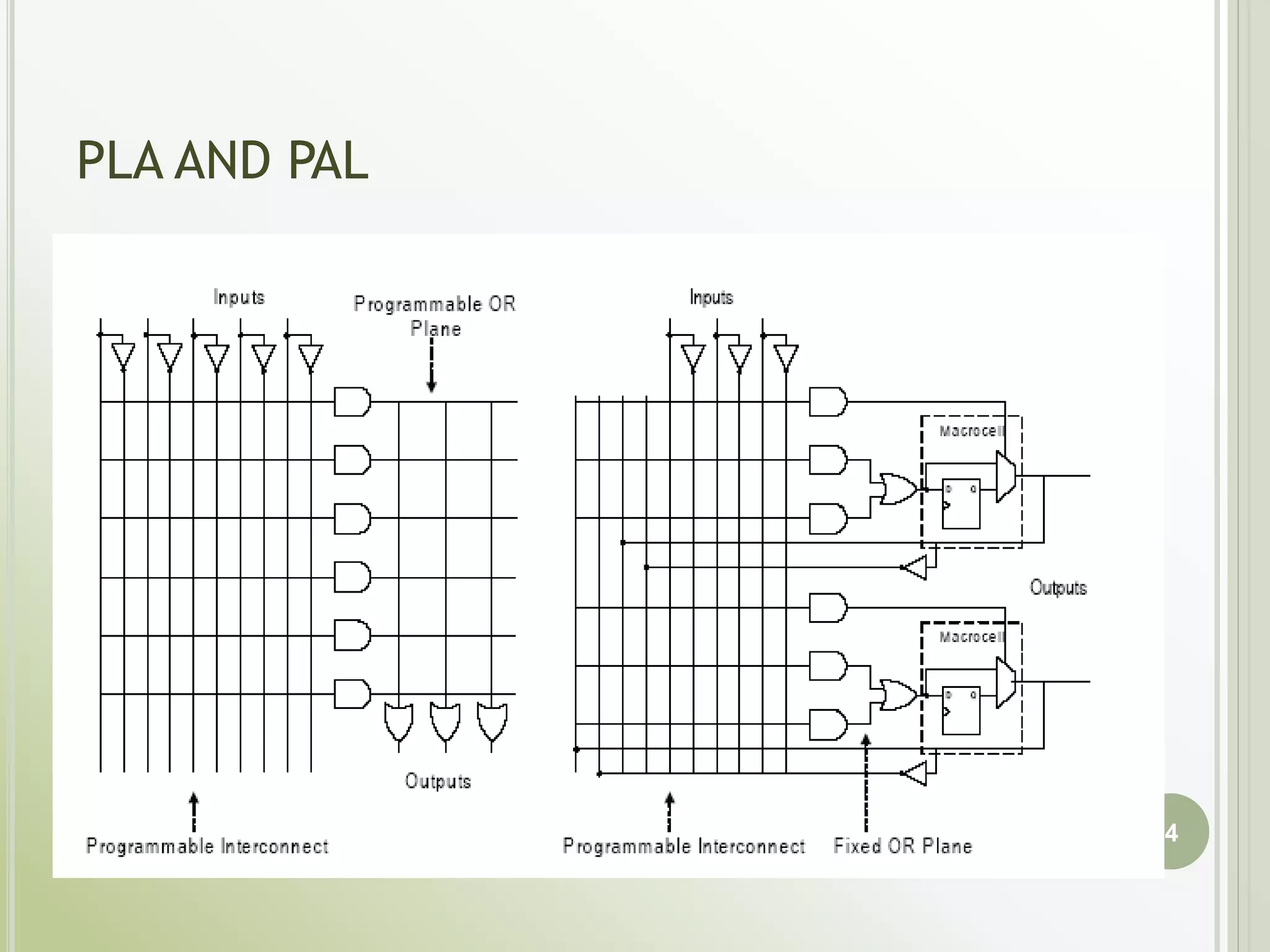
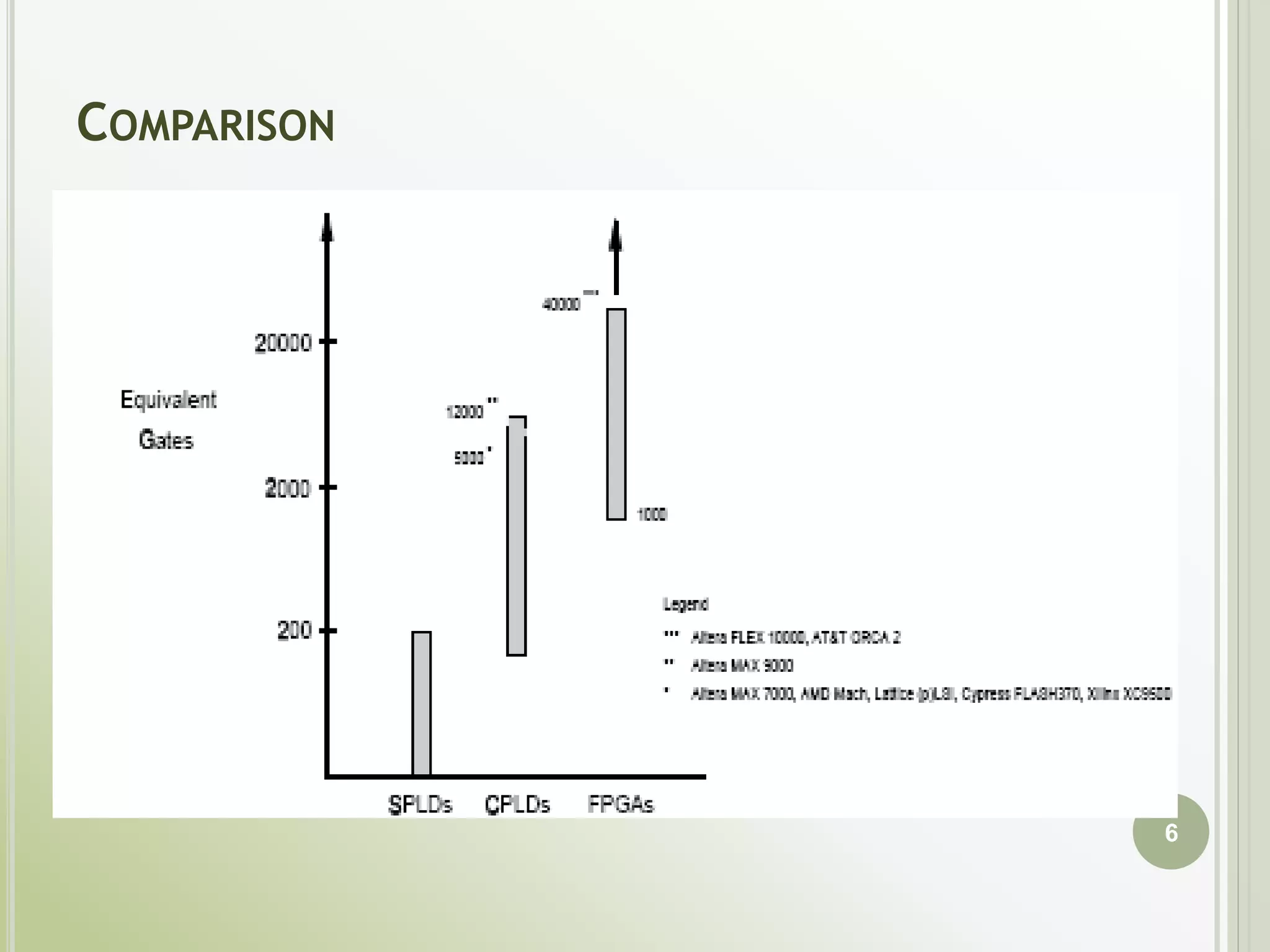
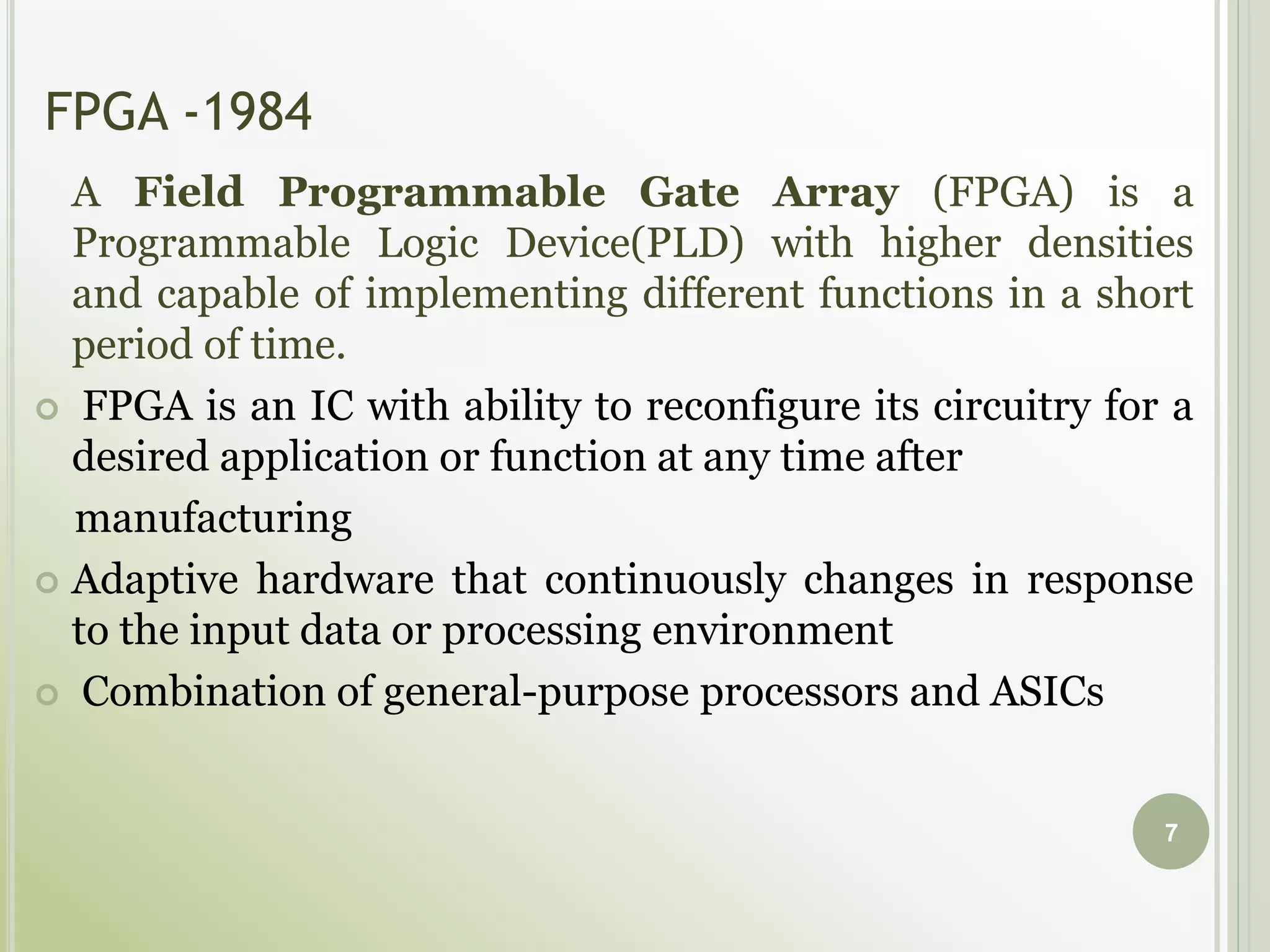
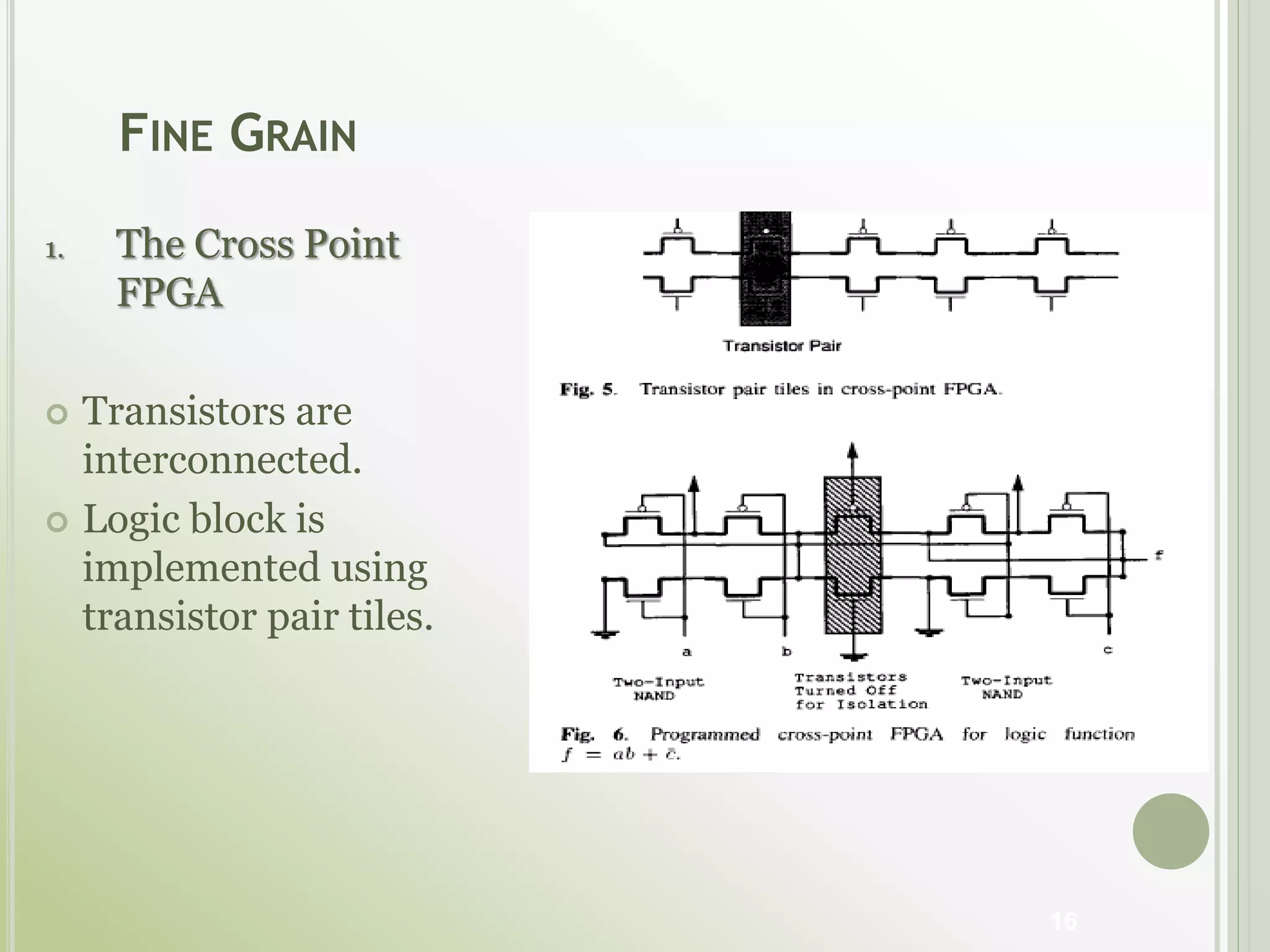
