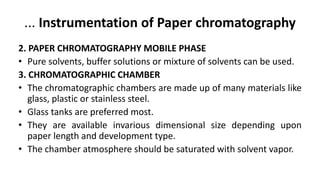
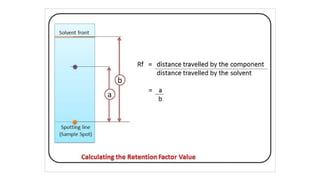
Paper chromatography is a simple and inexpensive analytical technique used to separate mixtures and identify compounds. It works by separating compounds based on how they partition between a stationary phase, such as filter paper, and a mobile phase, such as a solvent. The sample mixture is applied to filter paper and allowed to travel up the paper via capillary action. Compounds separate based on differences in how they interact with the mobile and stationary phases. The distance traveled by each compound is used to calculate Rf values for identification. Paper chromatography has various applications and advantages like low cost and simplicity, but is not as accurate as other techniques.