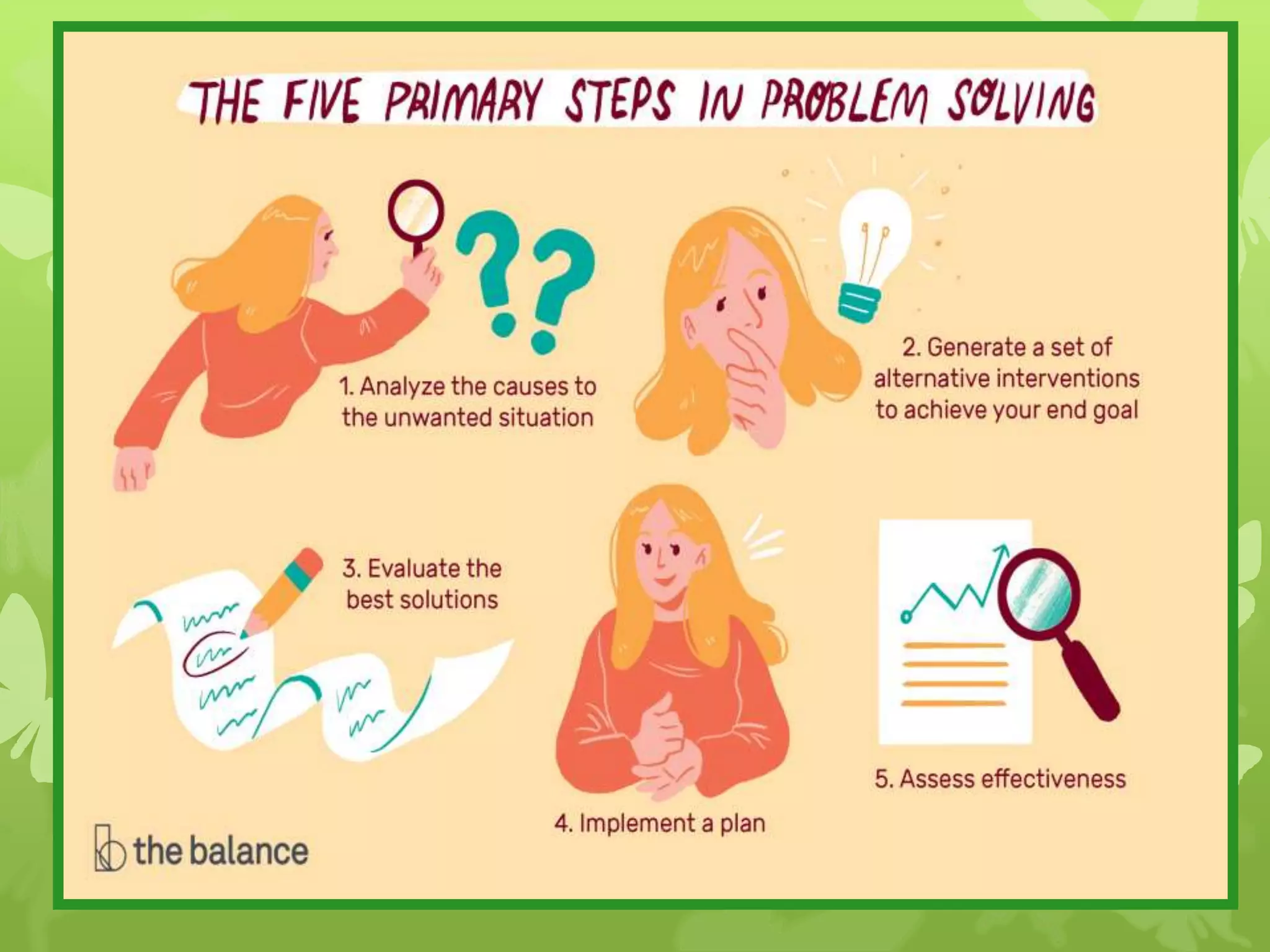
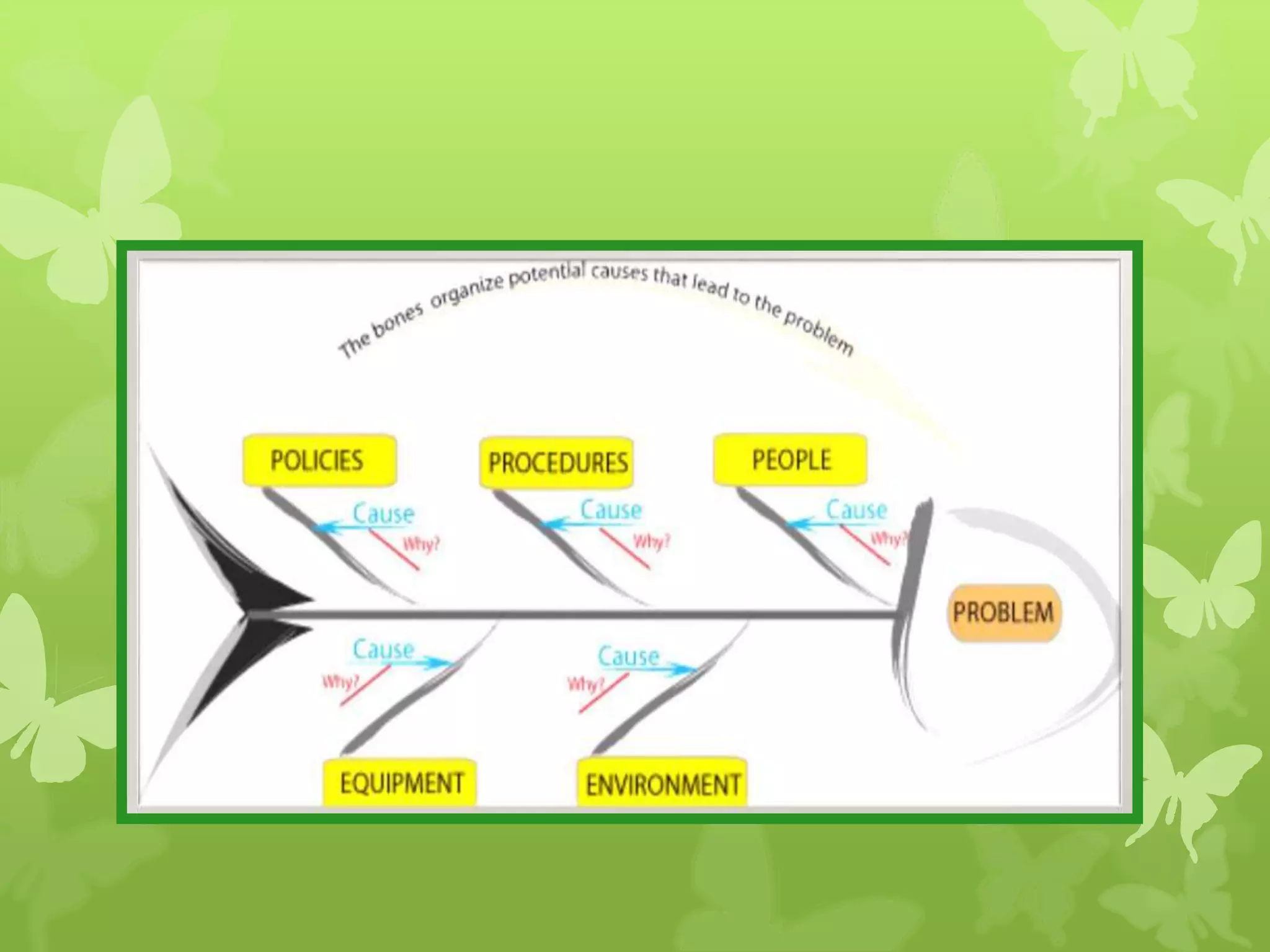
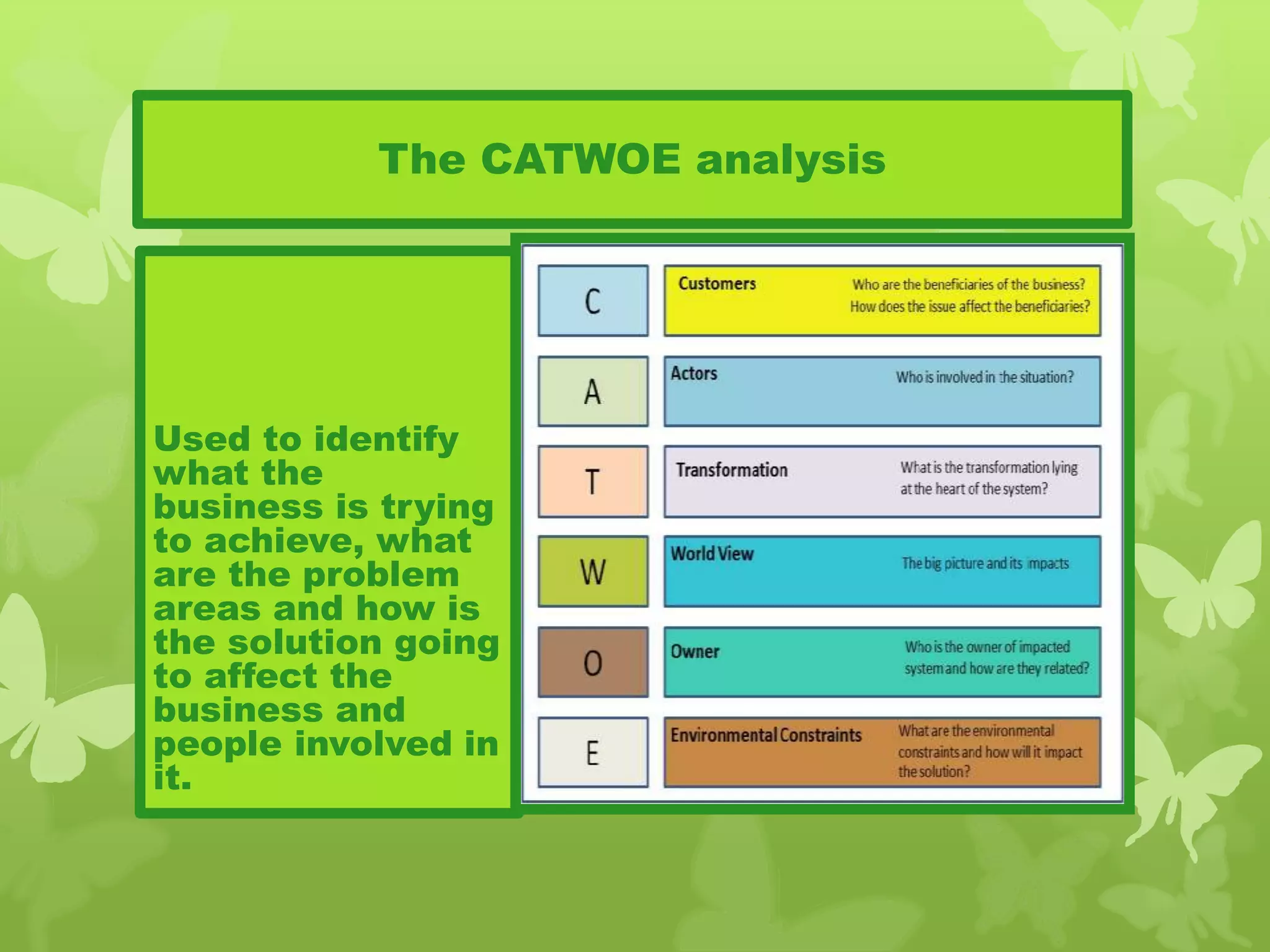
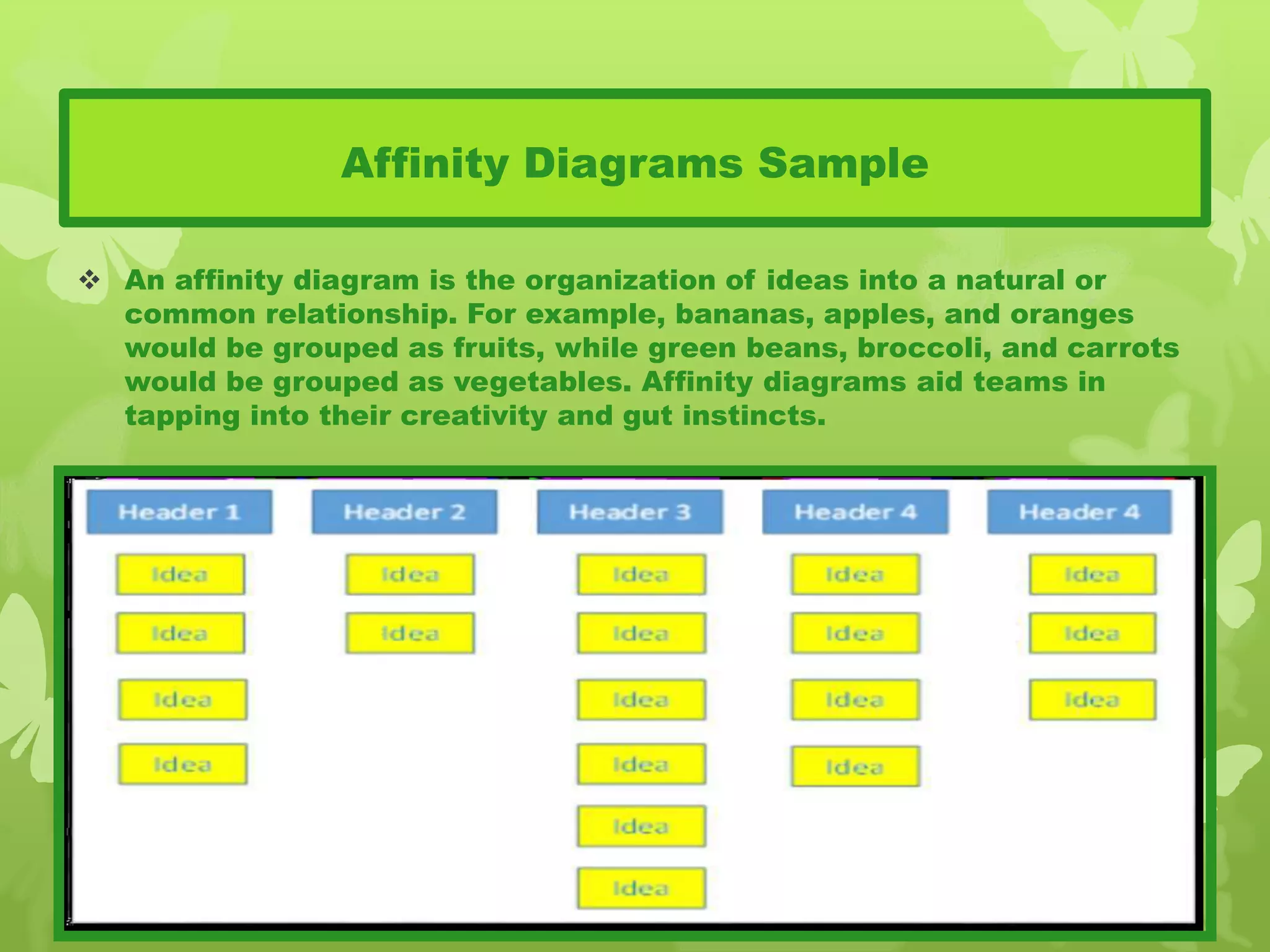
