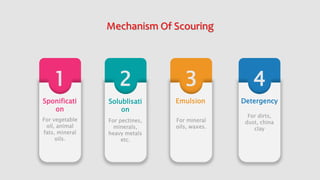
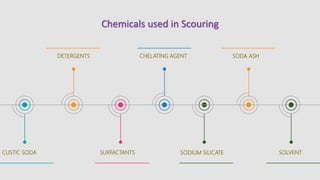
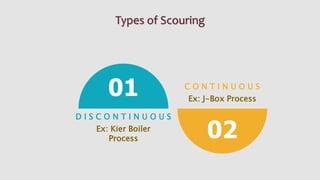
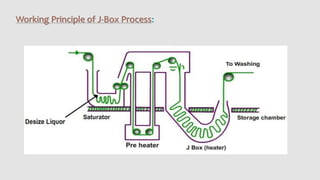
The document summarizes the scouring process used in textile manufacturing. Scouring involves removing natural and added impurities from textiles using chemicals like caustic soda and detergents to produce a clean and hydrophilic material. The objectives of scouring are to make the fabric highly absorbent, remove oils, waxes and other impurities, and prepare the textile for downstream processing. Scouring can be carried out via continuous processes like the J-Box or discontinuous batch processes using a Kier boiler. The effectiveness of scouring is assessed through tests like drop, immersion and spot tests.