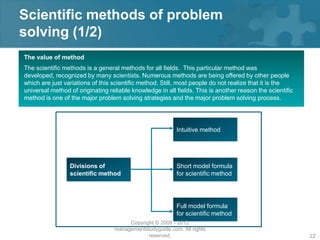
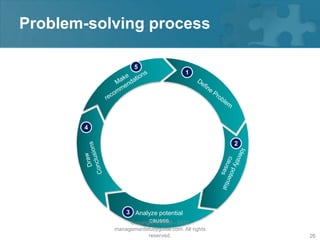
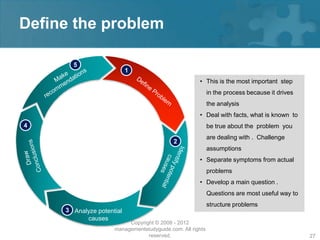
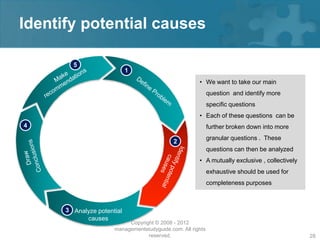
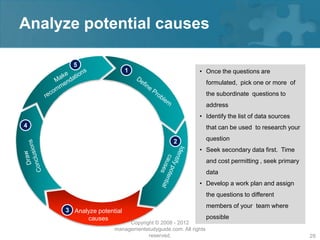
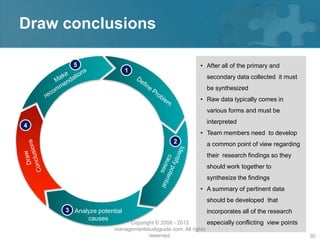
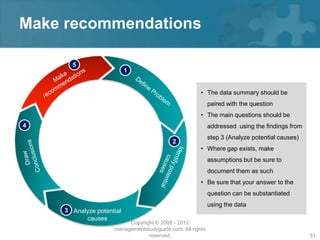
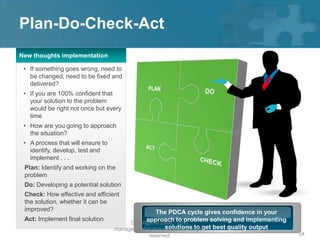
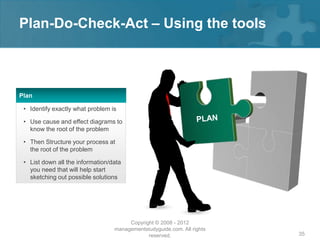
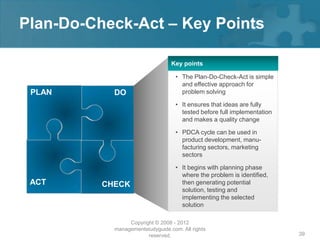
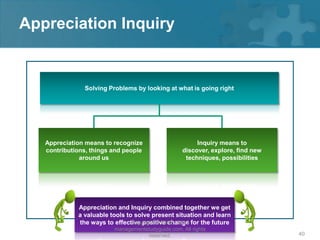
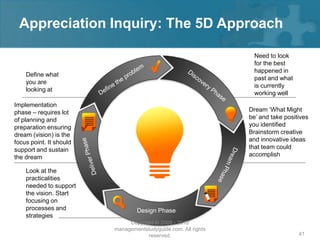
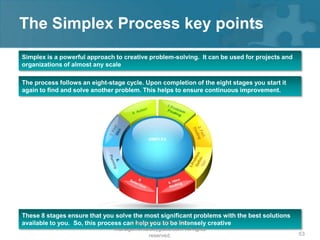
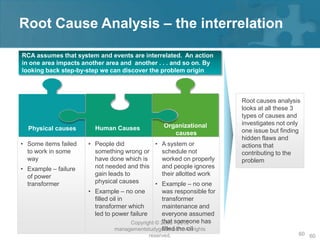
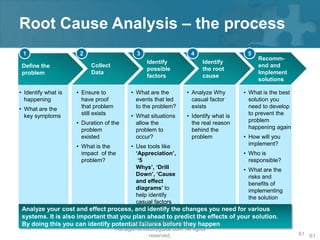
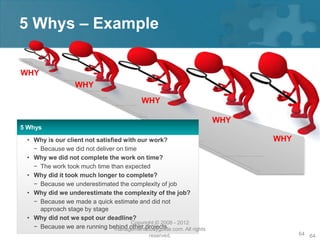
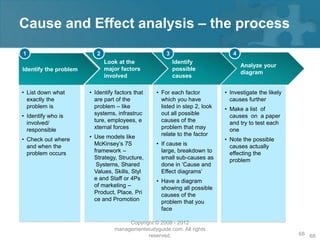
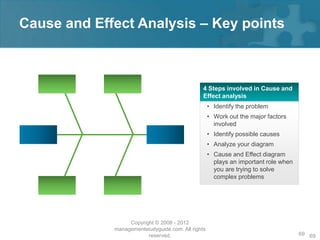
Here are the key steps of the scientific method:
1. Observation and description of a phenomenon or group of phenomena. This includes how it was measured or counted, under what conditions, and other relevant qualitative and quantitative details.
2. Development of a hypothesis to explain the phenomena. A hypothesis is not yet a theory - it is an educated guess or supposition.
3. Use of the hypothesis to predict the existence of other phenomena, or to predict quantitatively the results of new observations and experiments.
4. Performance of experimental tests of the predictions by several independent experimenters and researchers.
5. Iterative refinement of the hypothesis based on the experimental evidence, or development of alternative hypotheses.
6.