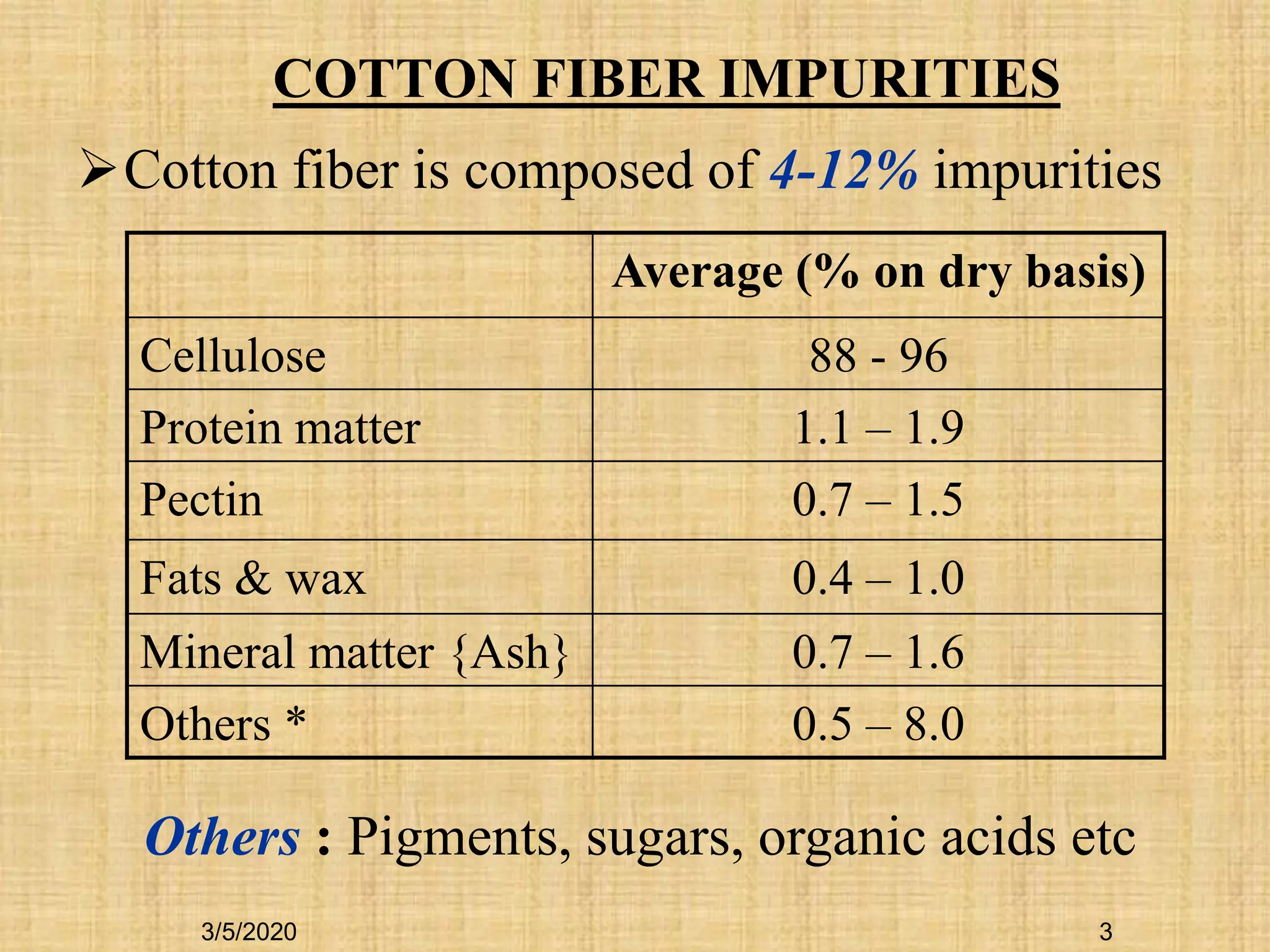
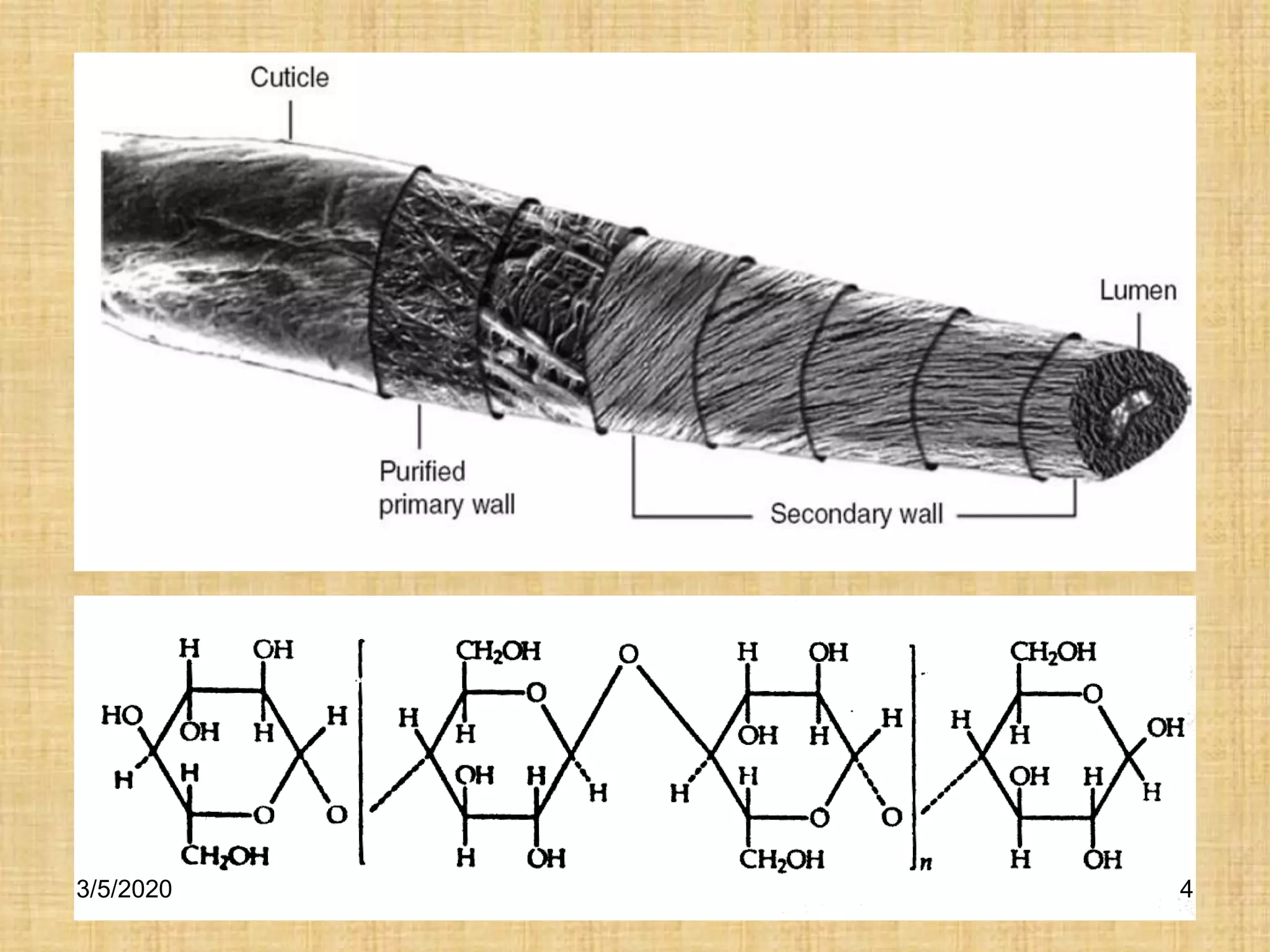
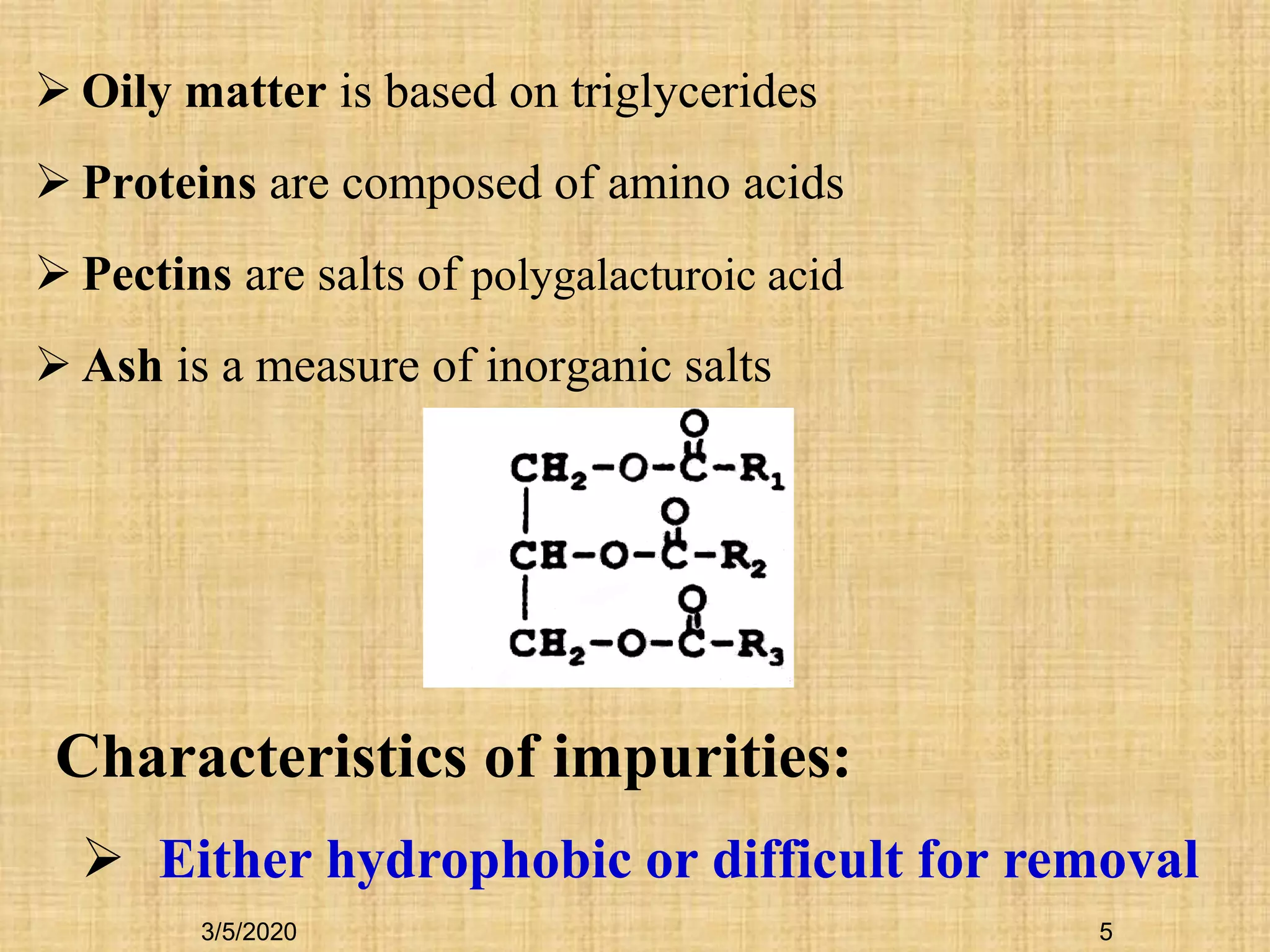
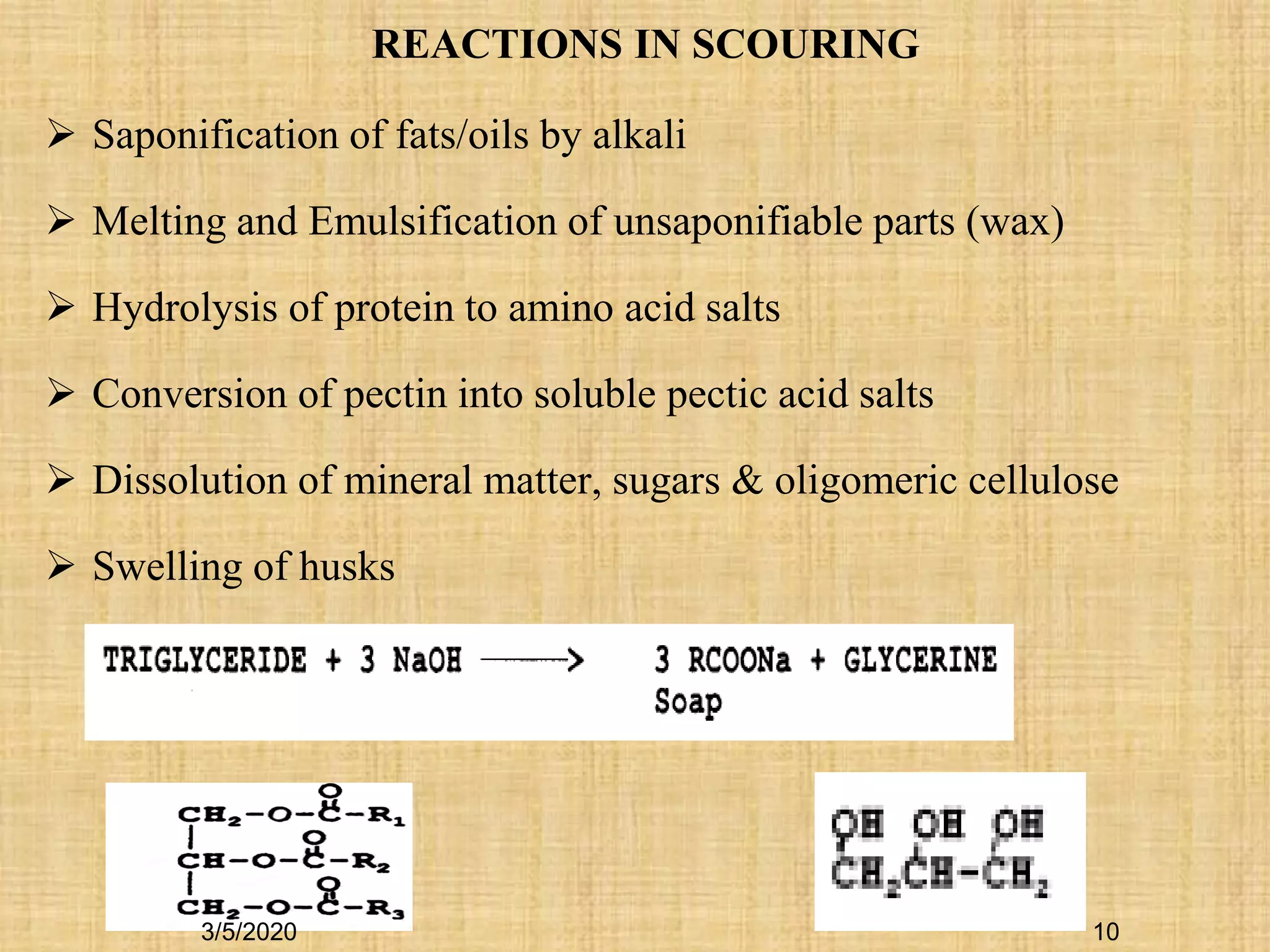
