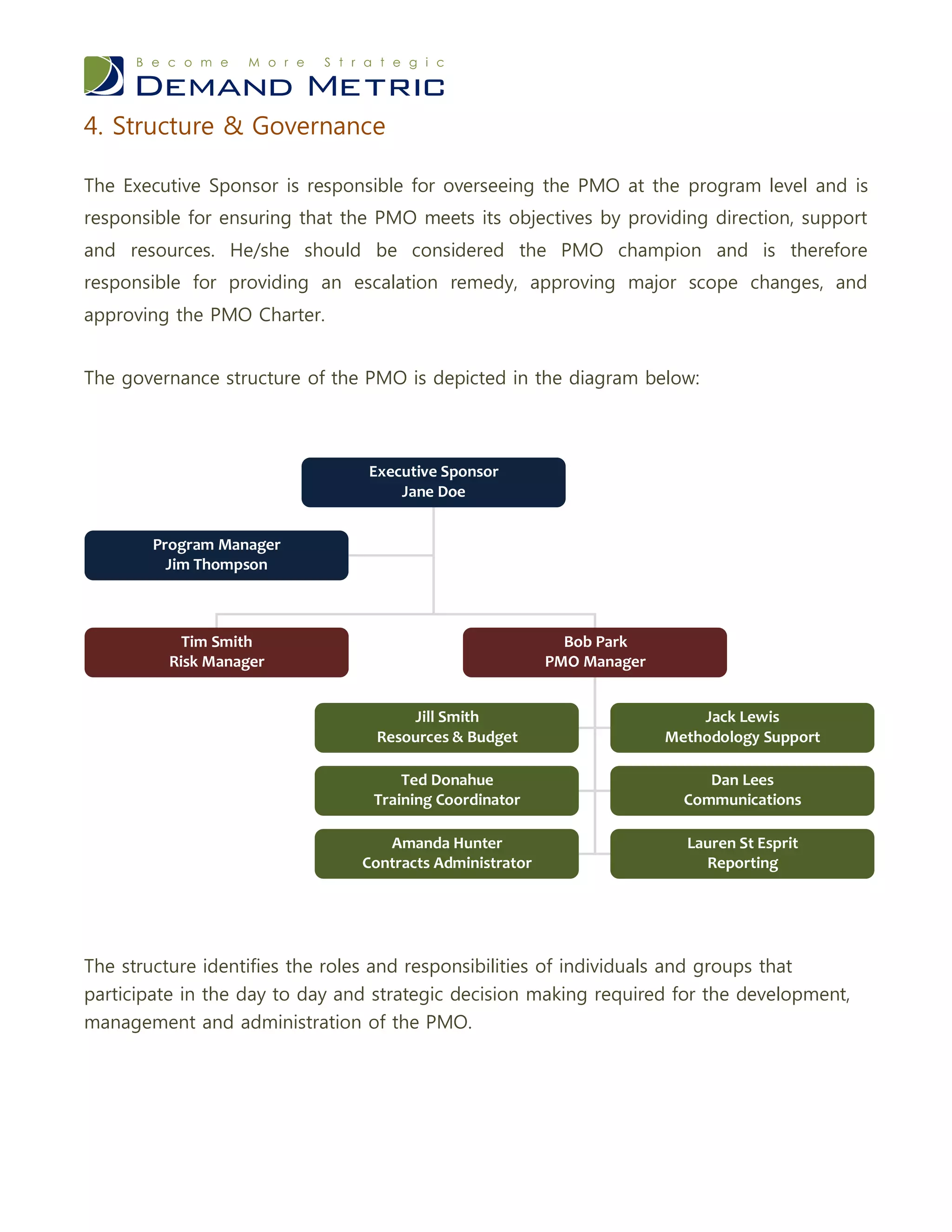
The PMO charter template is designed to set the foundation for establishing a project management office, detailing its scope, goals, and responsibilities. It outlines the framework for effective project management within the organization, emphasizing the necessity of executive sponsorship and defined objectives to enhance efficiency. Key elements include a governance structure, risk identification, a communication plan, and decision rights to guide the PMO's operations.

![[Company Name]
Project Management Office Charter
By
[Enter Name Here]
For
[Enter Name Here]
Effective Date:
Document Owner:
Version:
Version Date Revision / Description Author:
Approval:
Approver Title:
Approval Date:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmochartertemplate-121031135527-phpapp01/75/PMO-Charter-Template-2-2048.jpg)