Embed presentation
Download to read offline



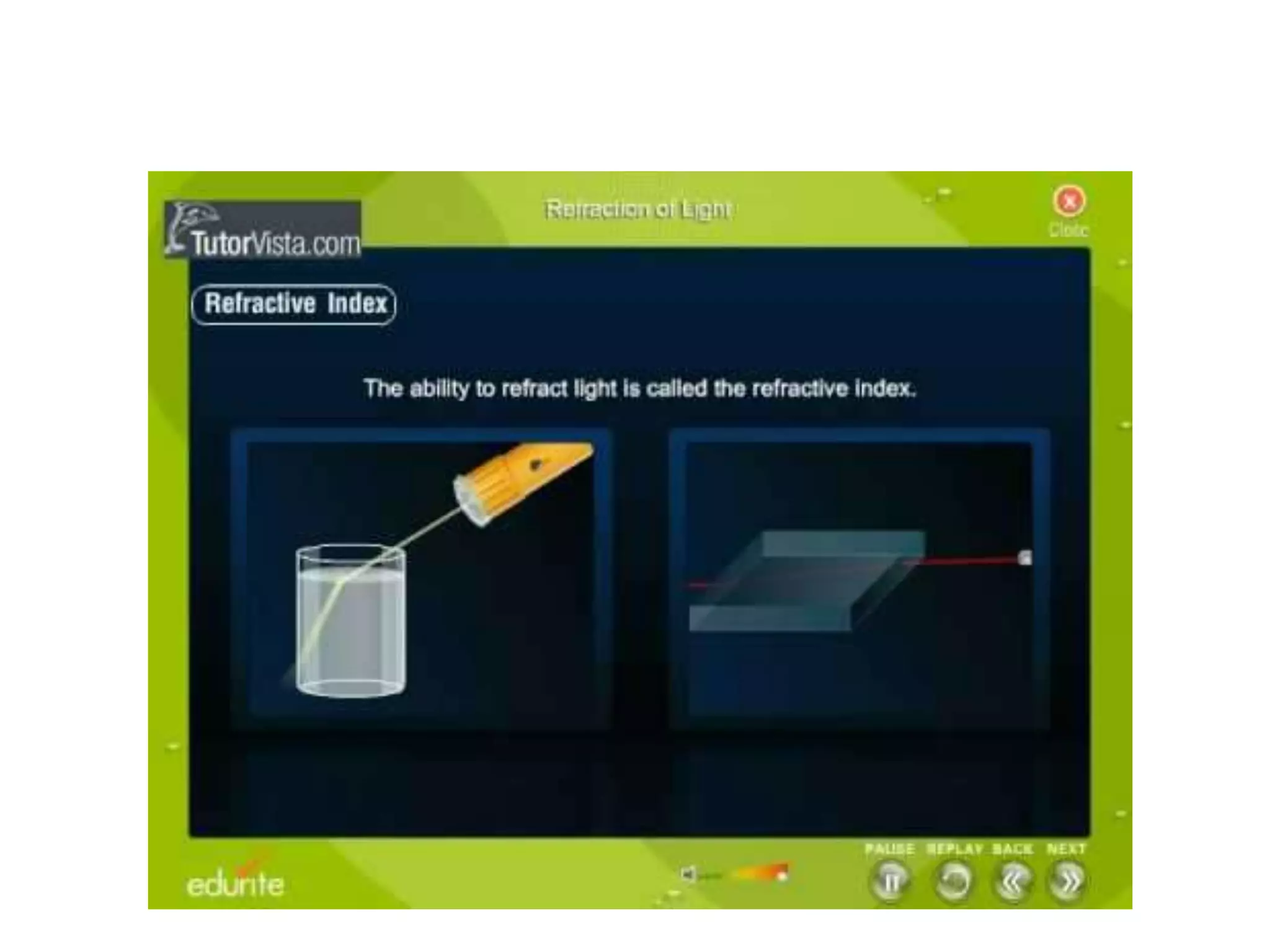


