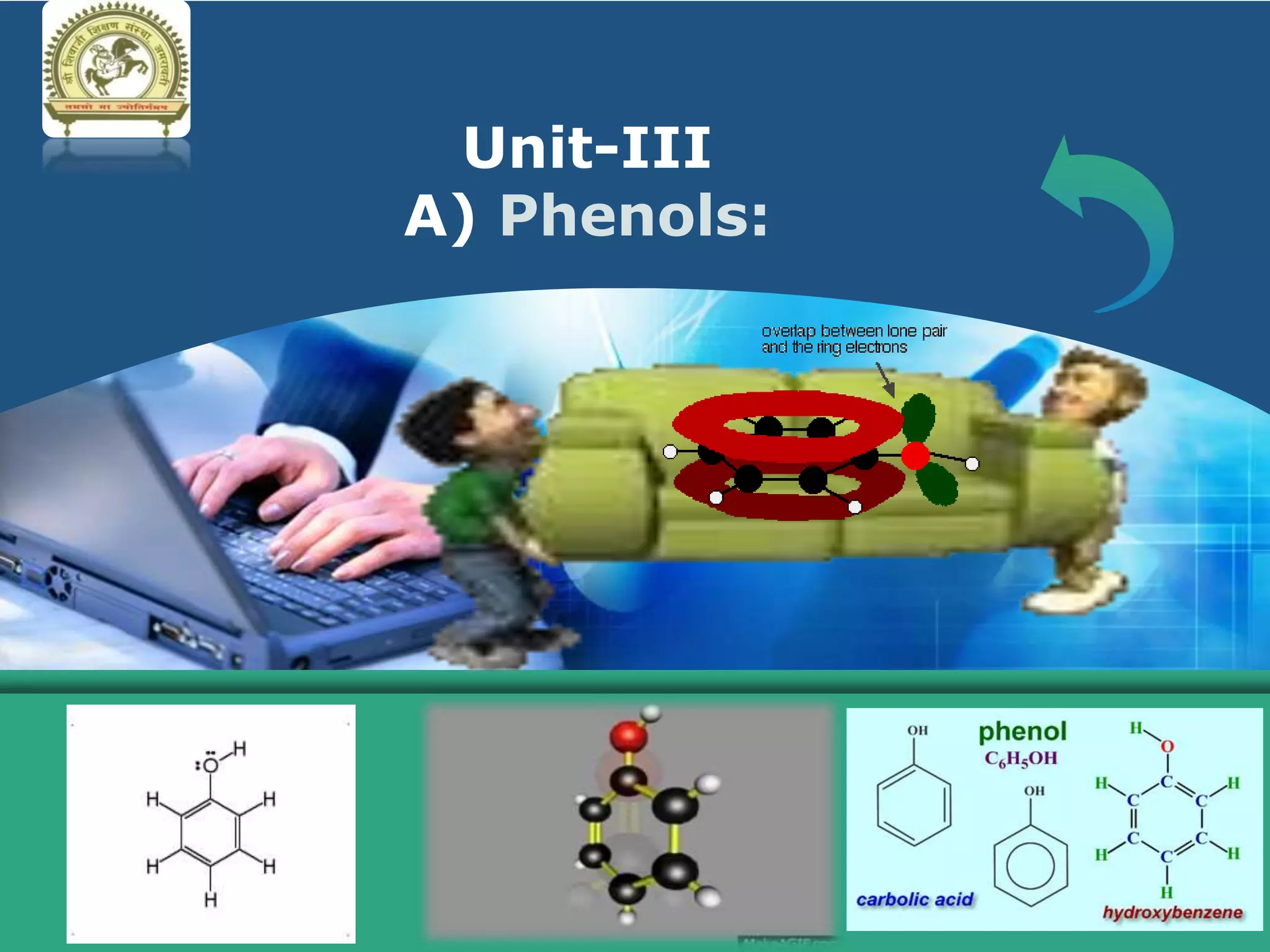