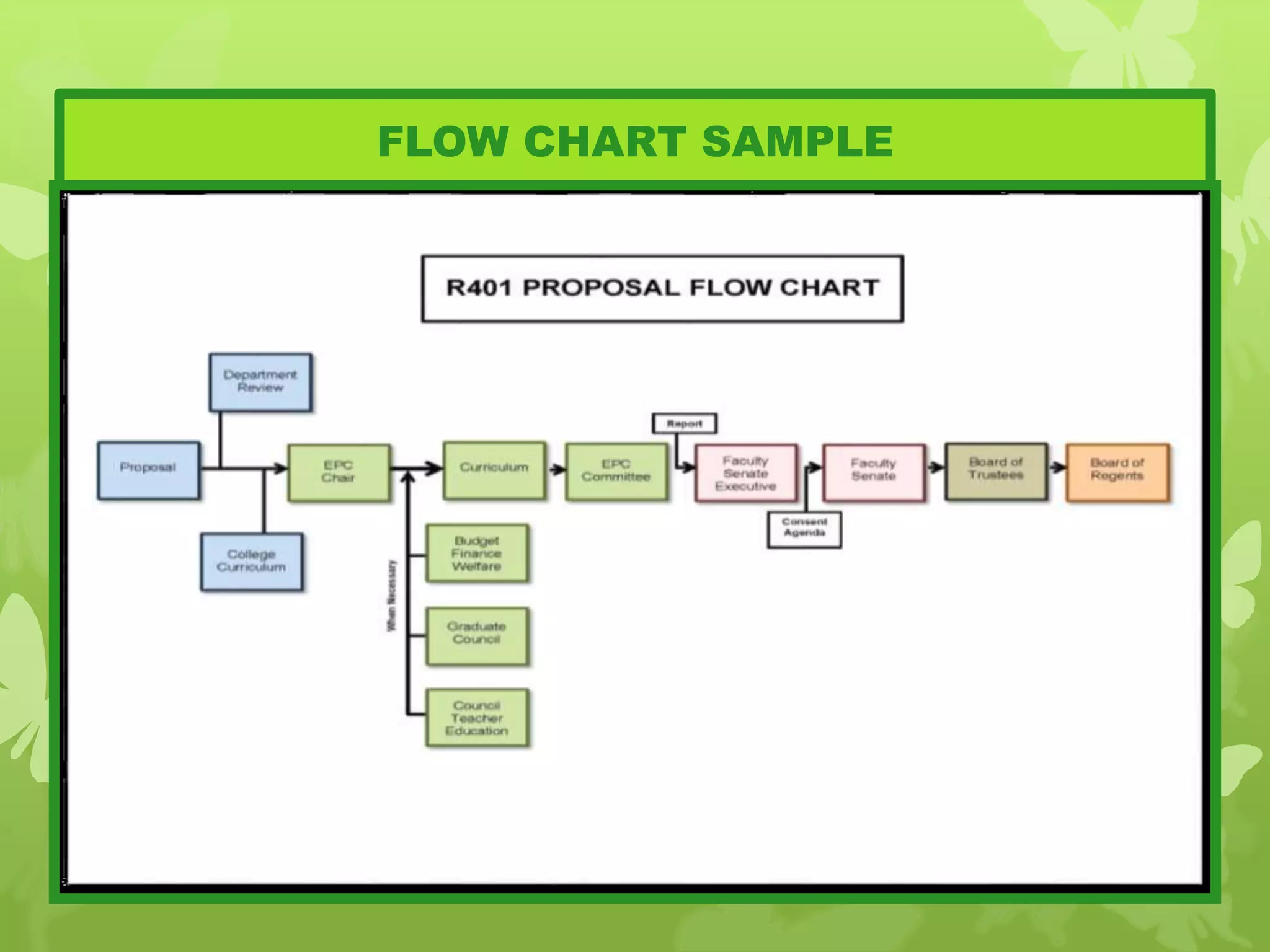
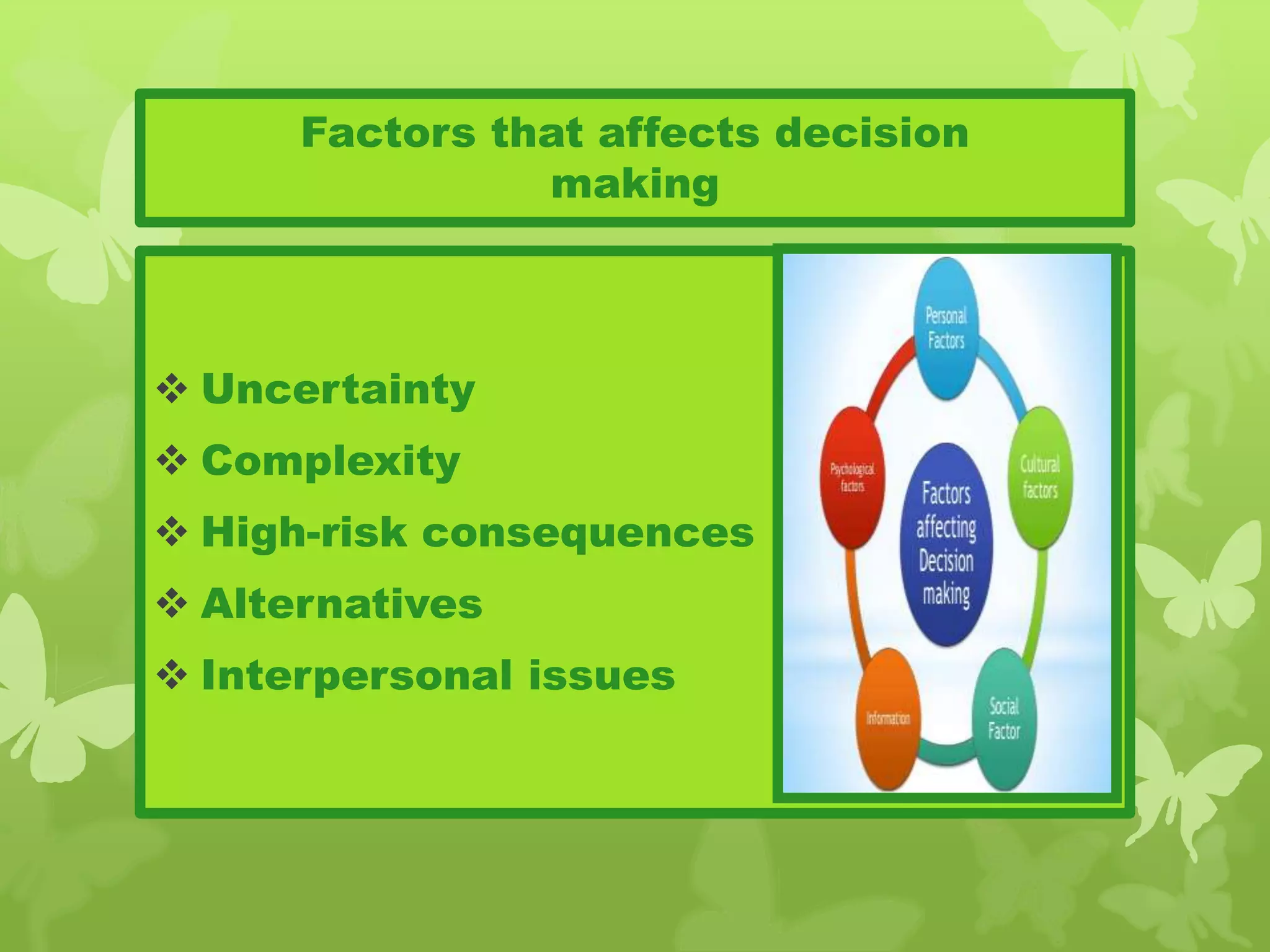
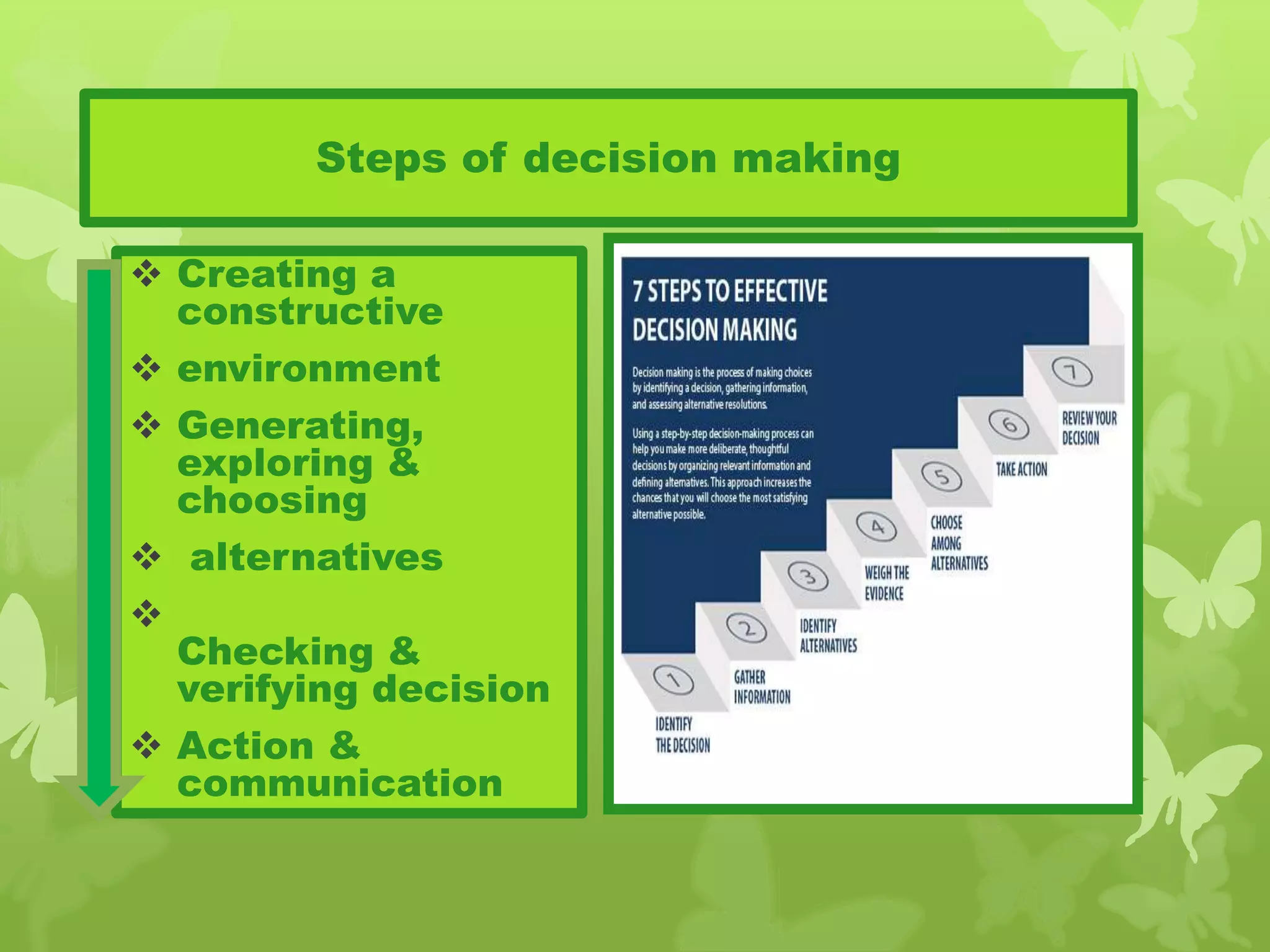