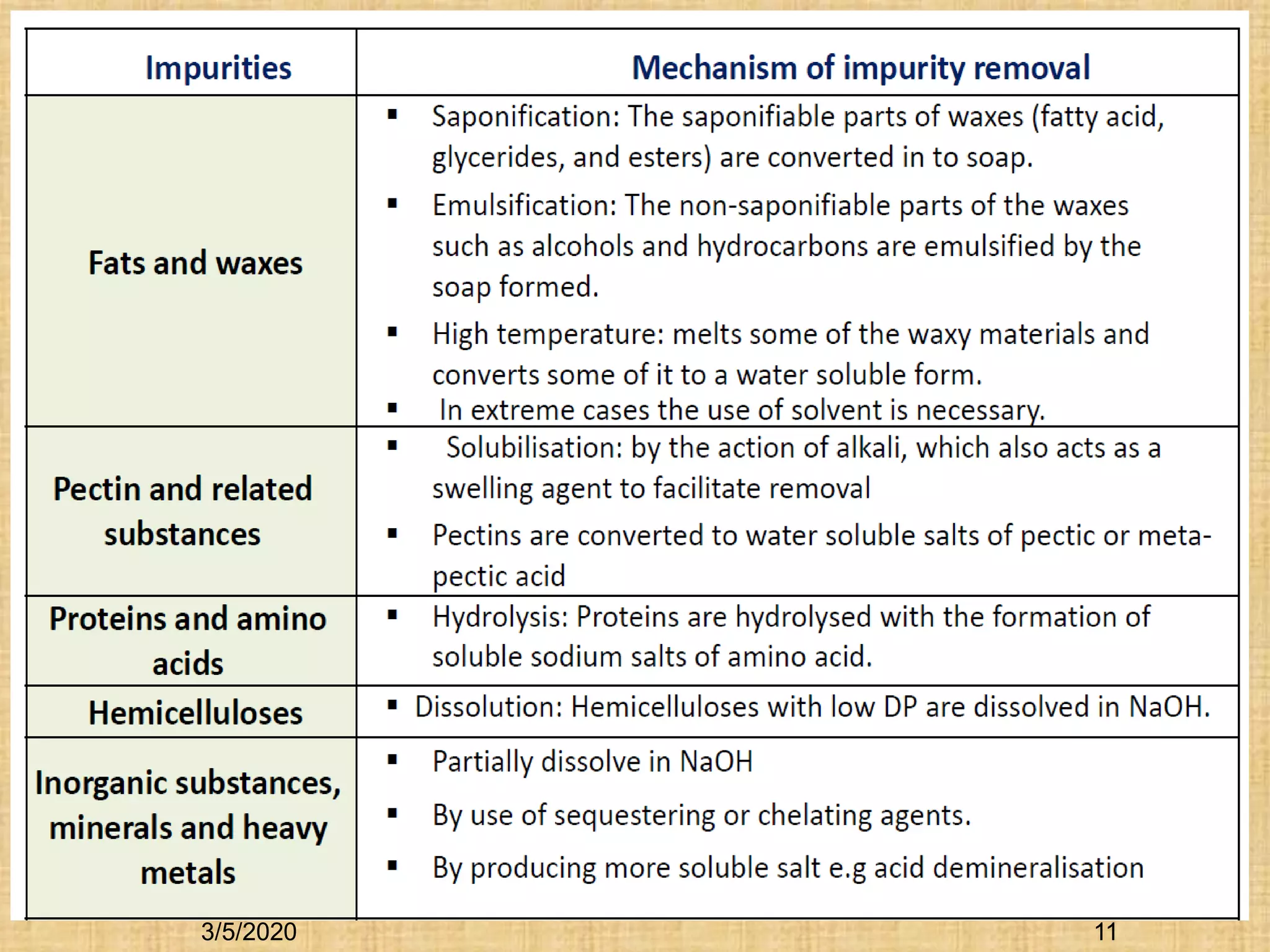
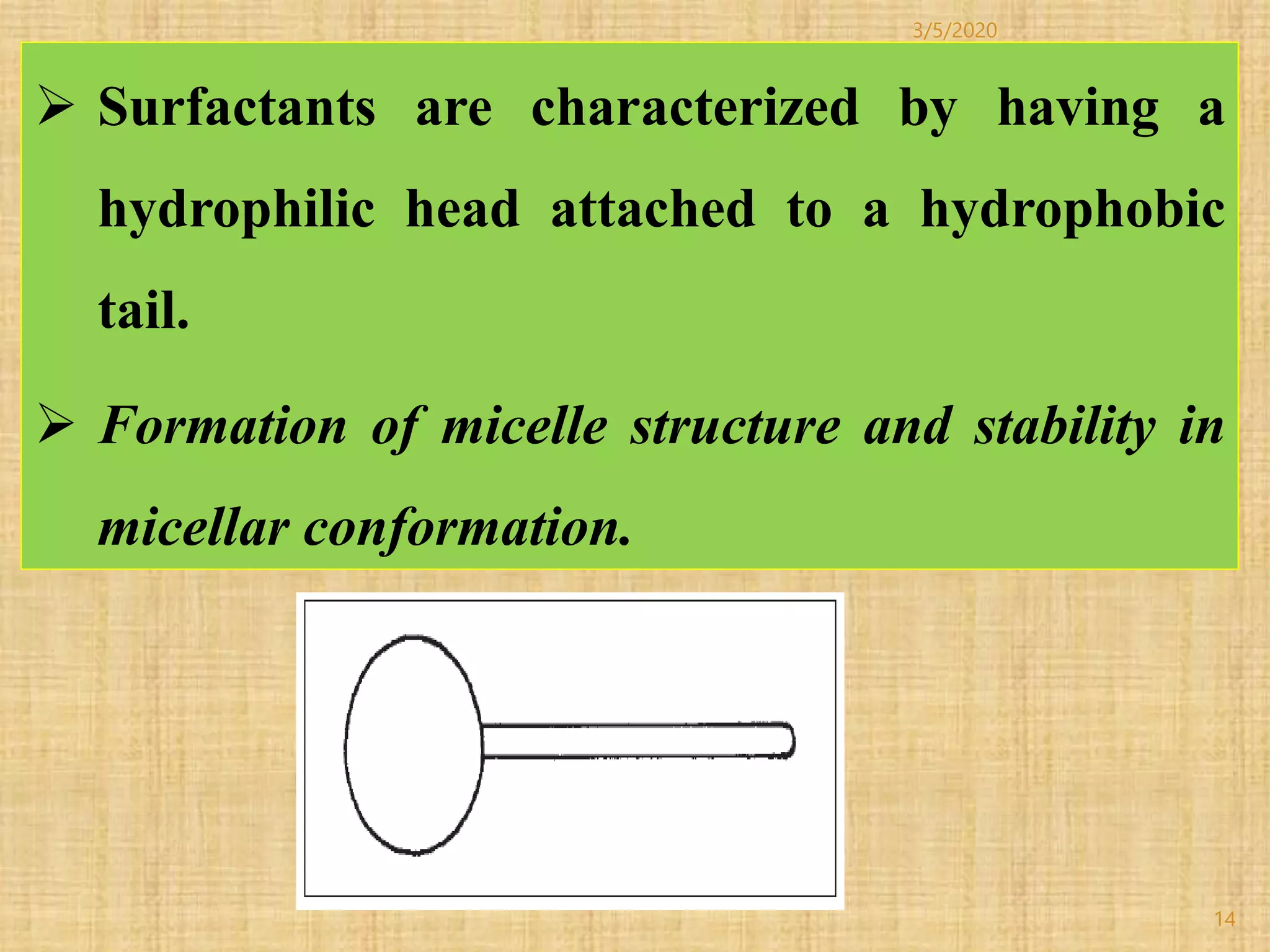
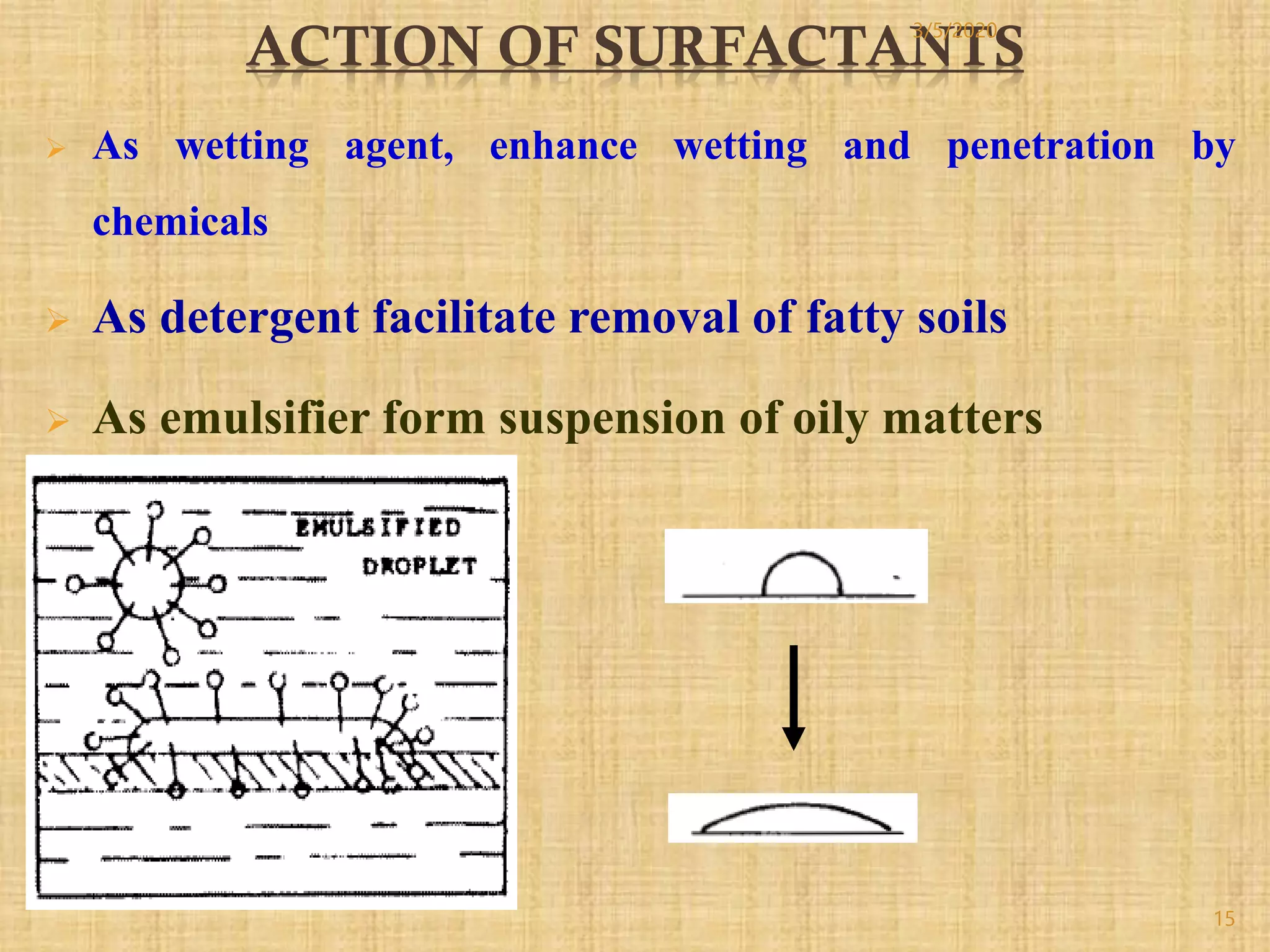
Cotton fibers contain 4-12% impurities such as proteins, fats, waxes and minerals that must be removed through a scouring process. The classical scouring method uses an aqueous alkaline solution with caustic soda as the alkali to saponify and emulsify impurities. Surfactants and sequesterants are added to the scouring bath to improve wettability, detergency and emulsification and counteract water hardness. Scouring makes cotton fibers highly hydrophilic and responsive to subsequent dyeing and finishing processes.


![SCOURING PROCESS
The mentioned impurities together with added lubricants are
removed by the so called scouring process.
In general, scouring removes fat/wax based hydrophobic
impurities & other impurities in association in the fiber.
Varity of scouring agents can be used for cotton.
[Alkalis, surfactants, organic solvents]
The classical scouring method is aqueous alkaline
scouring using caustic soda (NaOH) as alkali.