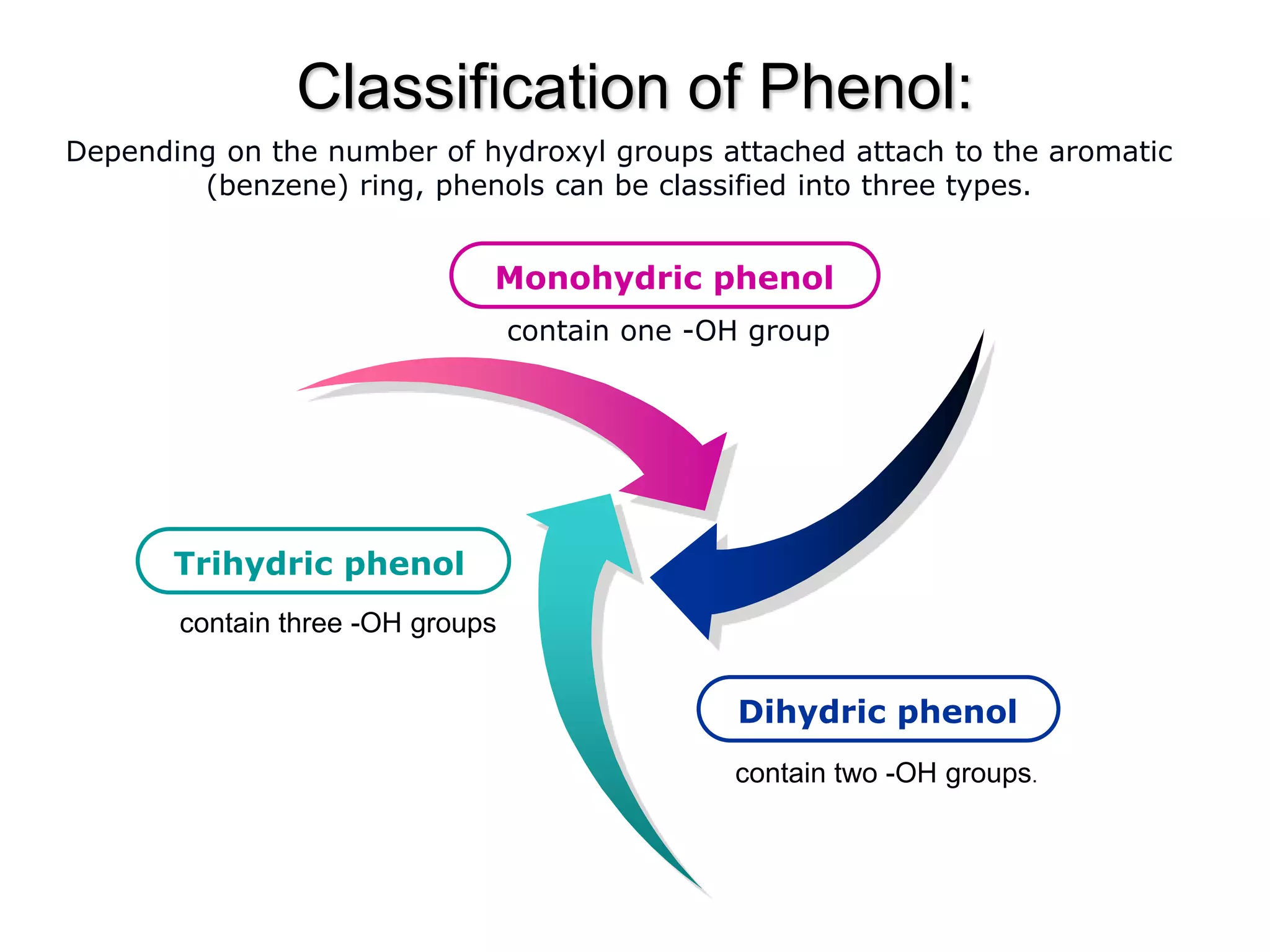