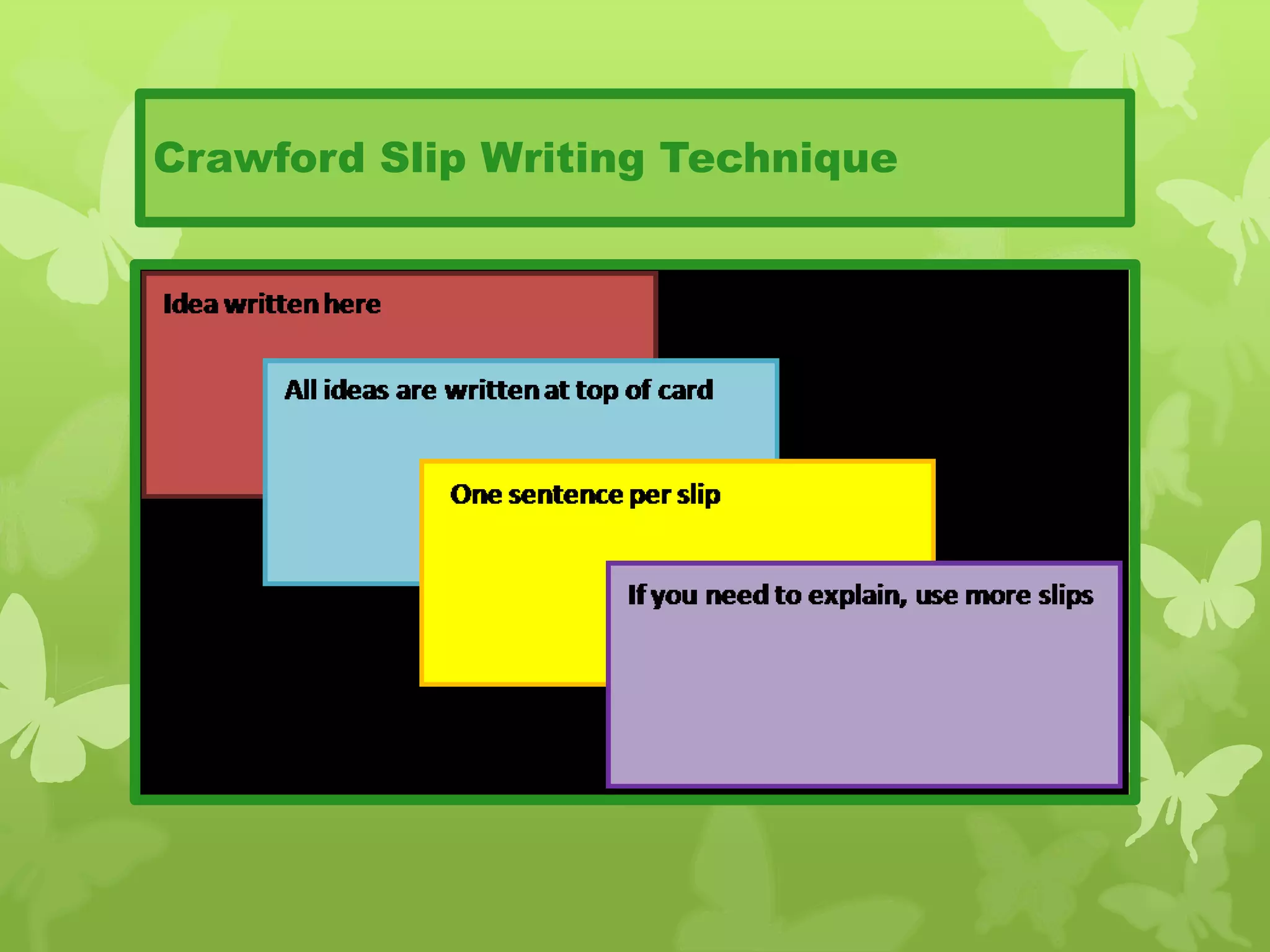
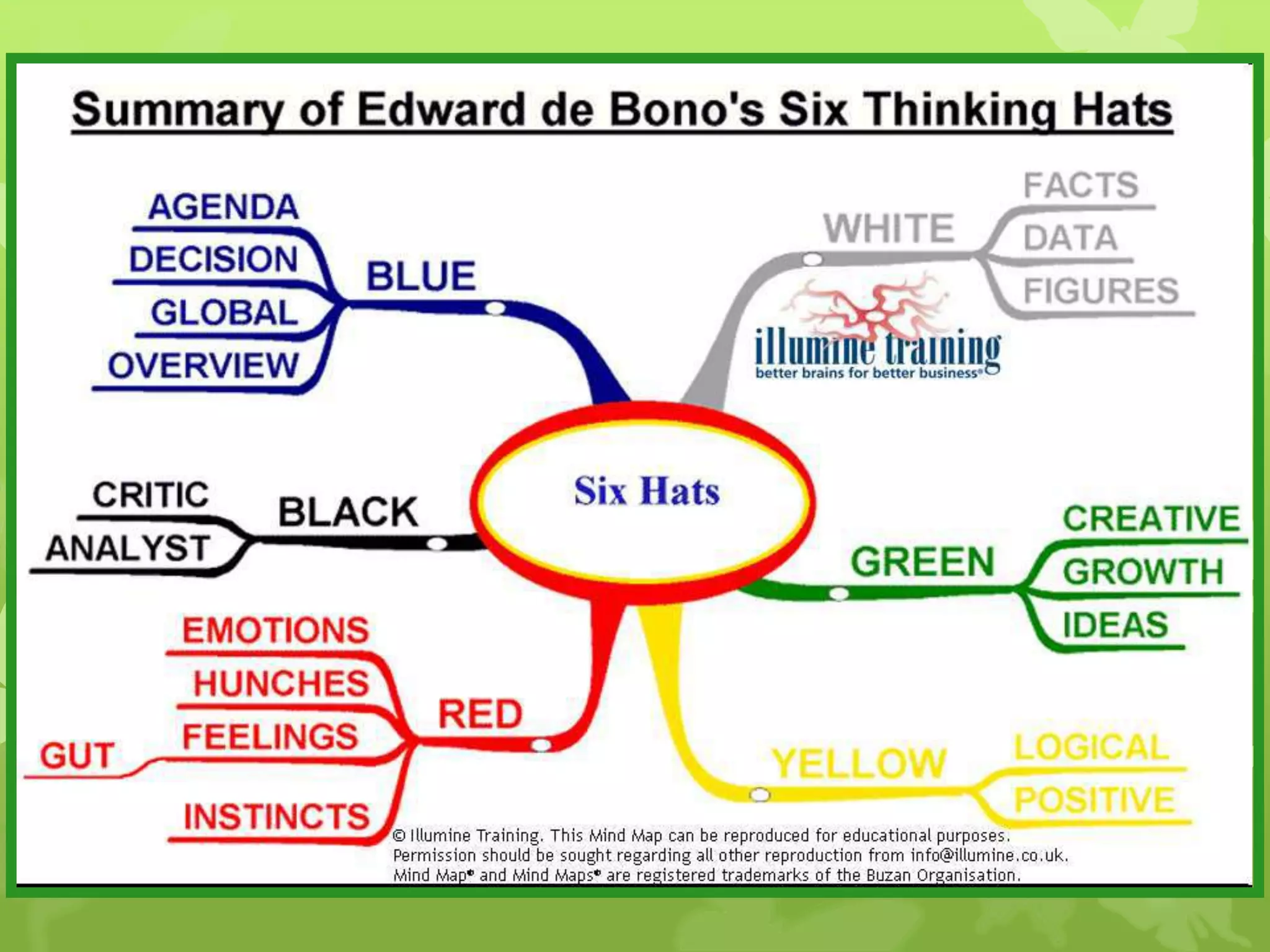
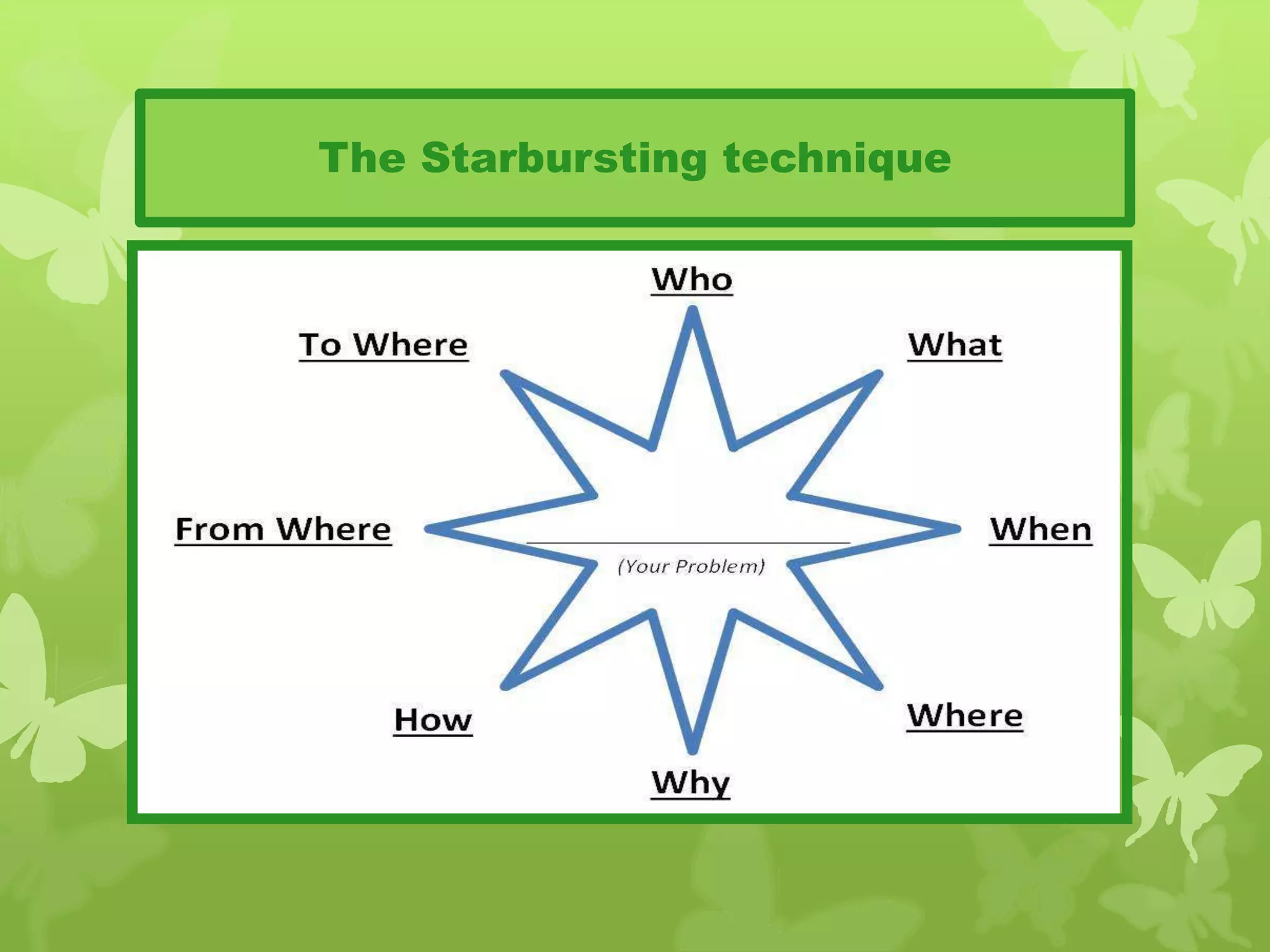
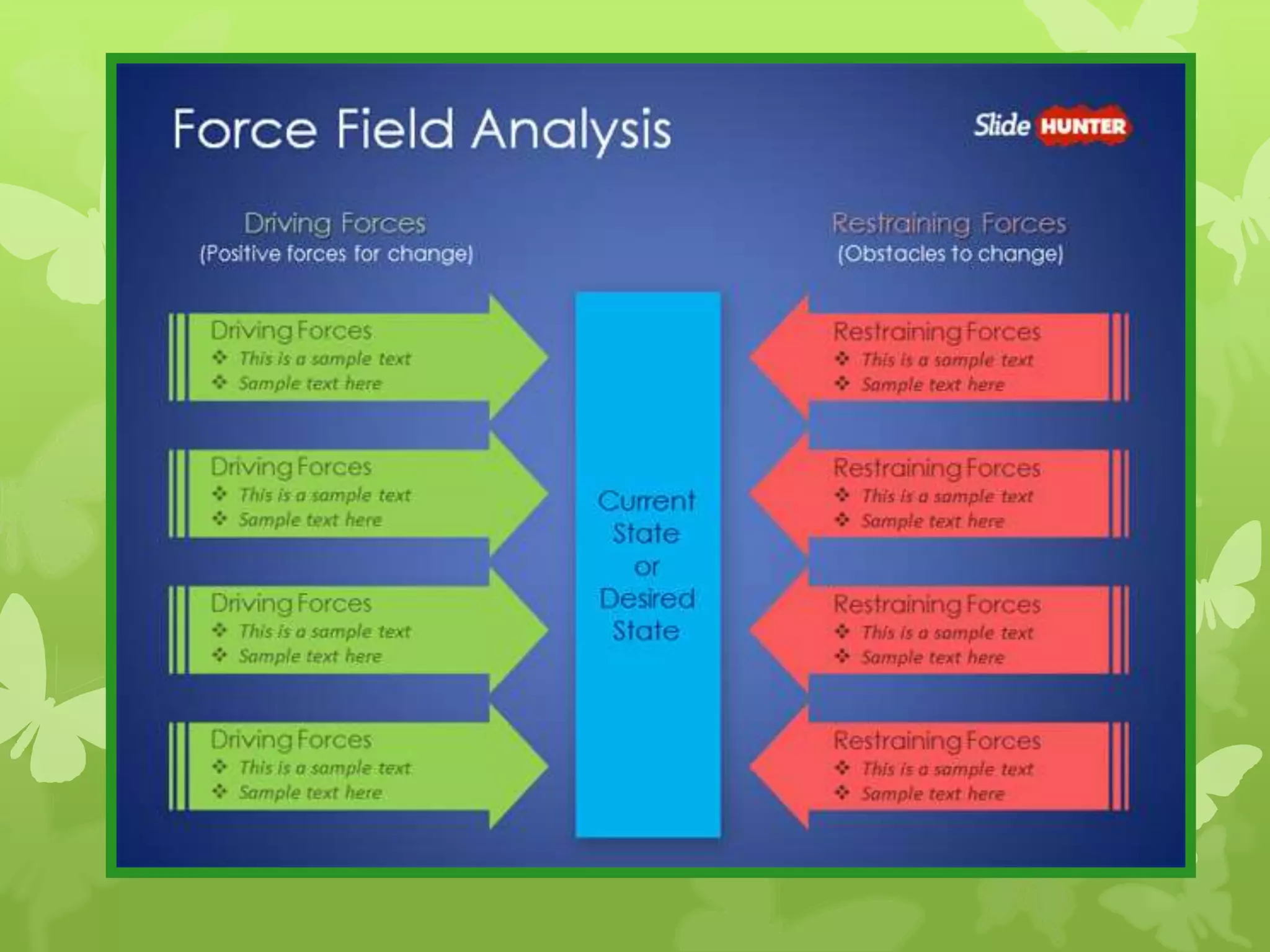
