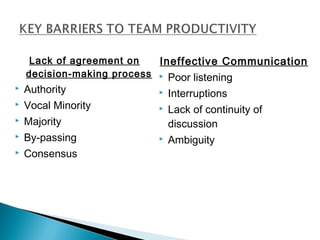
The document discusses the benefits of teamwork over individual work. It states that teams outperform individuals because they allow for sharing of knowledge and experiences between members. Teams can respond quickly to new challenges because of this collaboration. Effective teamwork facilitates communication, motivation, creativity, problem-solving skills, and breaking down of barriers. The document then discusses different types of teams like project teams, cross-functional teams, and self-directed work teams. It also outlines the typical stages of team development like forming, storming, norming, performing, and dissolving. Key skills for effective team management are also highlighted such as delegating, motivating, managing conflicts, communicating, and avoiding common mistakes.