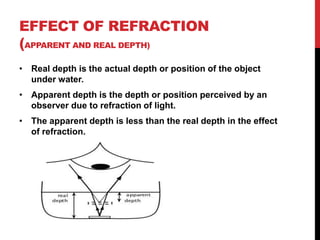
This document discusses key properties of light, including that it travels in straight lines at 3x10^8 m/s in a vacuum. It describes rays and beams of light and the reflection and refraction of light, including the laws of reflection. Reflection is when light bounces off surfaces, and refraction is when it bends when moving between materials of different densities. Refractive index measures the bending of light, and refraction makes objects appear at a different depth than their real depth under water.