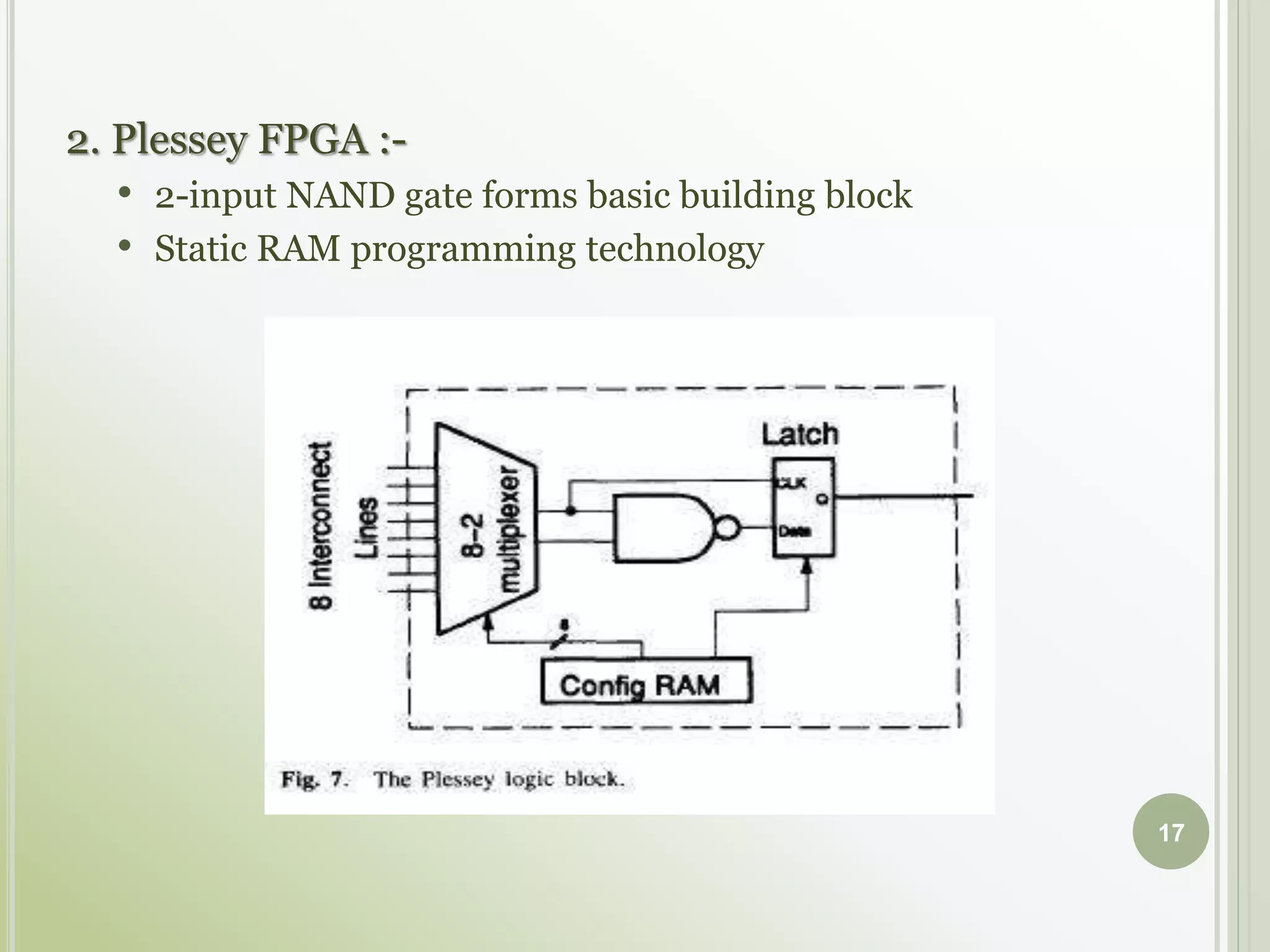
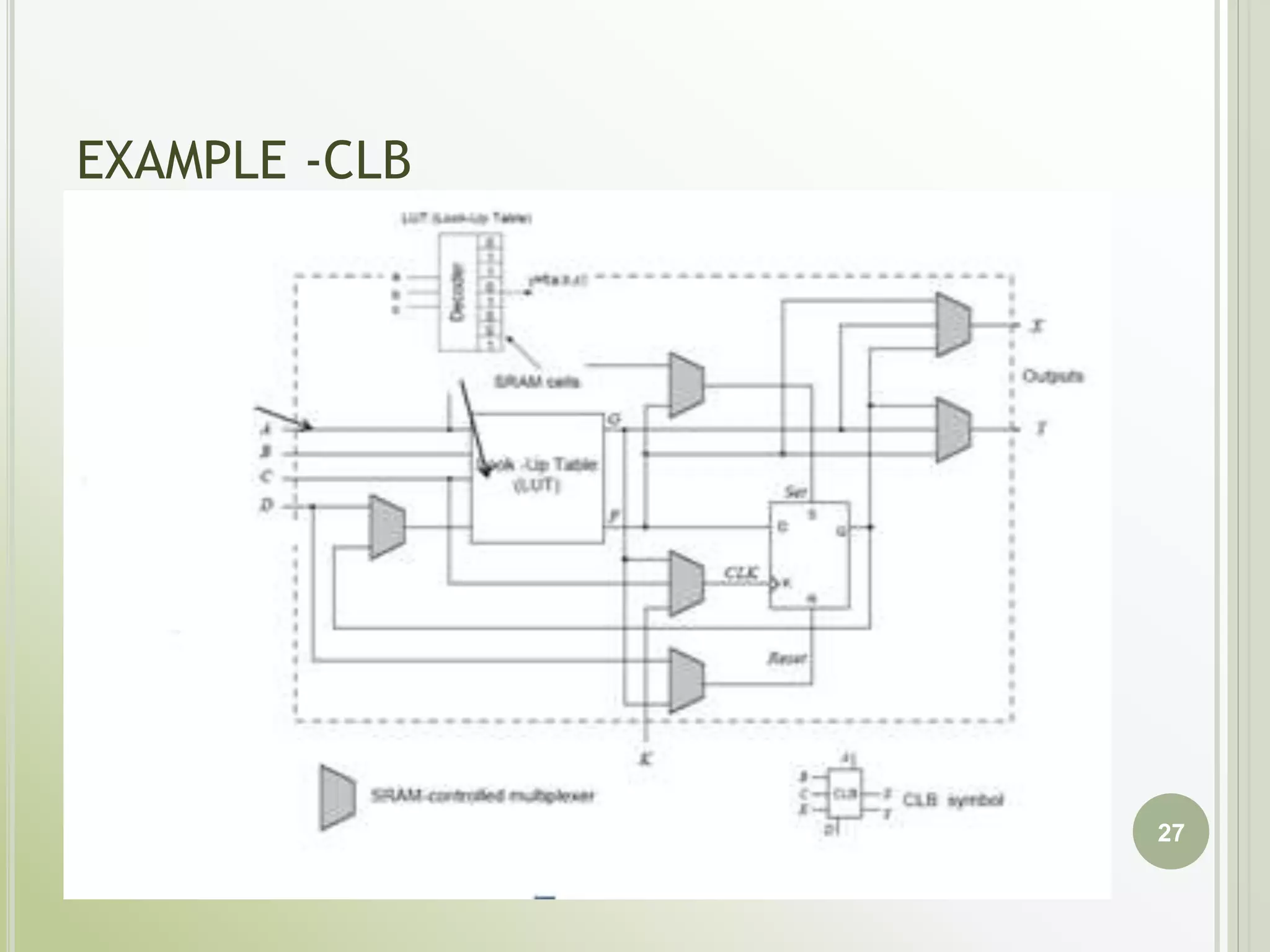
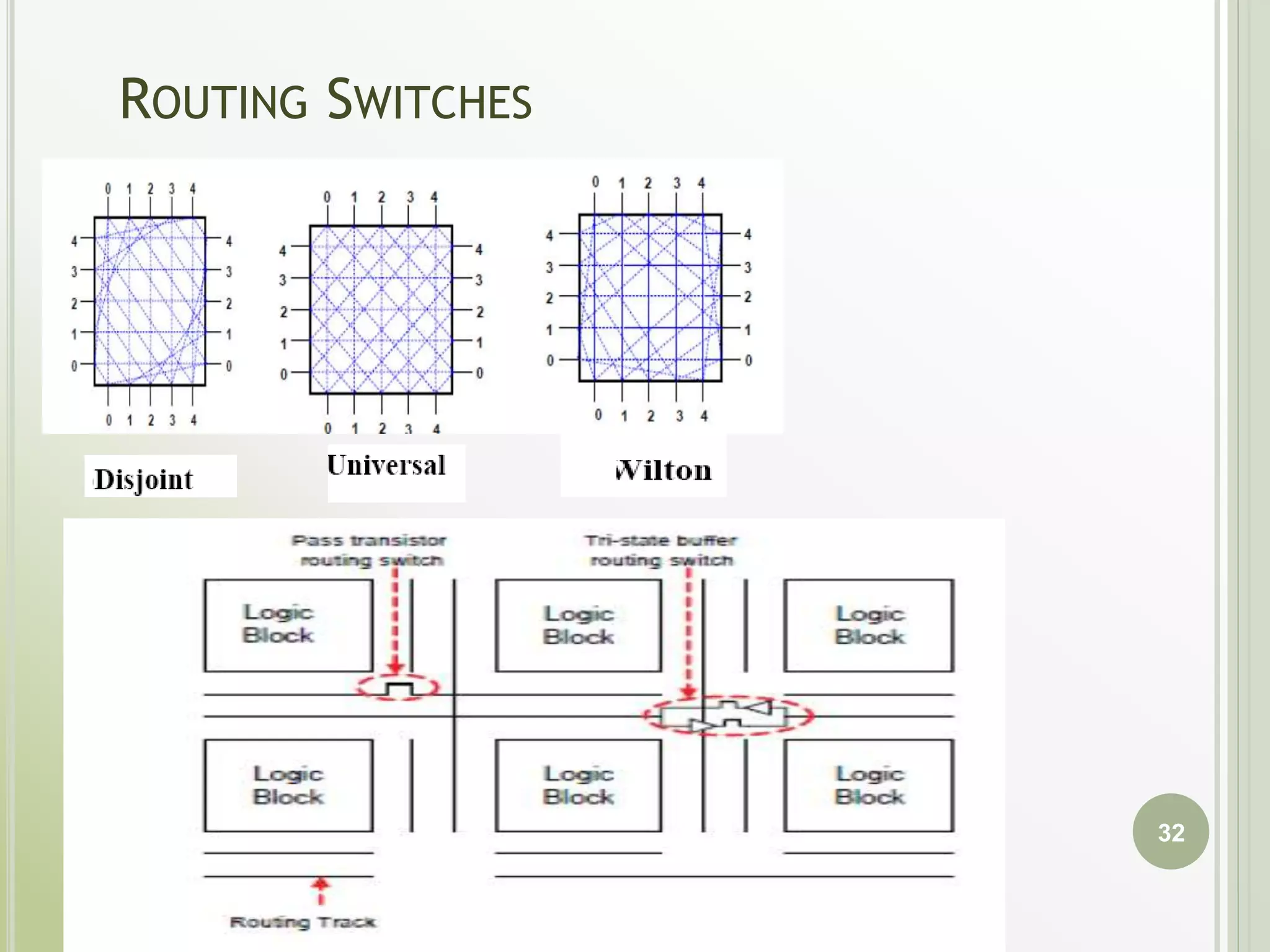
