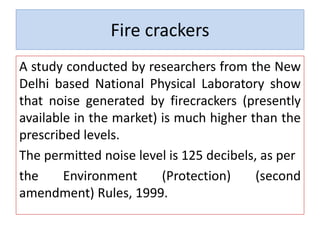
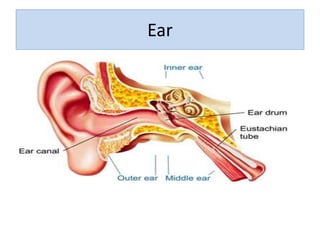
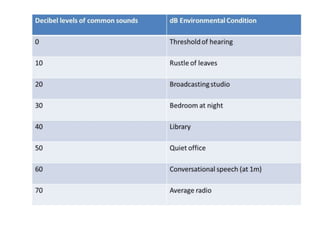
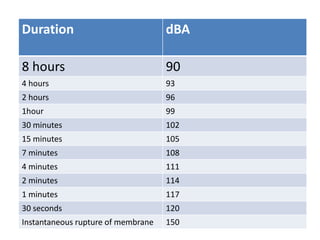
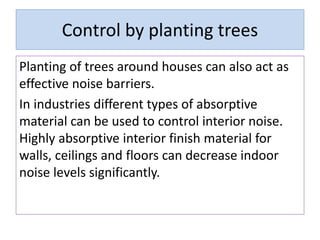
Noise pollution can negatively impact human health and the environment. It is caused by loud sounds from sources like vehicles, construction sites, and industrial activity. Prolonged exposure to noise above safe levels can lead to hearing loss, cardiovascular issues, and disrupted sleep. Methods to reduce noise pollution include using barriers around noisy machinery, limiting vehicle speeds, planting trees as buffers, and protecting workers' hearing with earplugs. Controlling noise at the source is the most effective approach.