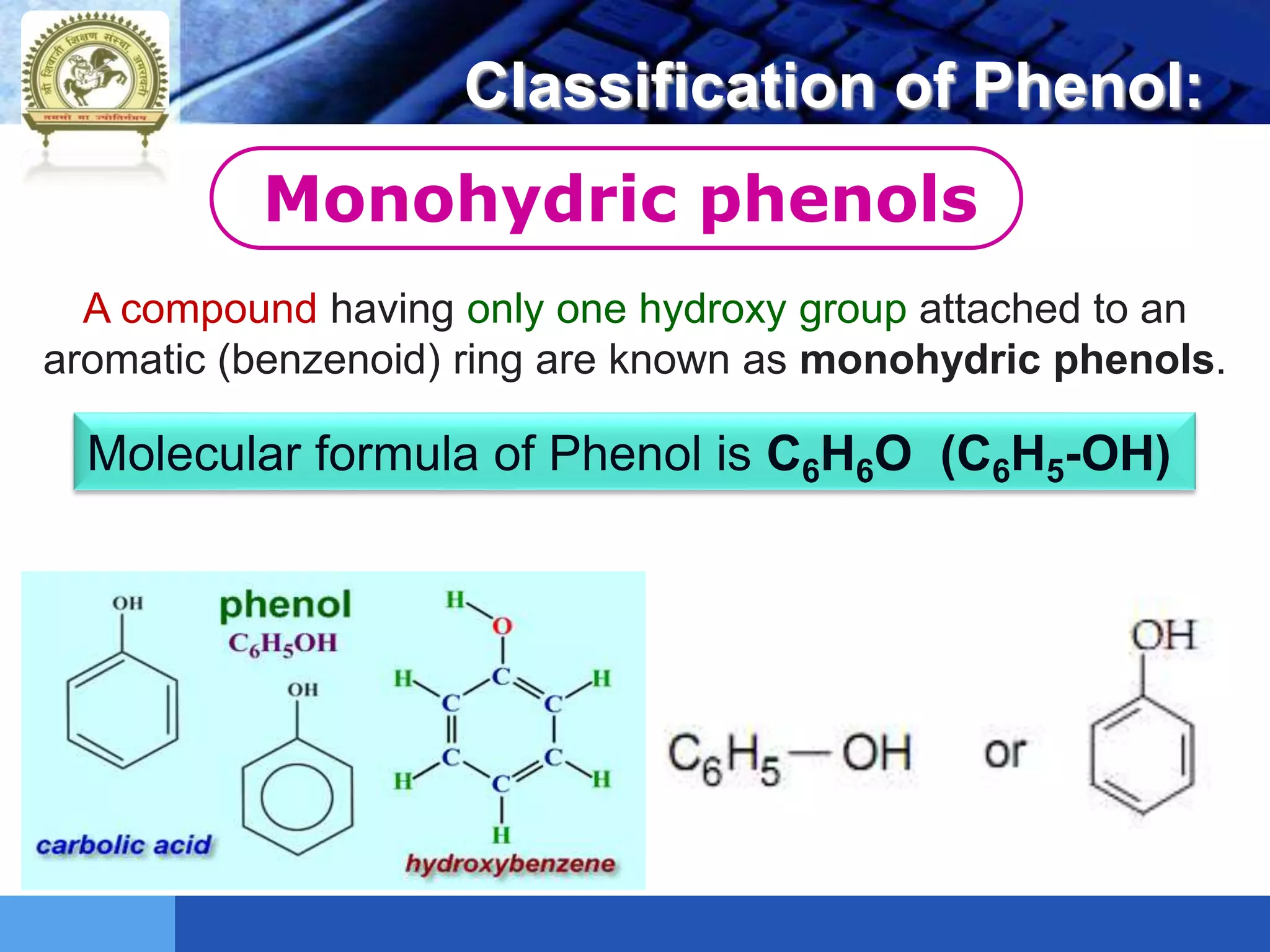