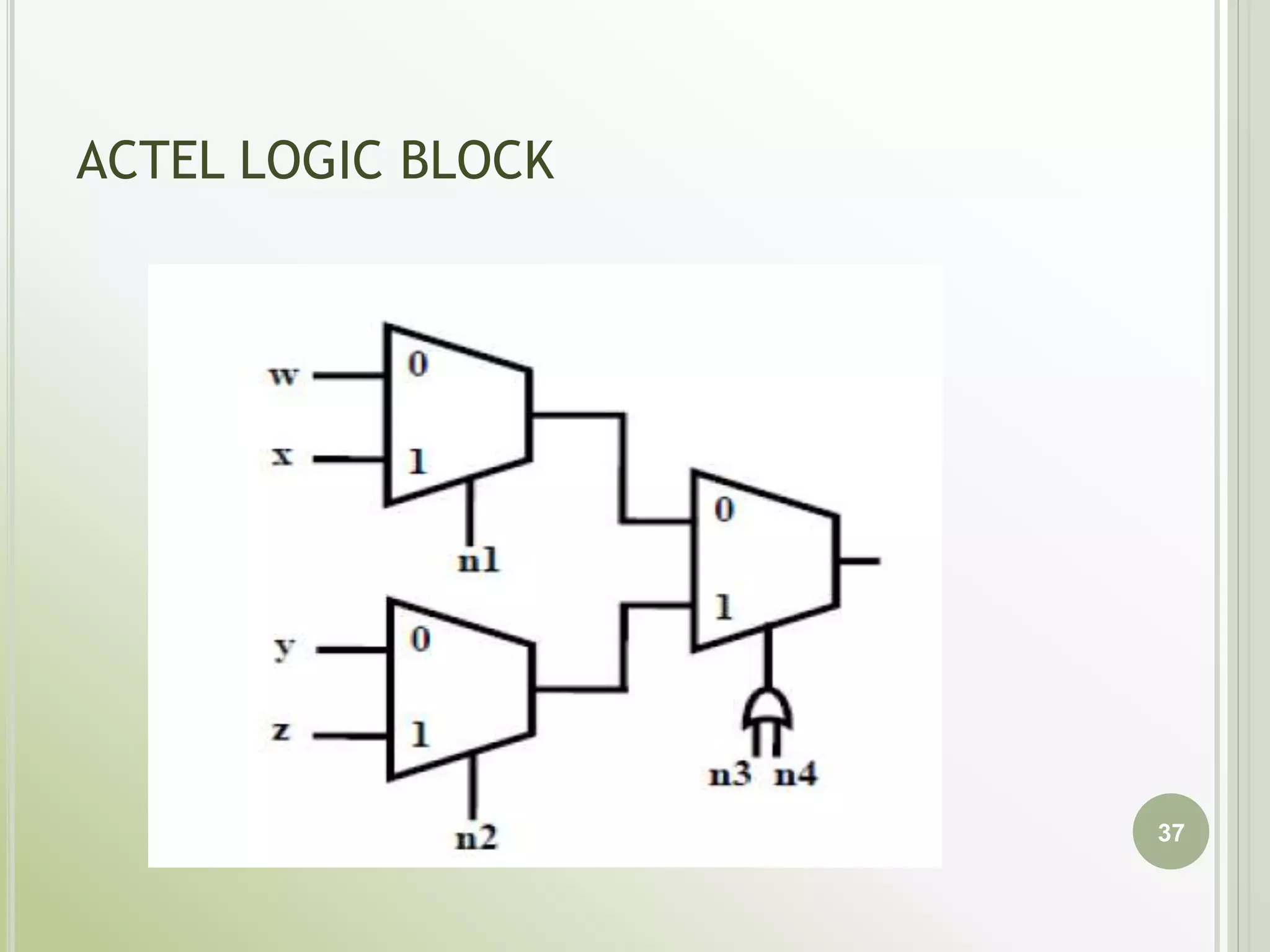
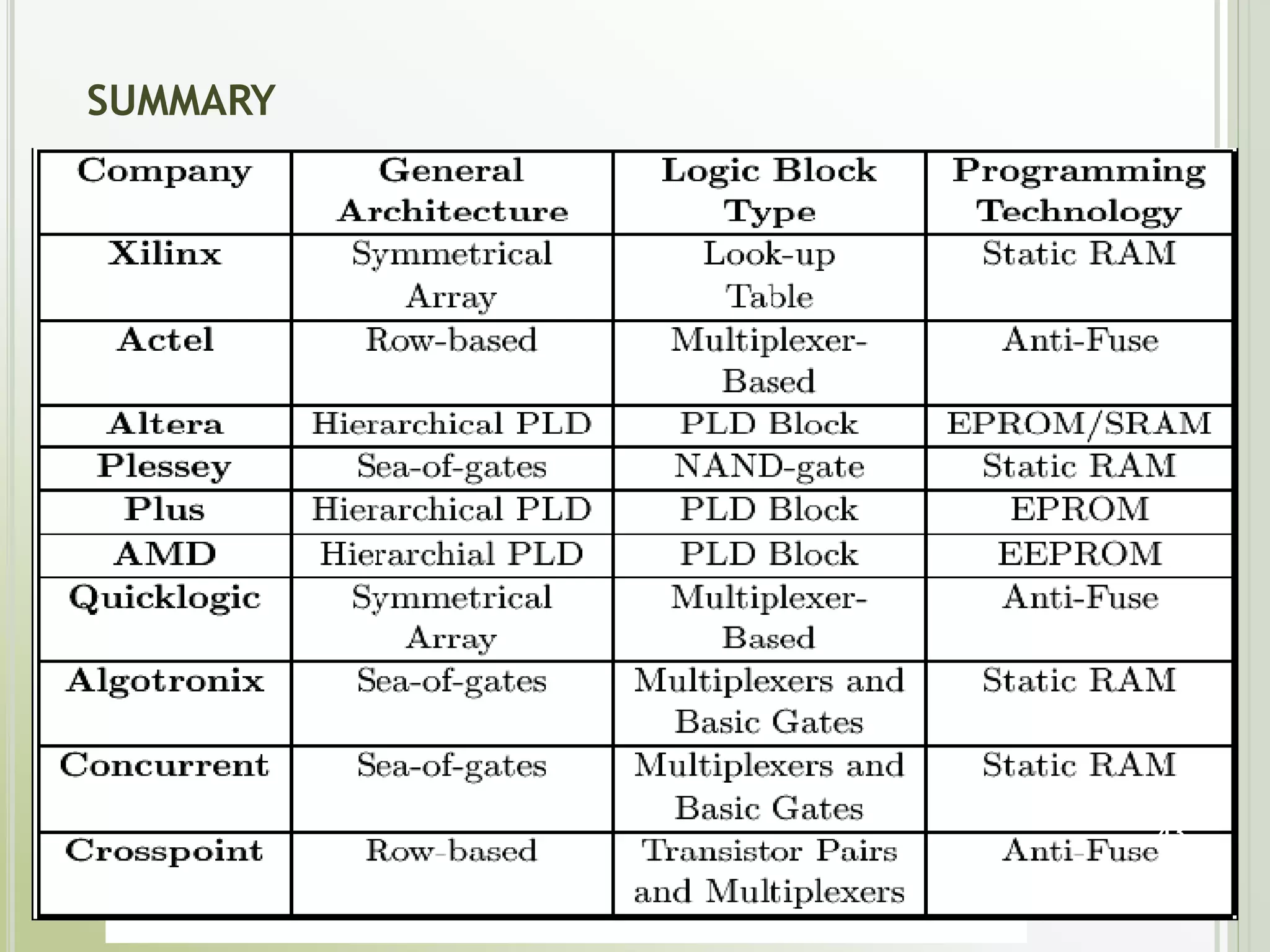
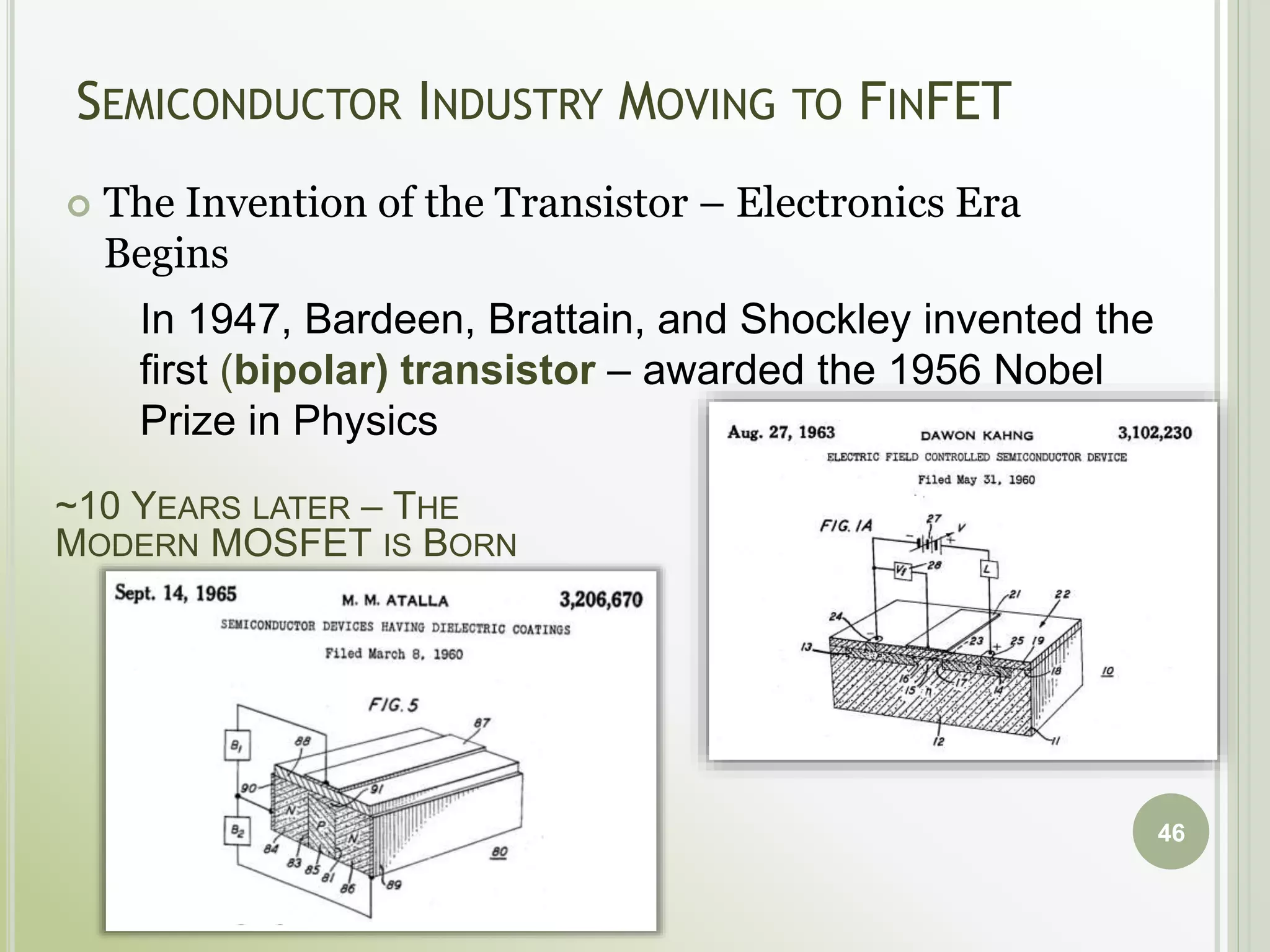
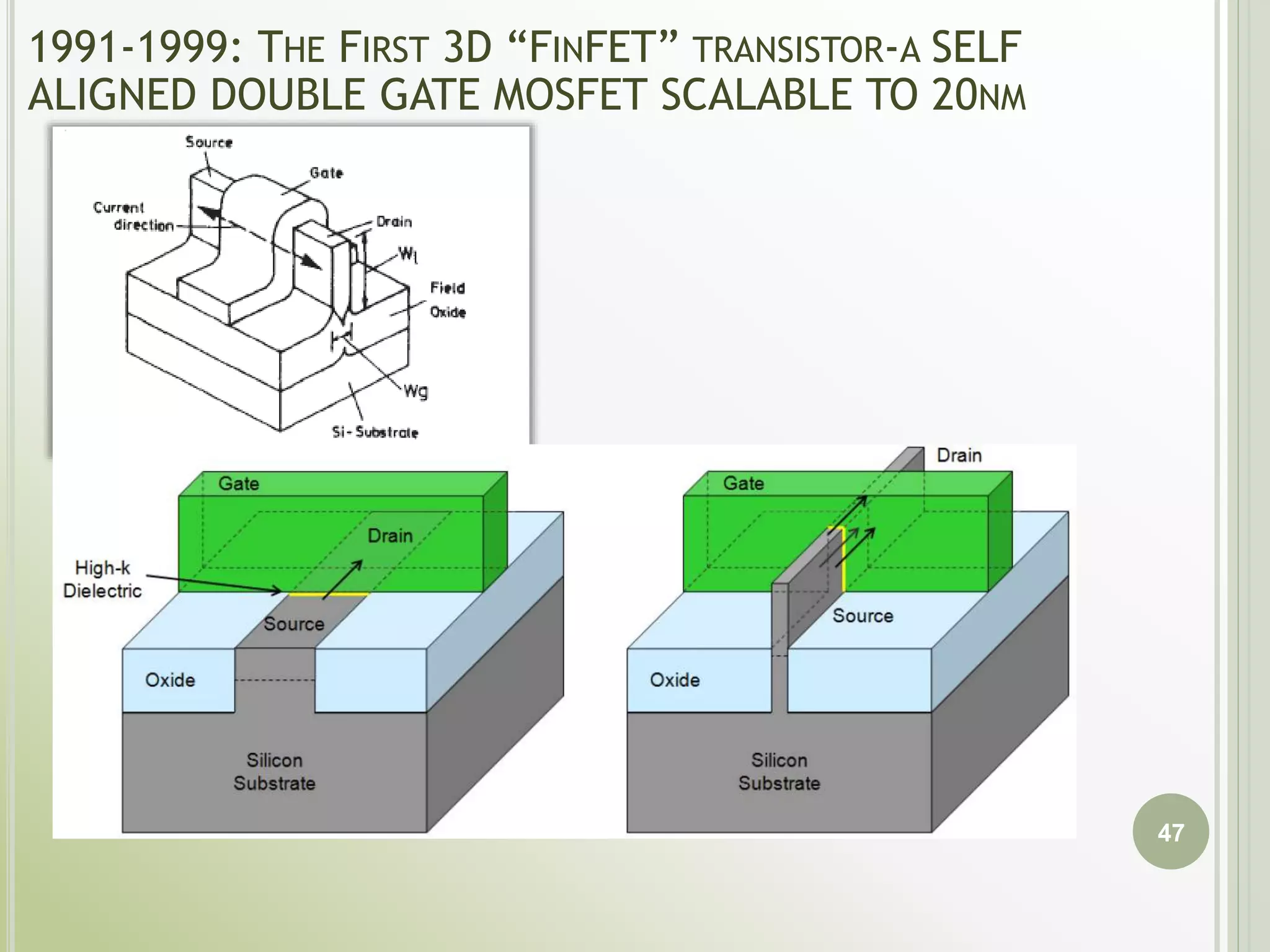
