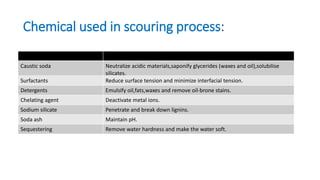
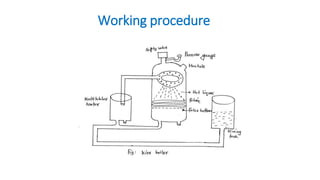
This presentation summarizes the scouring process used in textile engineering. Scouring involves treating textiles with alkali to remove oils, fats, waxes and other impurities. It increases the absorbency of textiles. There are two main scouring methods - discontinuous scouring using a kier boiler, and continuous scouring using a J-box system. The kier boiler involves loading fabric into a cylindrical vessel and spraying it with hot alkaline liquor over several hours. The J-box method scours open-width fabric using rolls to impregnate it with alkali and heat it in the J-shaped box for 30 minutes. Both processes aim to saponify oils and emuls