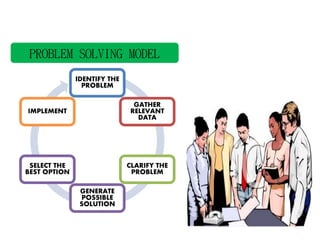
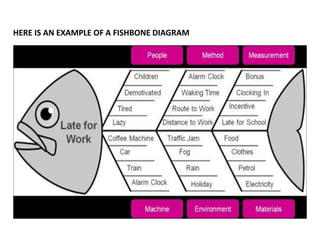
This document discusses problem solving in the workplace. It defines a problem and problem solving. There are common problems that arise in any workplace due to collaboration, deadlines, budgets, and organizational culture/norms. Specific problems include communication issues, attitudes, performance, discrimination, and policies. Effective problem solving requires clearly defining the problem, gathering relevant data, generating possible solutions, selecting the best option, and implementing it. Approaches like trial and error, experimentation, and fishbone analysis can be used. Characteristics of good problem solvers are outlined.