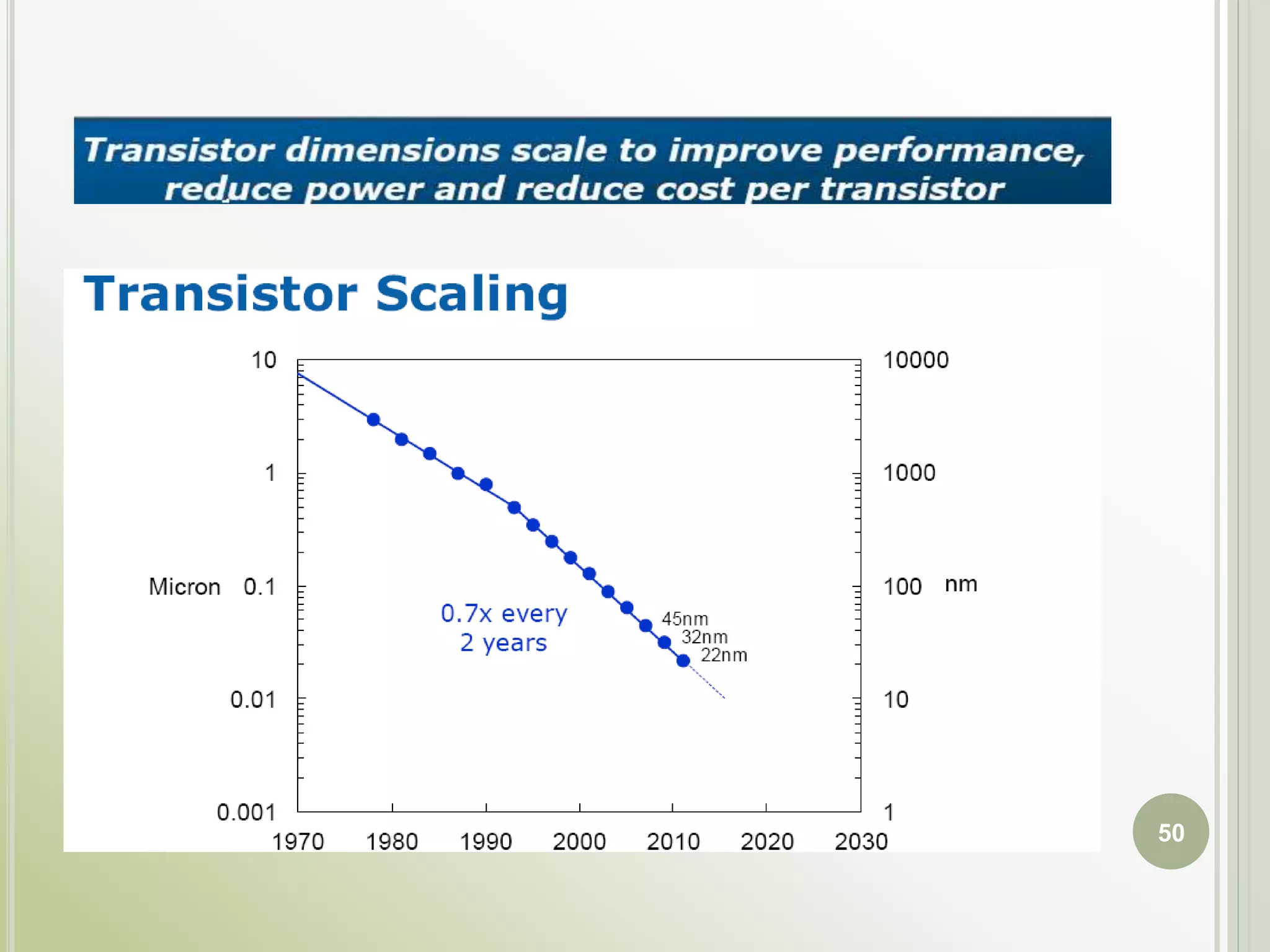
This document discusses FPGAs and their low power techniques. It begins with a brief history of programmable logic devices including PROMs, PLAs, and PALs which were the precursors to FPGAs. FPGA advantages are their reprogrammability, faster design times, and ability to fix designs by reprogramming compared to ASICs. The document then covers FPGA architecture including logic blocks, interconnects, and different routing architectures from vendors. Programming techniques like SRAM, antifuse, and floating gate are described. Low power design is an important aspect for FPGAs. The semiconductor industry is moving towards 3D FinFET transistors which allow for lower power and higher densities than planar transistors.