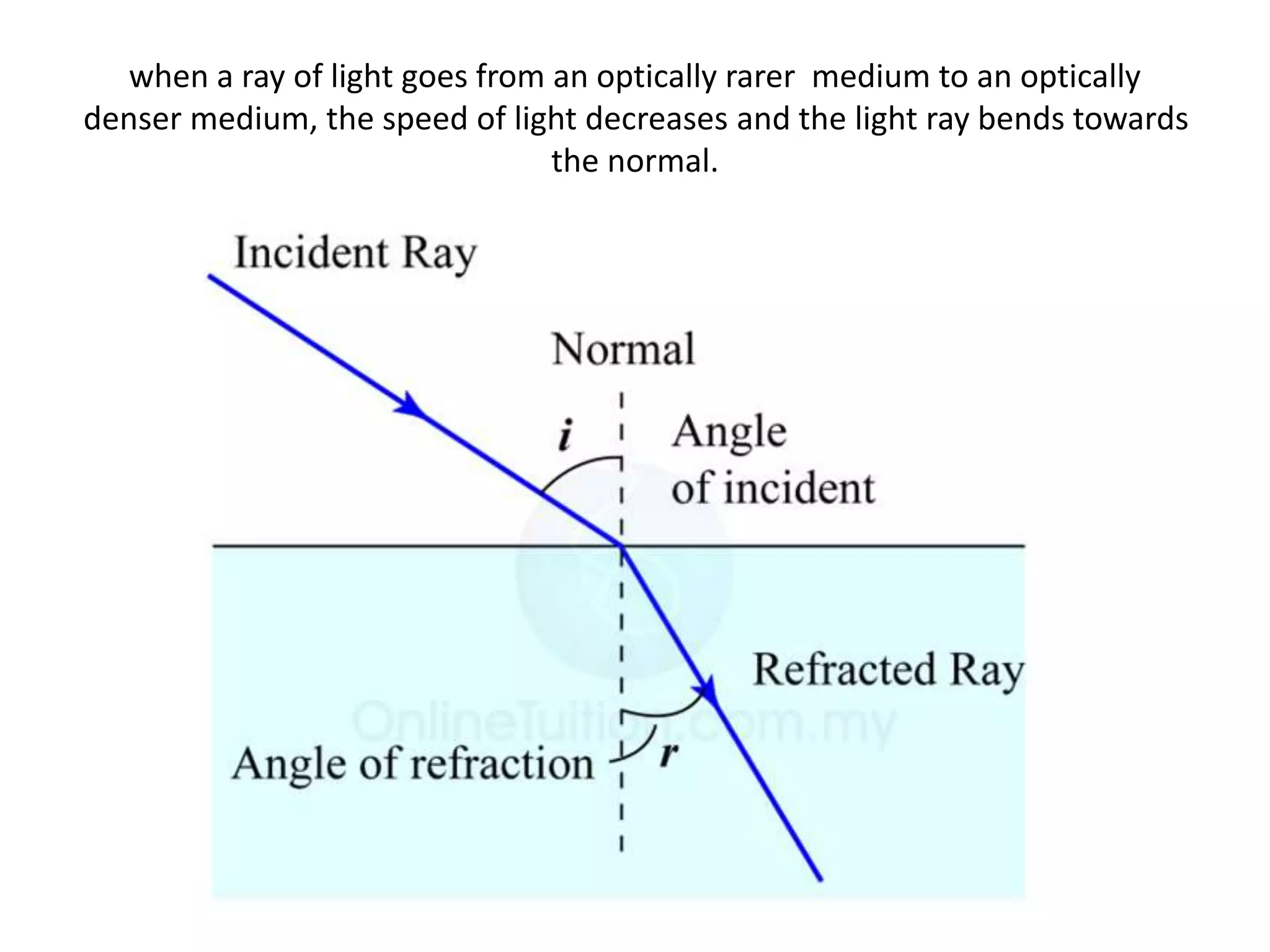
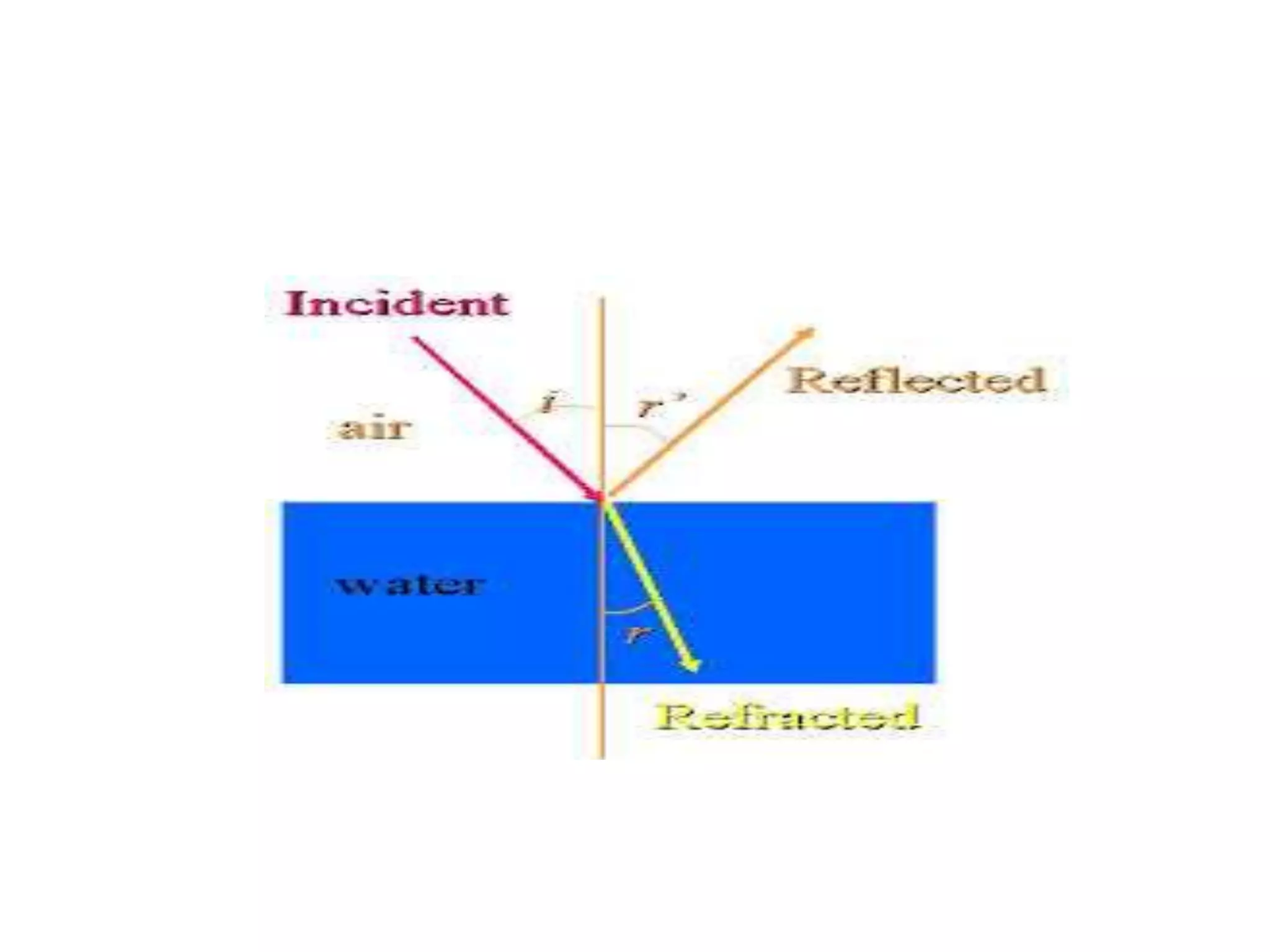
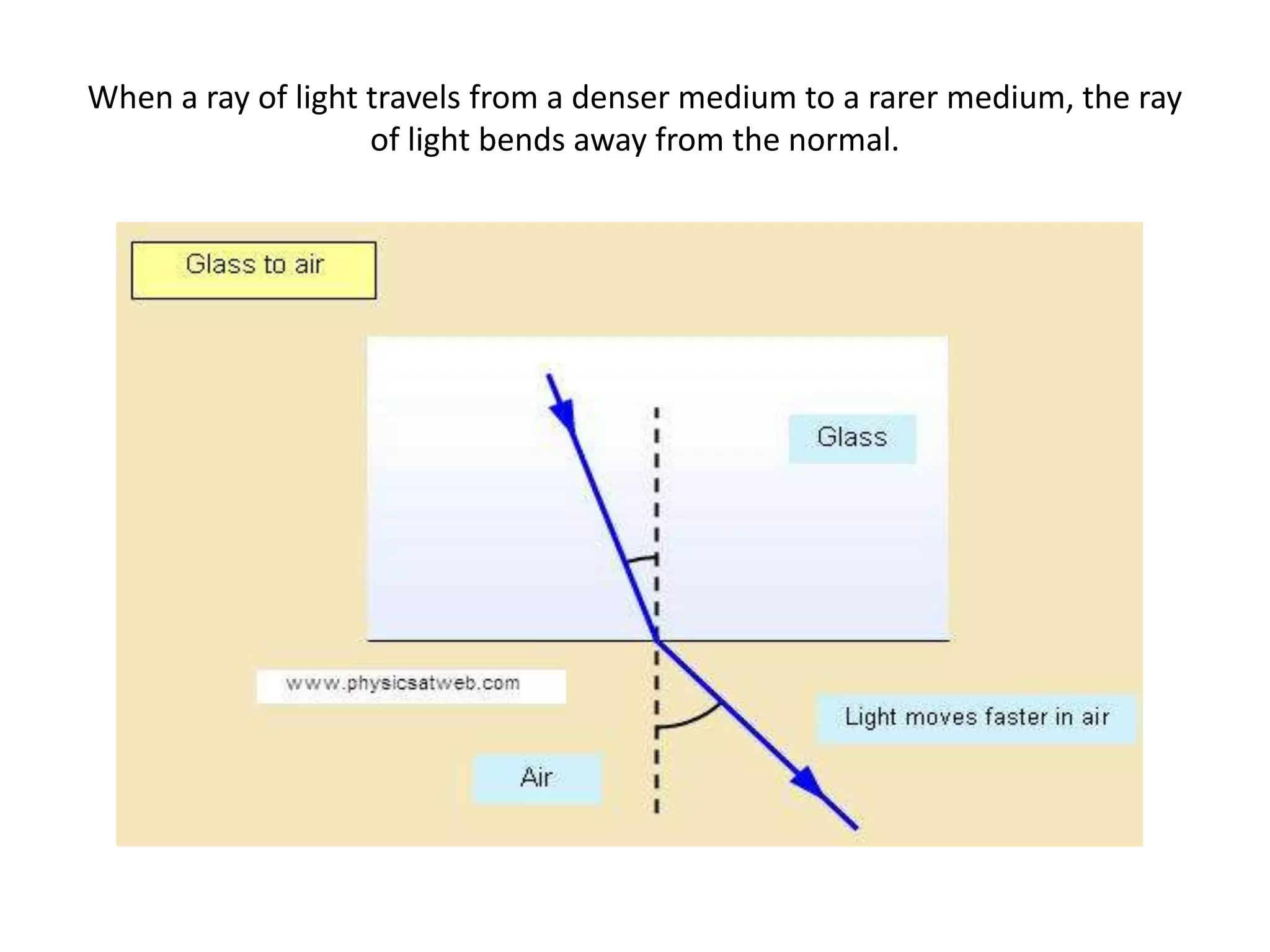