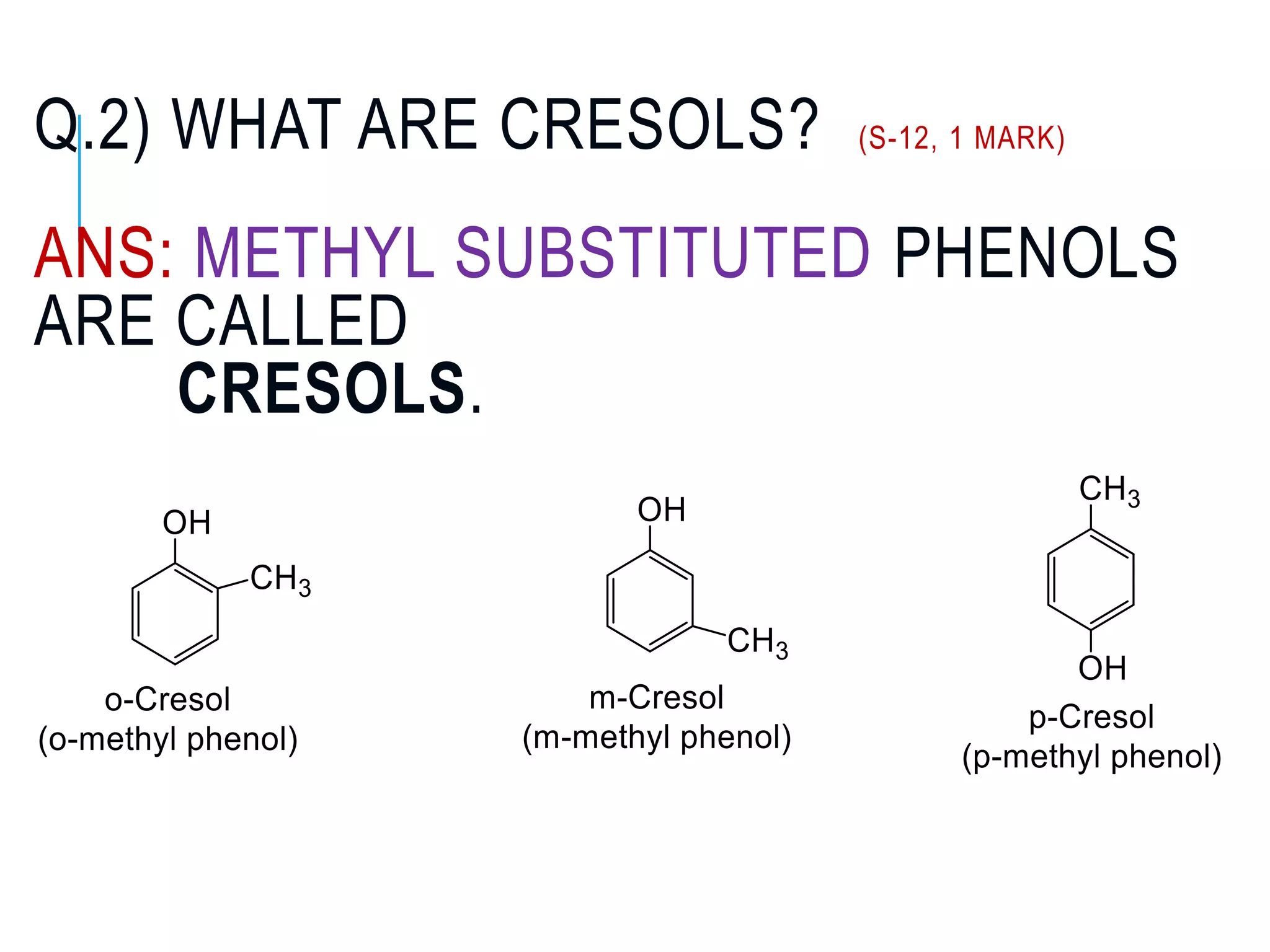