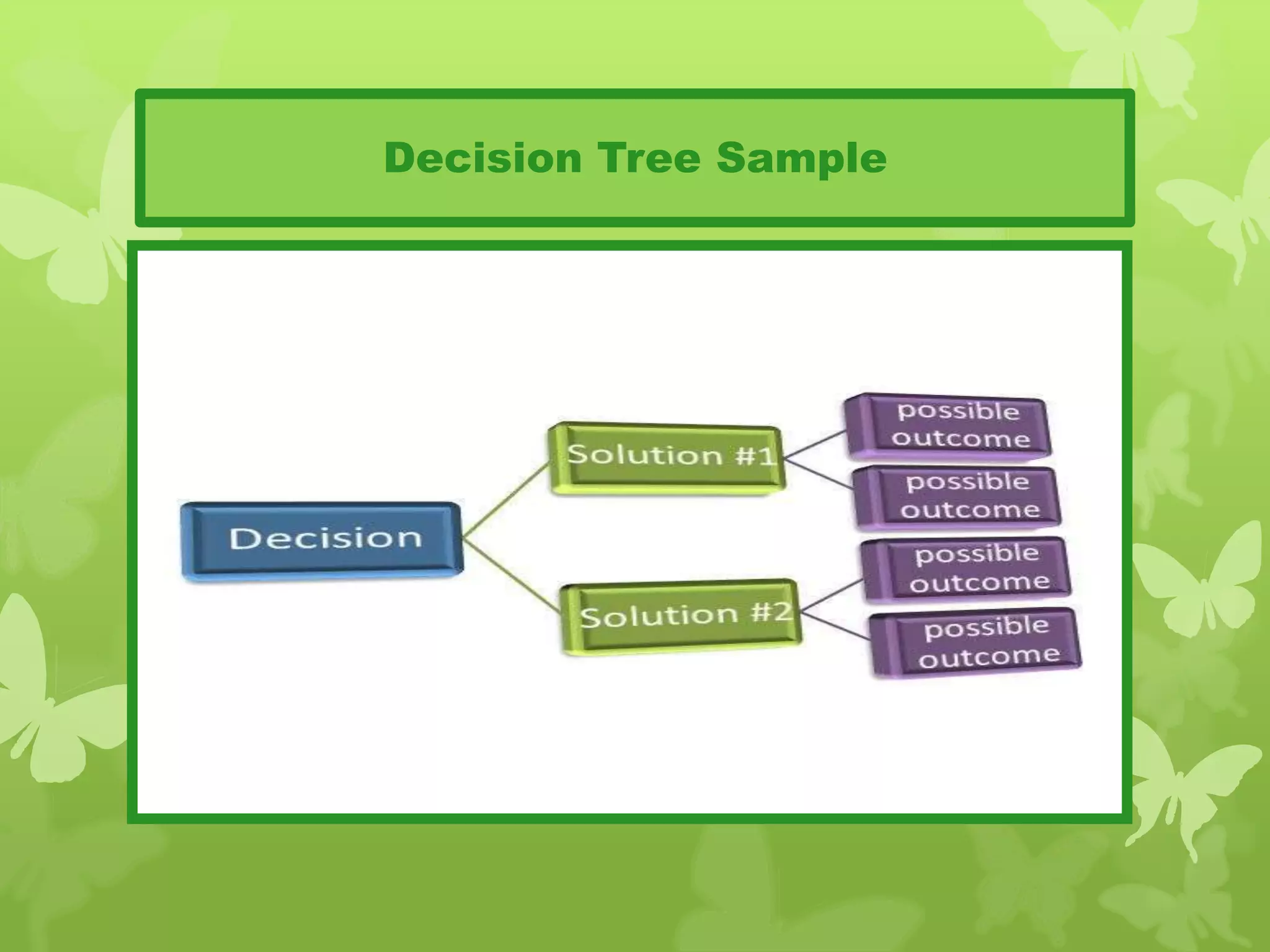
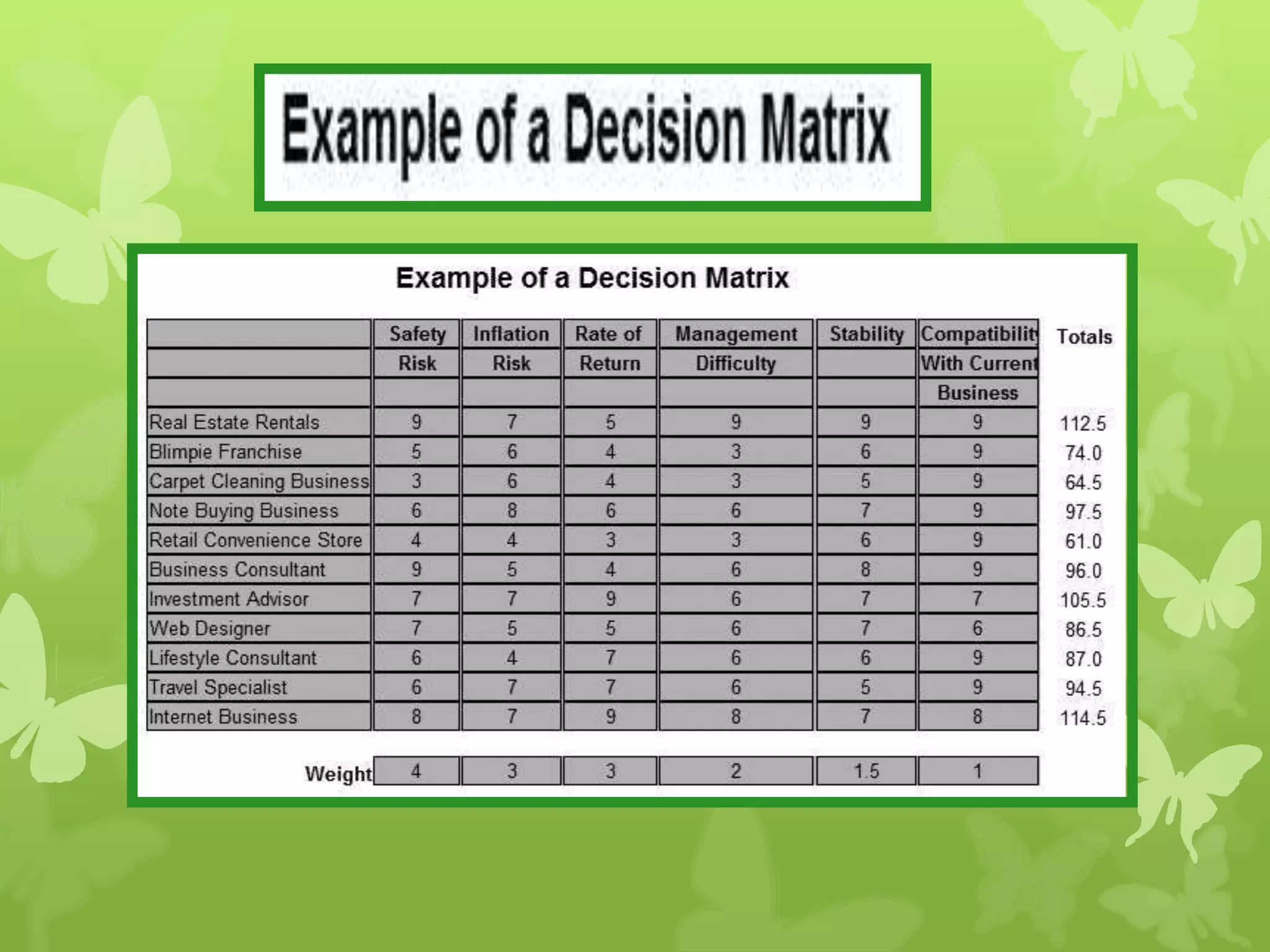
This document provides information on problem solving skills and the problem solving process. It discusses why problem solving skills are important, defines what a problem is, and outlines the main steps in the problem solving process as: defining the problem, generating alternatives, choosing the best alternative, and getting feedback. It then goes on to provide more details on various tools that can be used at each step, such as the 5 Whys technique for problem definition and decision matrices for choosing a solution. The document also discusses decision making skills and factors that can influence decision making.