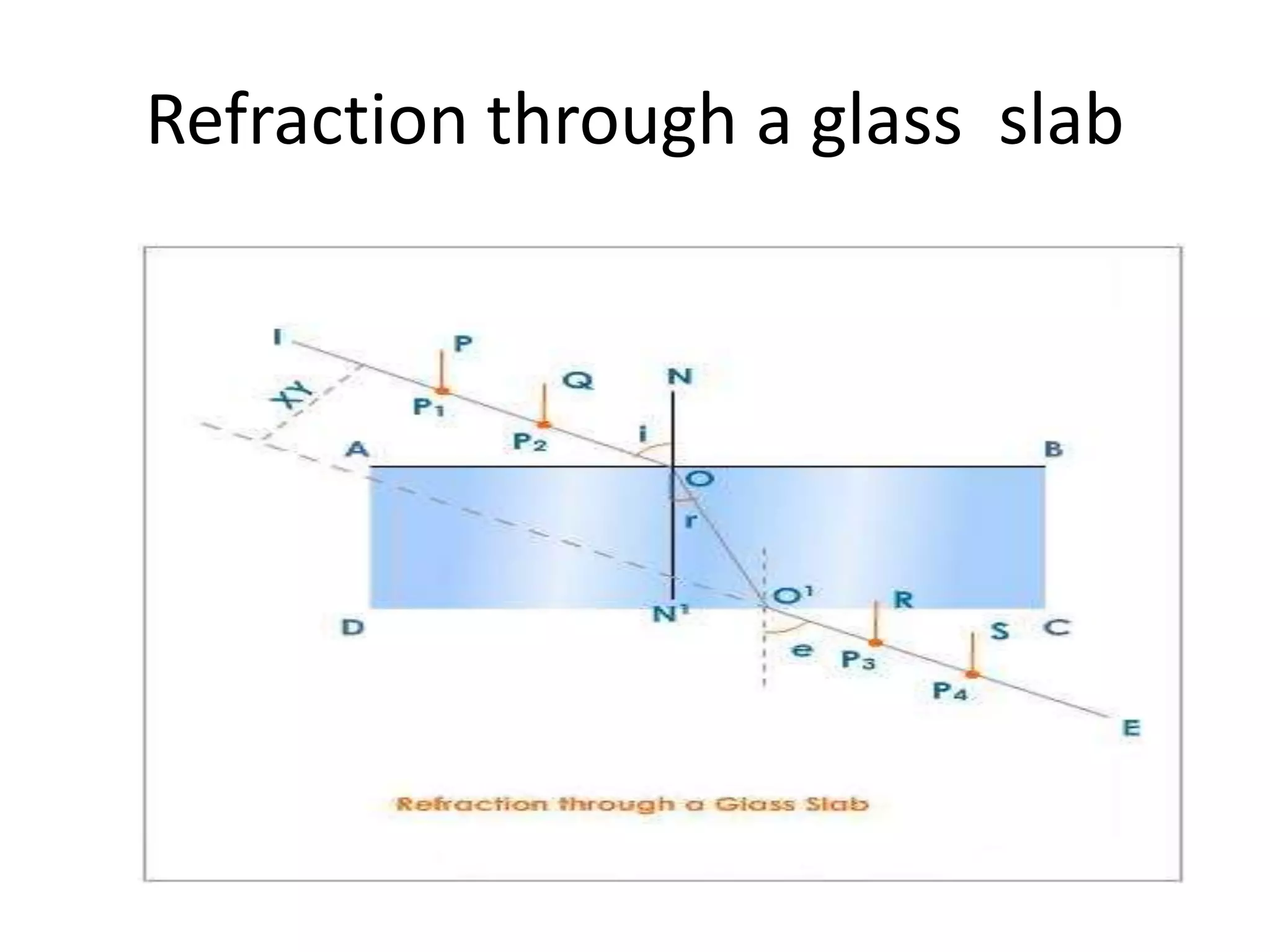

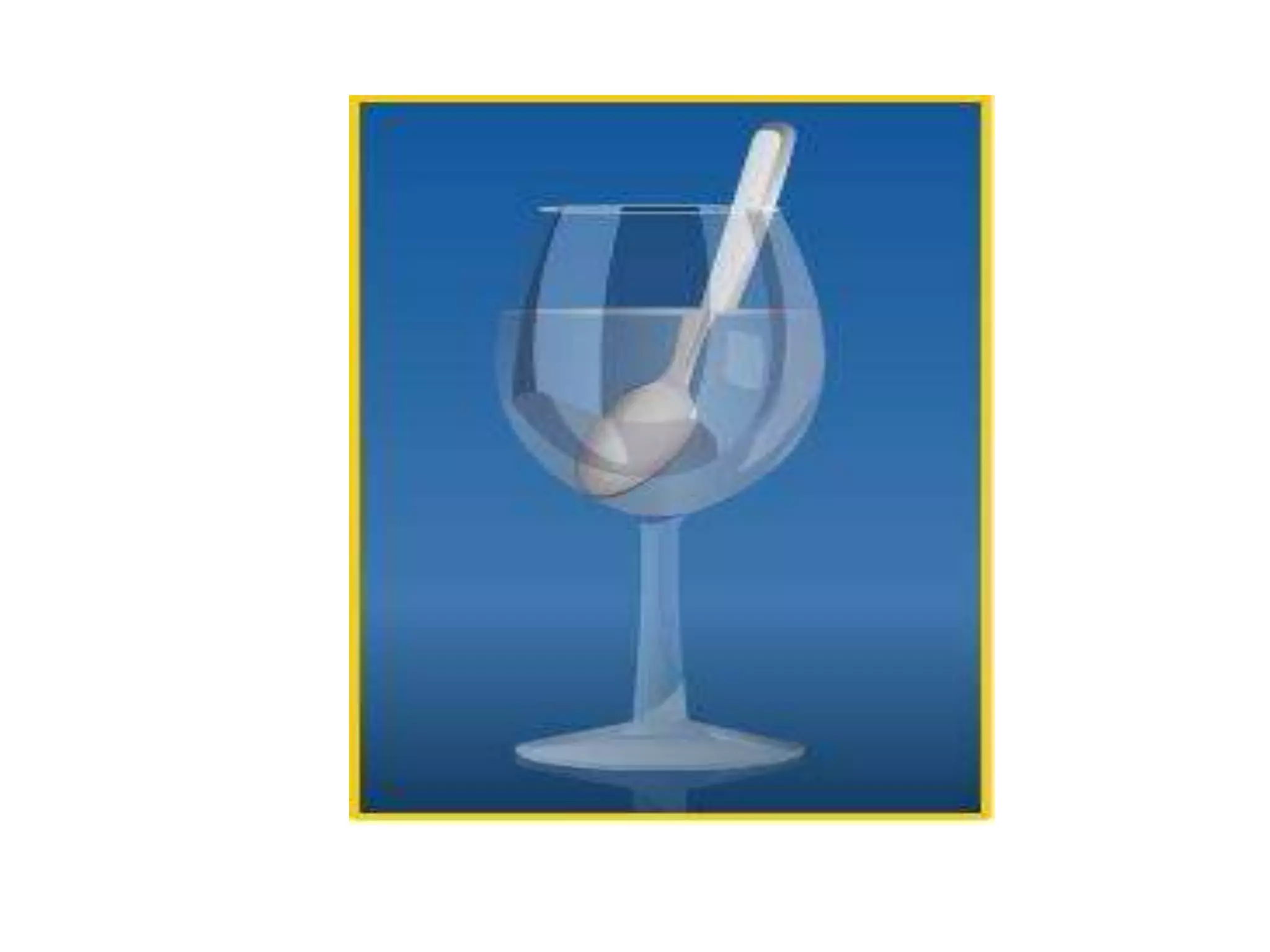