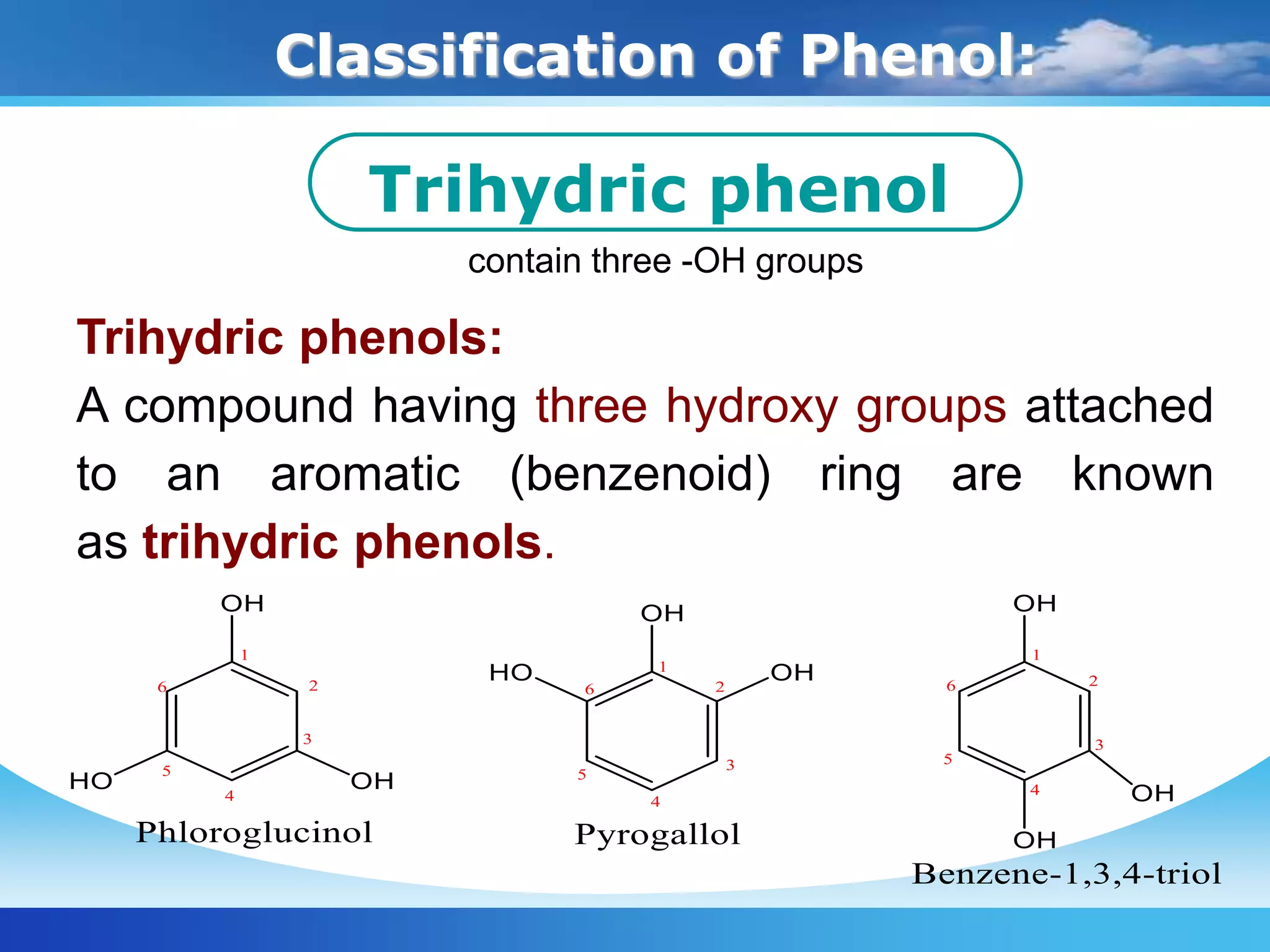
