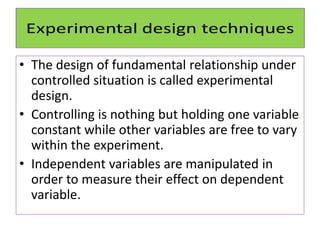
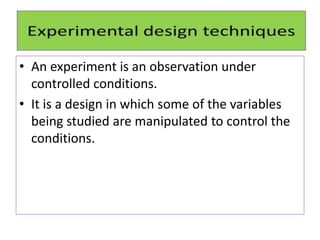
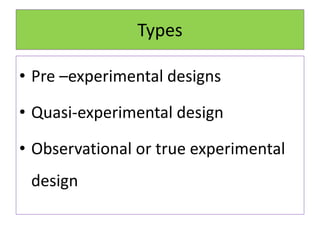
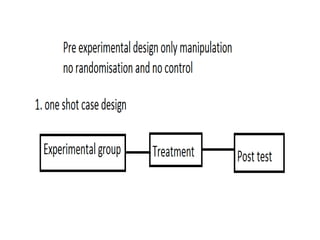
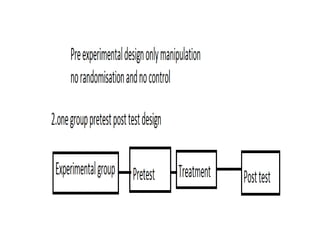
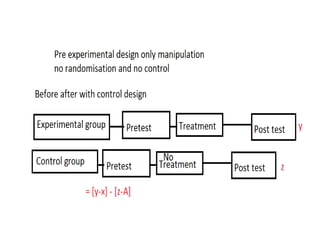
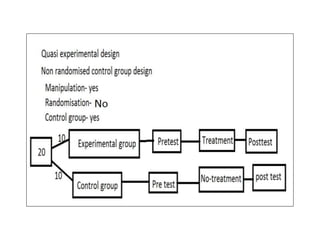
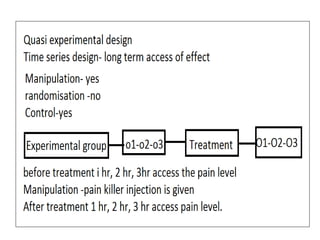
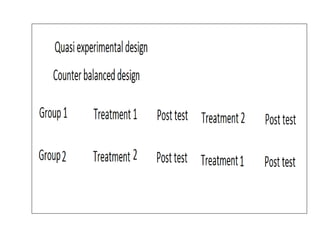
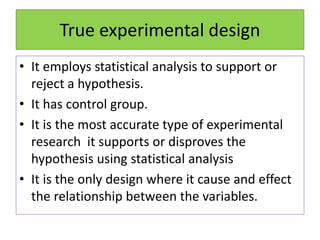
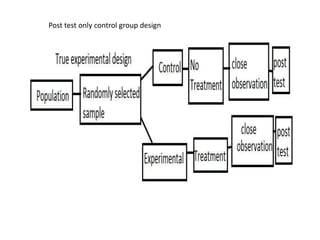
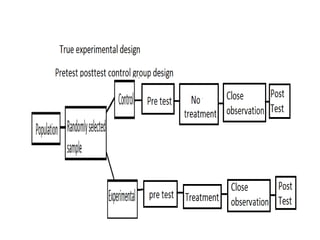
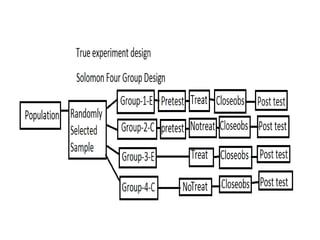
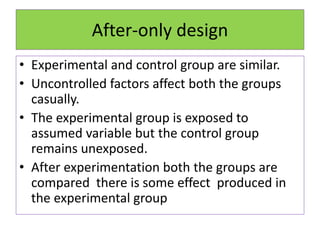
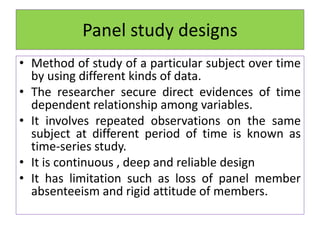
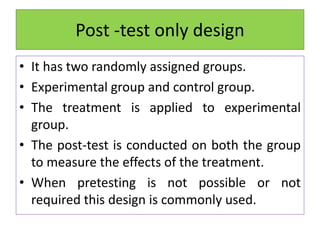
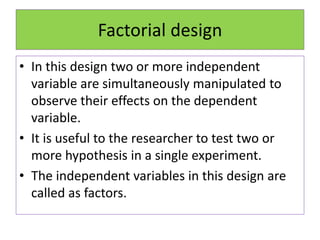
Experimental design techniques involve controlling variables to measure their effects. There are three main types of designs: pre-experimental (no control group), quasi-experimental (no random assignment), and true experimental (control group, random assignment, manipulation). True experiments allow cause-and-effect conclusions through statistical analysis and include variations like post-test only, pre-test post-test, and Solomon four-group designs. Factorial designs test multiple hypotheses simultaneously by manipulating multiple independent variables. Randomized block and cross-over designs help control for differences between subjects. The goal is to draw valid conclusions about variable relationships through controlled experimentation.









![Randomised block design
• Subject population is grouped into relatively
homogenous subgroups [ blocks] within which
the experiment is replicated
• It is used when there is inherent difference
between subjects and possible differences in
experimental conditions.
• If there are a large number of experimental group
the randomised block design is used because this
design make the group homogenous.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/experimentaldesigntechniques-210522073615/85/Experimental-design-techniques-28-320.jpg)


