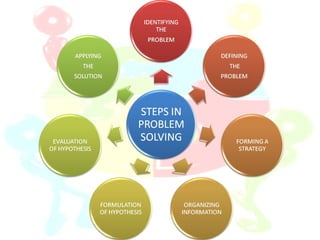
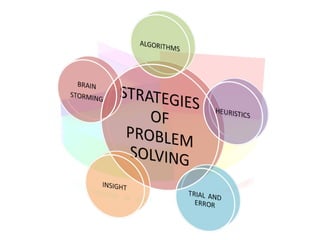
Problem solving is a mental process of discovering, analyzing, and solving problems to overcome obstacles and find the best solution. A problem exists when a problem solver has a goal but does not know how to reach it. Problem solving involves making adjustments despite interference to attain a goal, according to Skinner's definition. Common problem solving methods include algorithms, heuristics, trial-and-error, insight, and brainstorming. Factors like the nature of the problem, prior experience, and mental state can impact the problem solving process. Teachers can help by selecting problems, motivating students, encouraging divergent thinking, and providing guidance and practice.