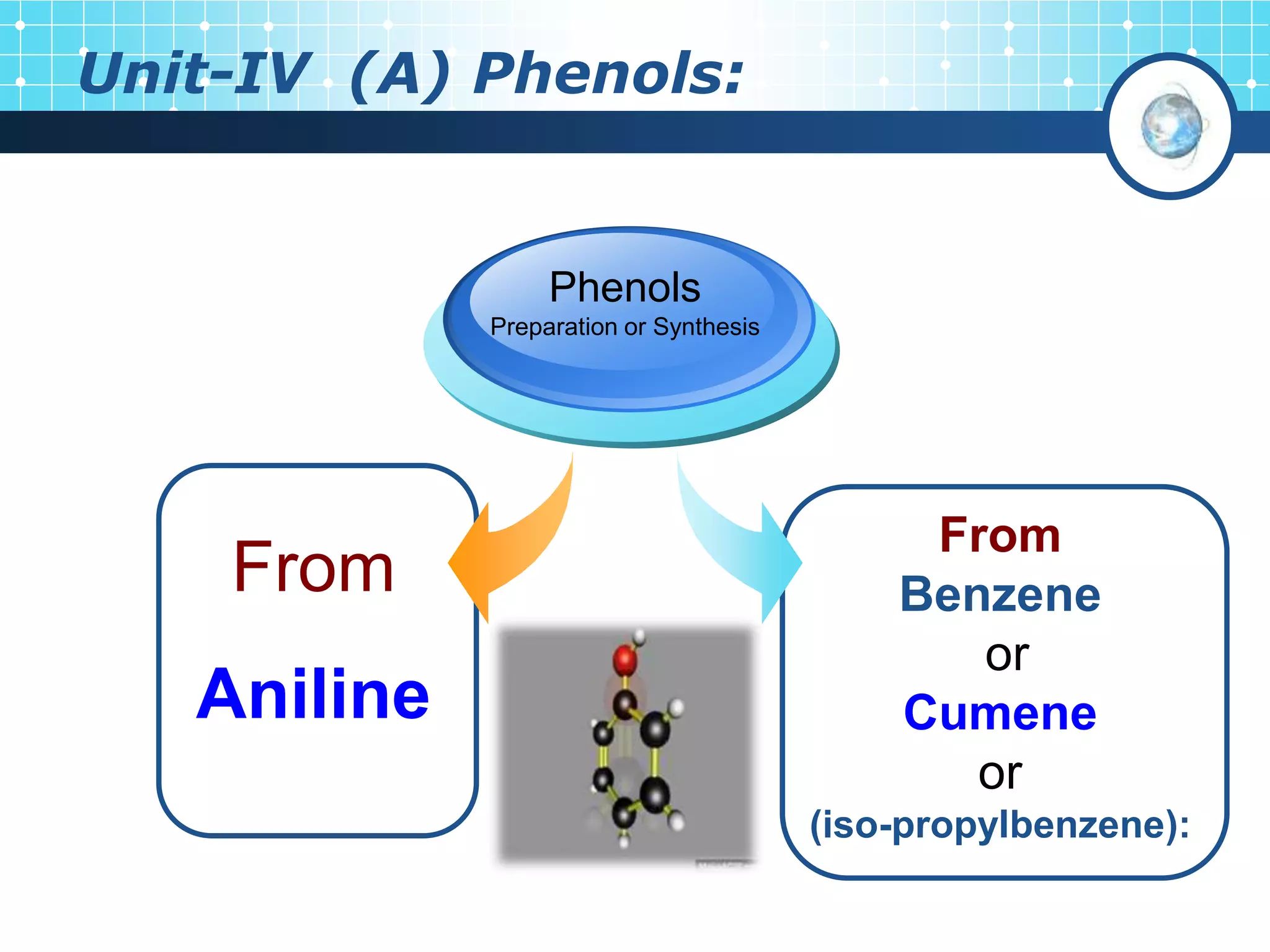
