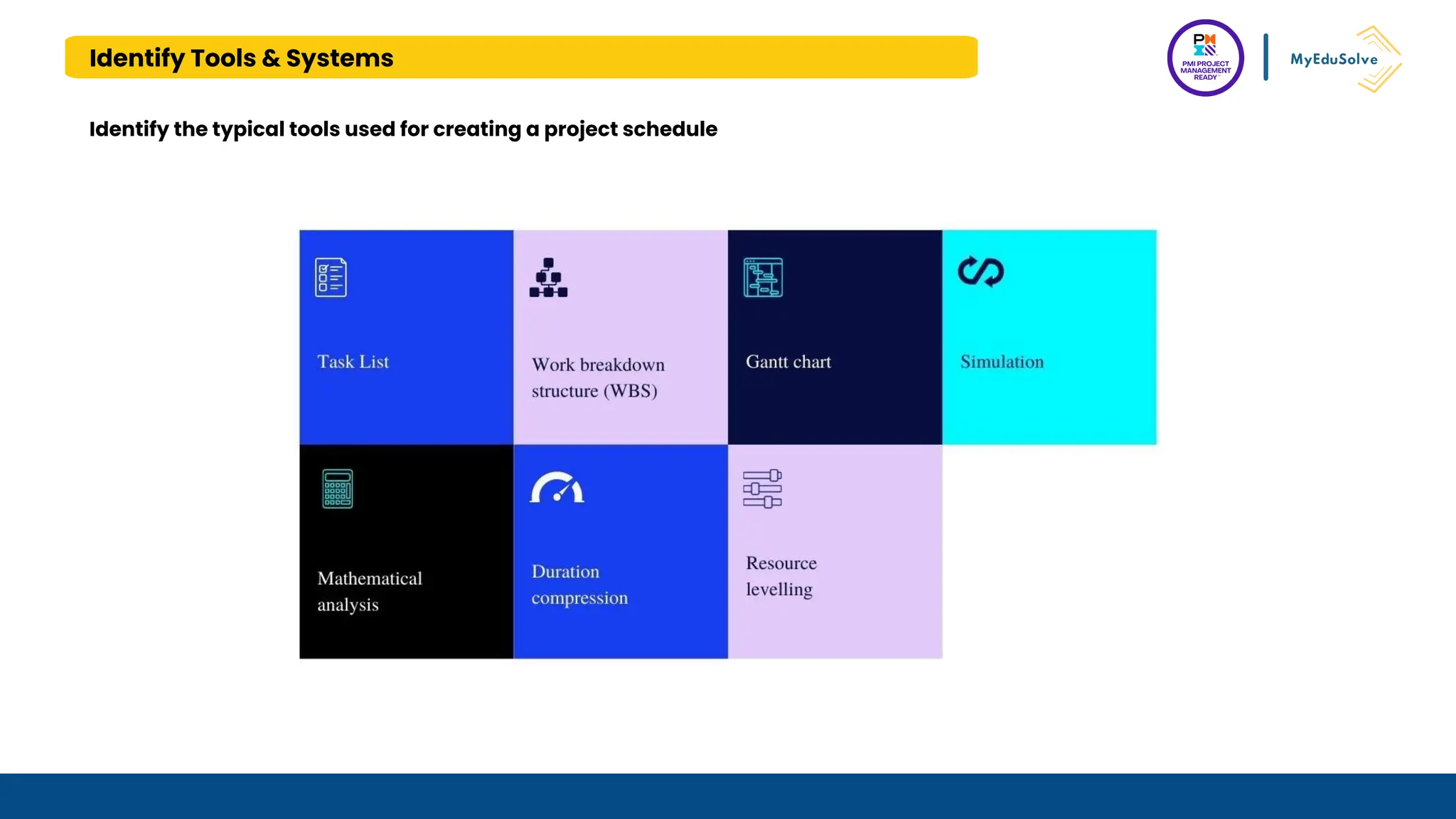
The document outlines the PMI Project Management Ready (PMR) certification designed for students, focusing on foundational project management concepts across multiple modules. Participants will learn essential terminology, project frameworks, stakeholder roles, and project management tools, covering both traditional and agile methodologies. This certification aims to prepare high school and post-secondary students for careers in project management and enhance technical education programs.