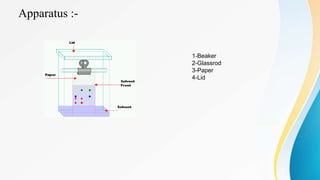
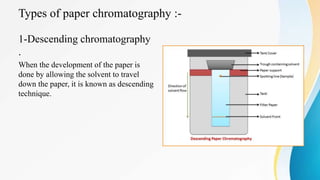
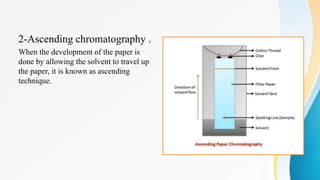
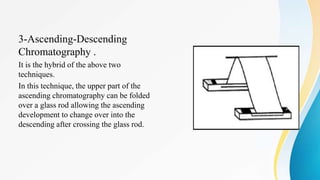
This document provides an overview of paper chromatography, including its principles, procedures, types, and applications. Paper chromatography is an analytical technique used to separate colored chemicals or substances based on their polarity. It works by partitioning the substances between a stationary phase (polar paper) and a mobile phase (non-polar solvent). The substances migrate at different rates depending on their interaction with the two phases, leaving visible spots on the paper. Key factors like the solvent, paper quality, temperature, and apparatus dimensions affect the migration of substances, quantified by their retention factor (Rf) values. Various types of paper chromatography techniques exist like ascending, descending, and two-dimensional. The document outlines the basic procedure and describes applications in qualitative and quantitative analysis



![Principle :-
This technique is a type of partition chromatography in which the substances are distributed between two
liquids .i.e, one is stationary liquid [usually water] which is held in the fibres of the paper and called the
stationary phase . Other is the moving liquid or developing solvent and called mobile phase . The
components of the mixture to be seperated migrate at different rates and appear as spots at different points
on the paper.Cellulose filter paper is often used as the stationary phase in paper chromatography.
Since it is hydrophilic, it is usually covered with thin film of water.
The procedure is often regarded as liquid-liquid chromatography.
The components of the separated migrate at different rates and appear as spots at different points on the
paper.
In this technique, a drop of the test solution is applied as a small spot on a filter paper and the spot is
dried.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paperchromatography-211128035738/85/Paper-chromatography-4-320.jpg)