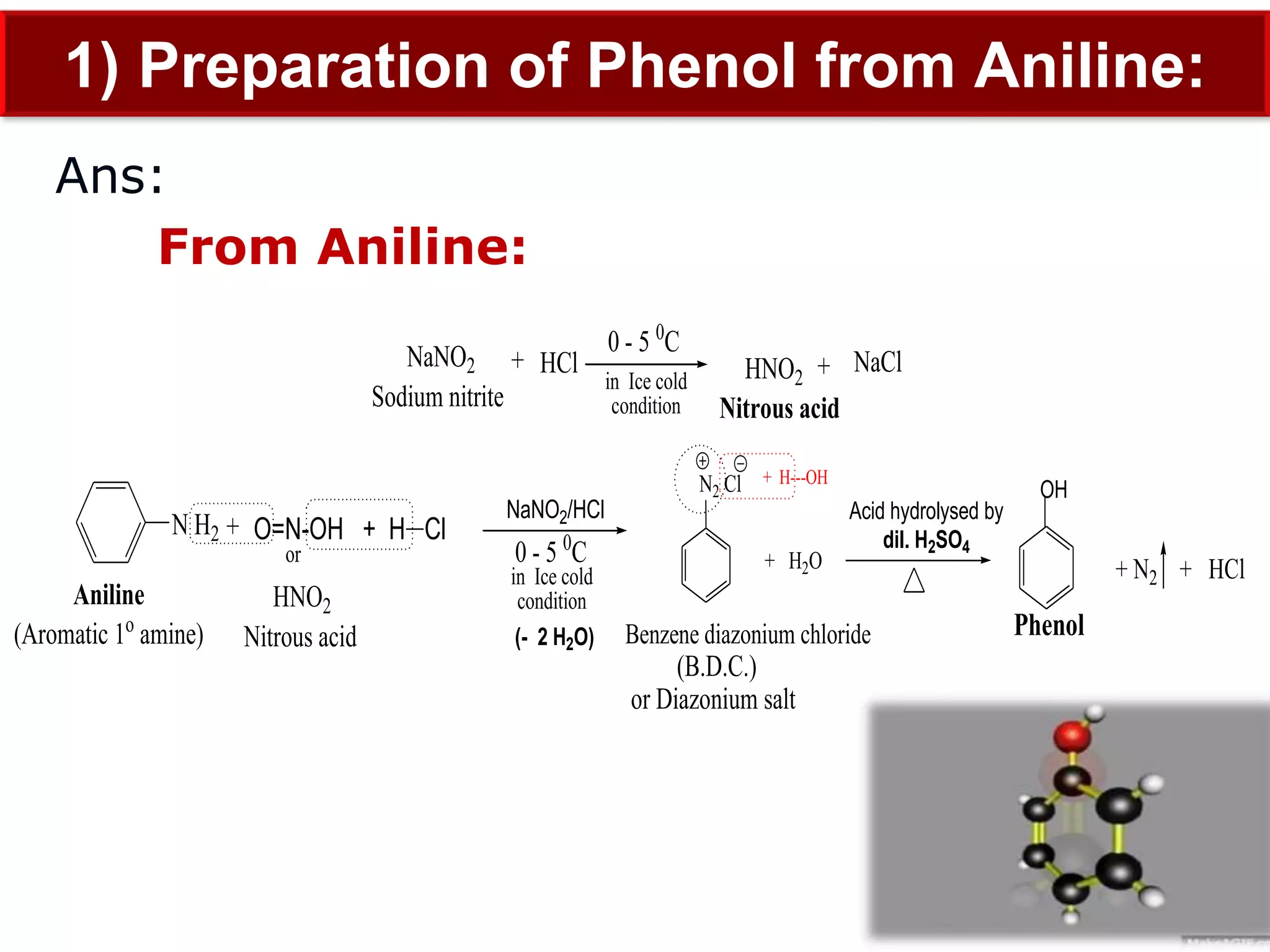