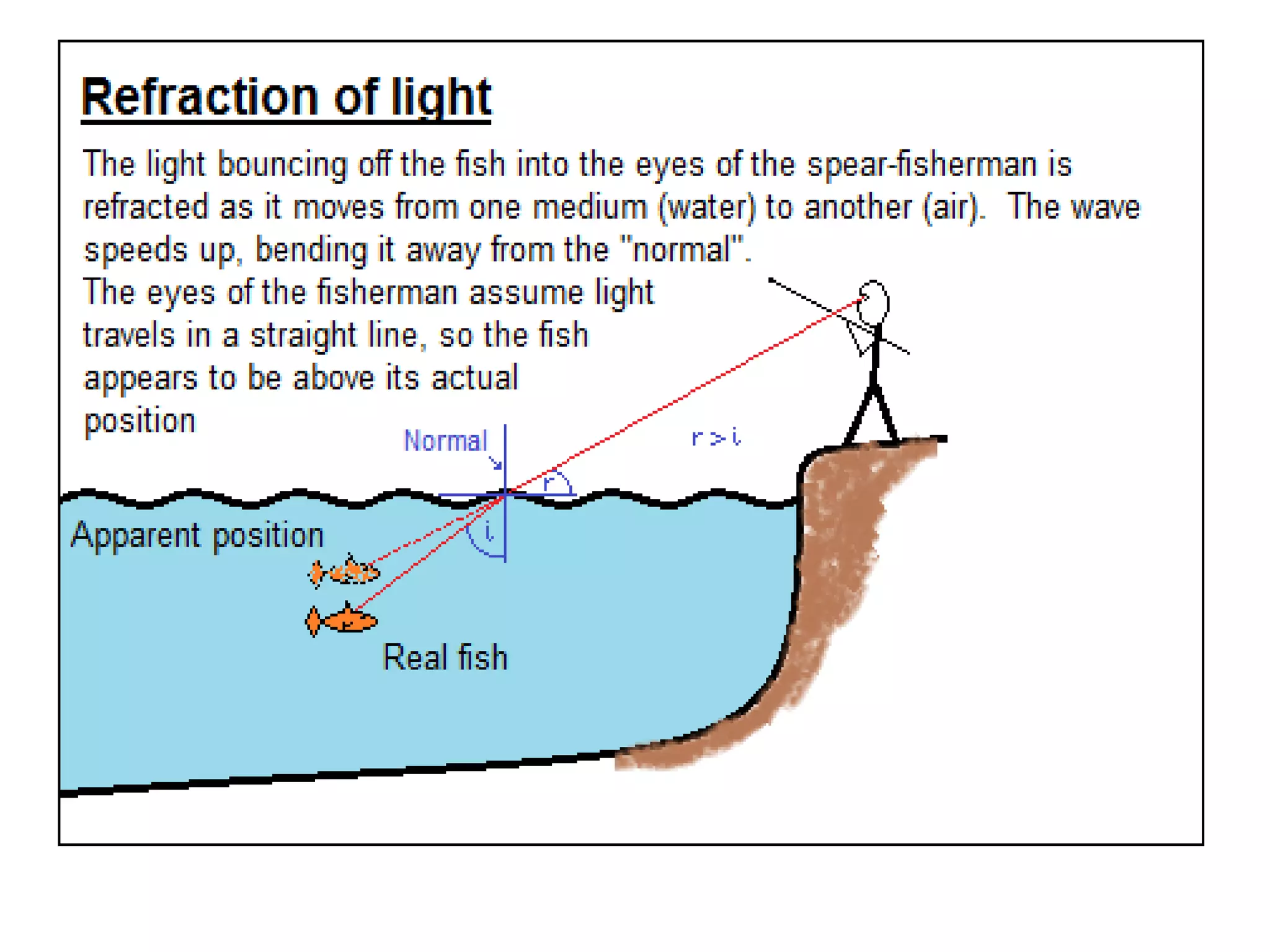
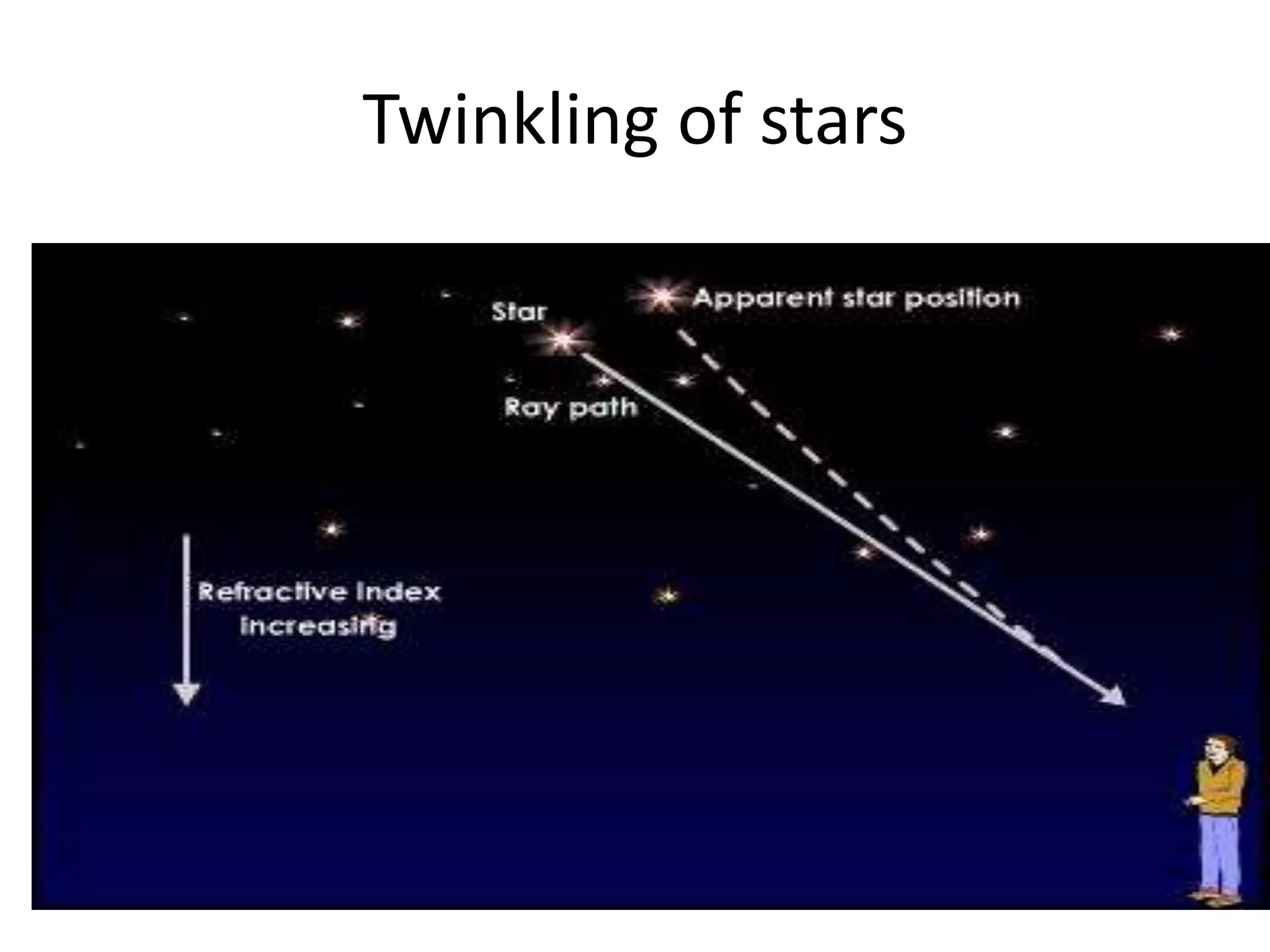