3/5/2020 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scouringlecture4-210208121407/75/Scouring-lecture-4-6-2048.jpg)






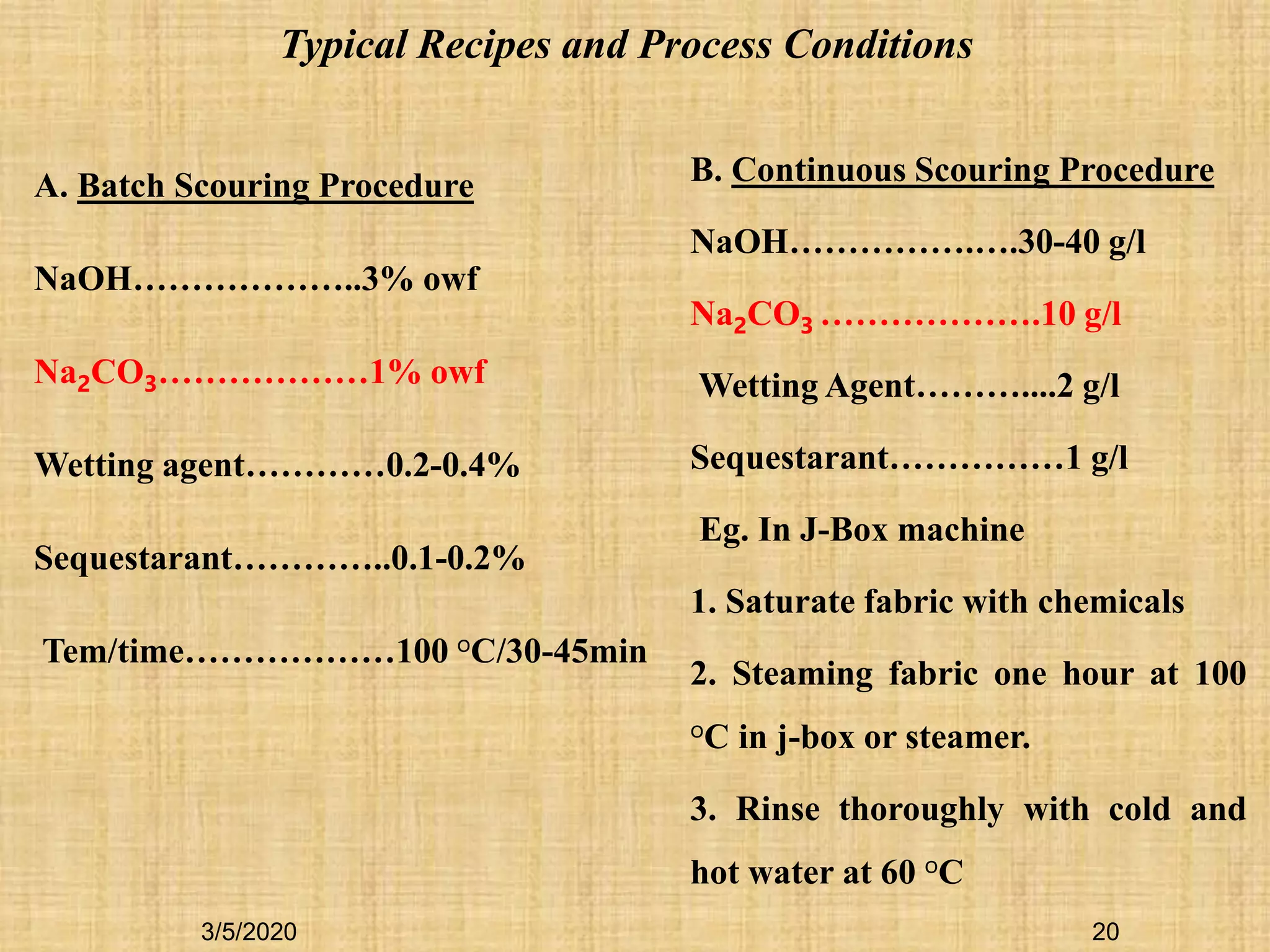
![19
Concentration of alkali
Temperature
Time
Type and amount of additives
Machine type [Material liquor ratio, MLR]
AQUEOUS ALKALINE SCORING CONTROLLING PARAMETERS
3/5/2020](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scouringlecture4-210208121407/75/Scouring-lecture-4-19-2048.jpg)