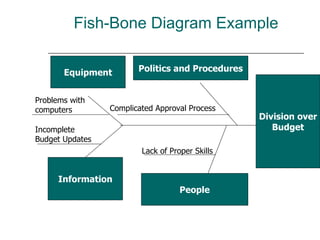
This document defines creativity and problem solving, outlining various models and techniques. It discusses Wallas' five stages of creativity (preparation, incubation, intimation, illumination, verification) and the standard five-step method for problem solving (stating the problem, identifying causes, choosing solutions, applying solutions, planning next steps). A variety of problem solving tools are also introduced, such as brainstorming, fishbone diagrams, and SWOT analysis, which is demonstrated with an example for analyzing a hypothetical organization.