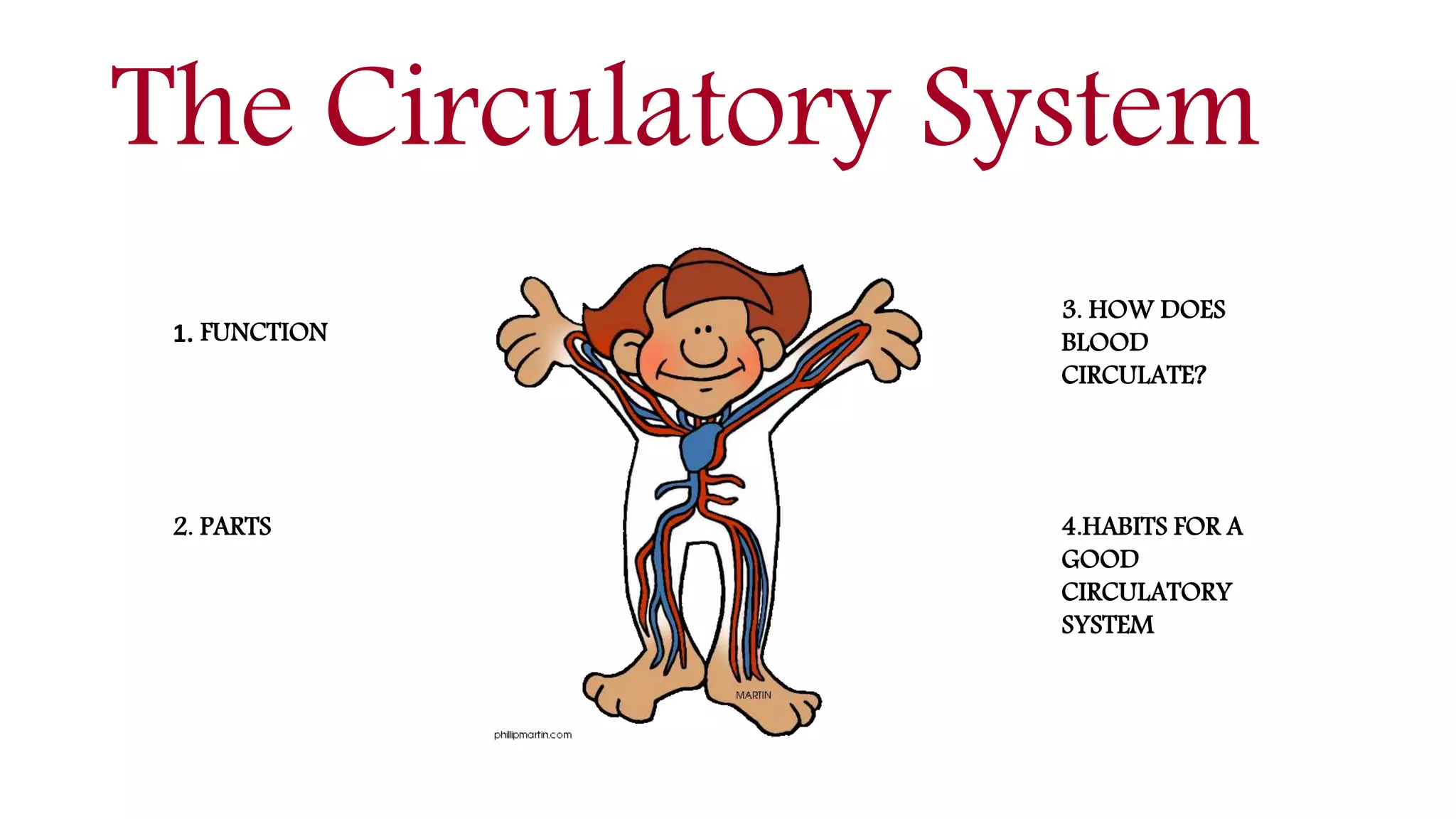
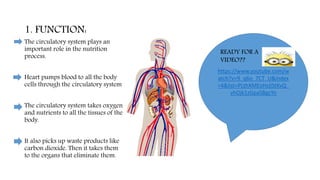
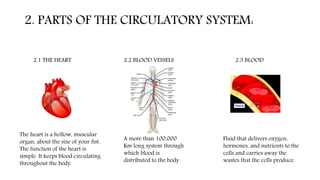
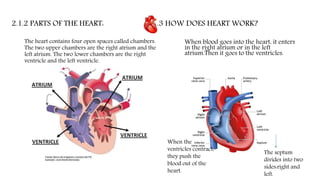
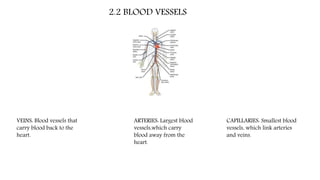
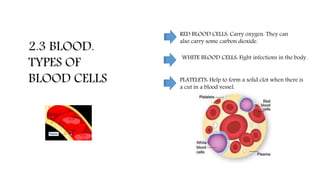
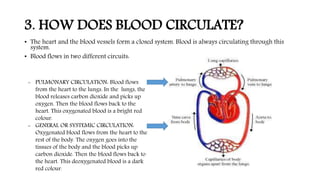
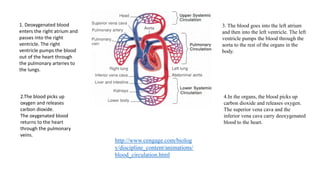
The circulatory system functions to transport oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body. It consists of the heart, blood vessels including arteries, capillaries and veins, and blood. The heart pumps blood through two circuits - pulmonary circulation to the lungs and systemic circulation to the rest of the body. Deoxygenated blood enters the heart's right side, is pumped to the lungs to receive oxygen, and enters the left side to be pumped through the body, where it releases oxygen and picks up carbon dioxide to be returned to the heart again.