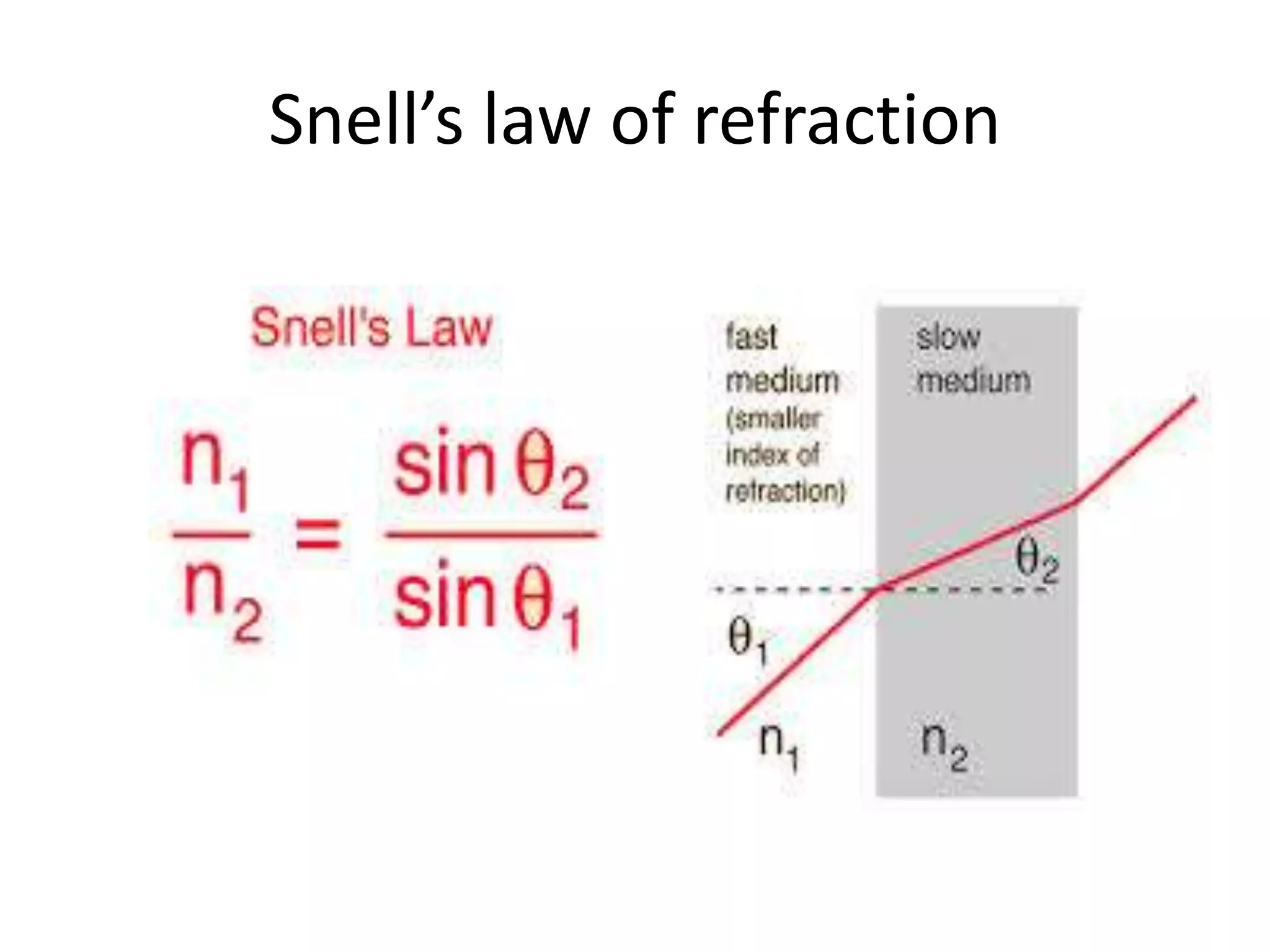

Light refracts when passing from one optical medium to another with a different density. When light travels from a denser to rarer medium, it bends away from the normal, and when traveling from rarer to denser, it bends towards the normal. The change in direction light undergoes when passing obliquely between media of different densities is called refraction.

















