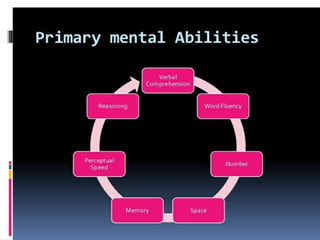
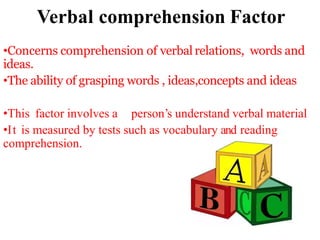
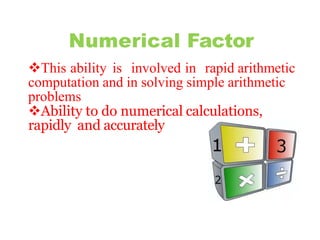
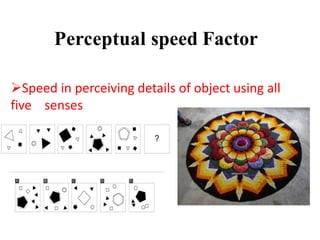
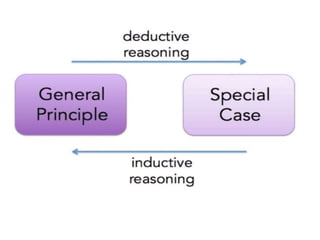
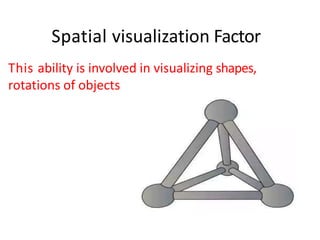
Thurstone proposed a theory of intelligence comprising multiple primary mental abilities. He identified 7 primary abilities initially - verbal comprehension, verbal fluency, numerical ability, perceptual speed, inductive reasoning, spatial visualization, and memory. He later added 2 more abilities - deductive reasoning and problem solving. According to Thurstone, intelligence is made up of these distinct but interrelated abilities rather than being a single general ability. His theory contributed to the measurement of attitudes and development of later theories of multiple intelligences. However, its limitation was discarding the concept of a common factor underlying all abilities.