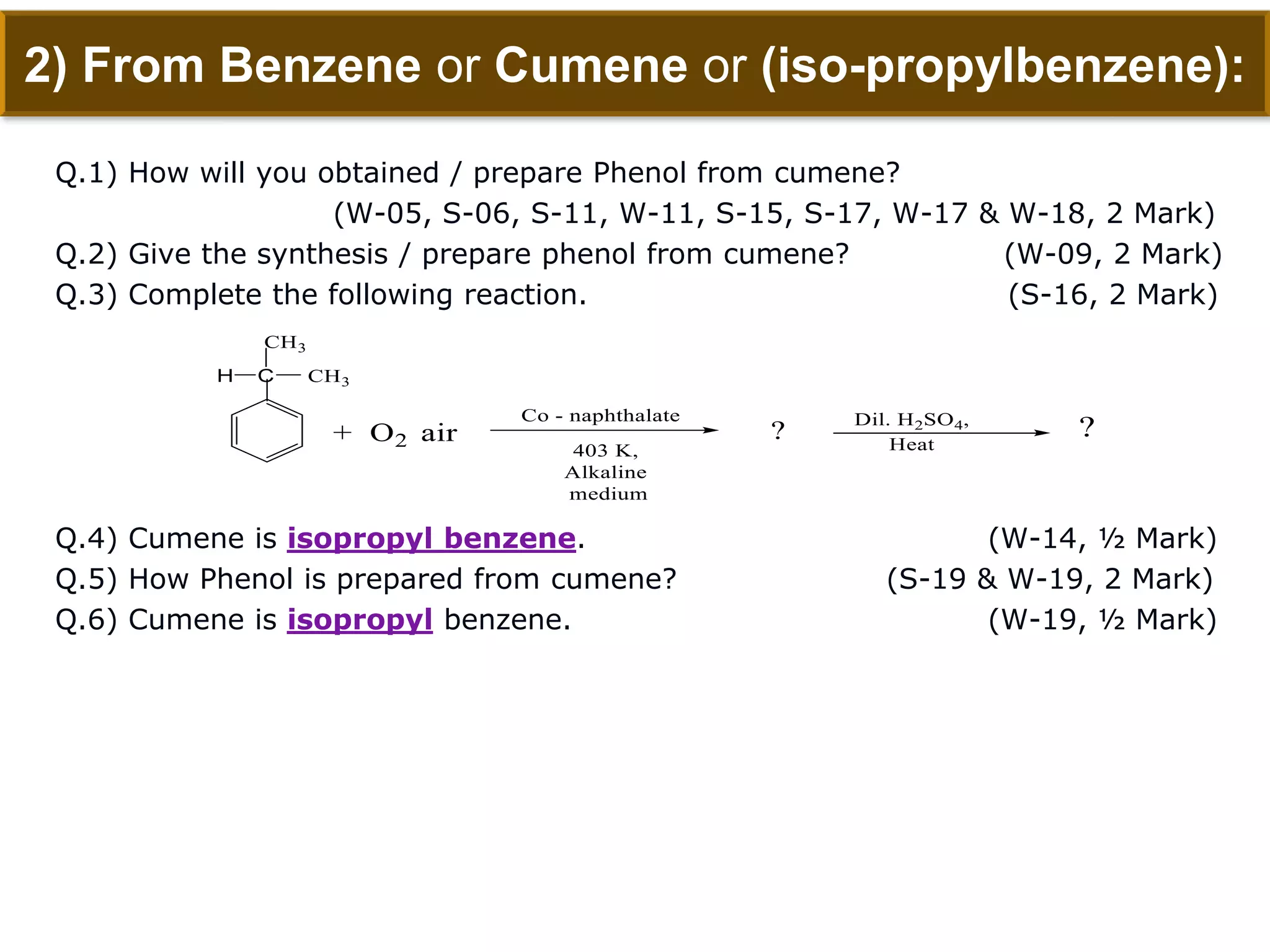
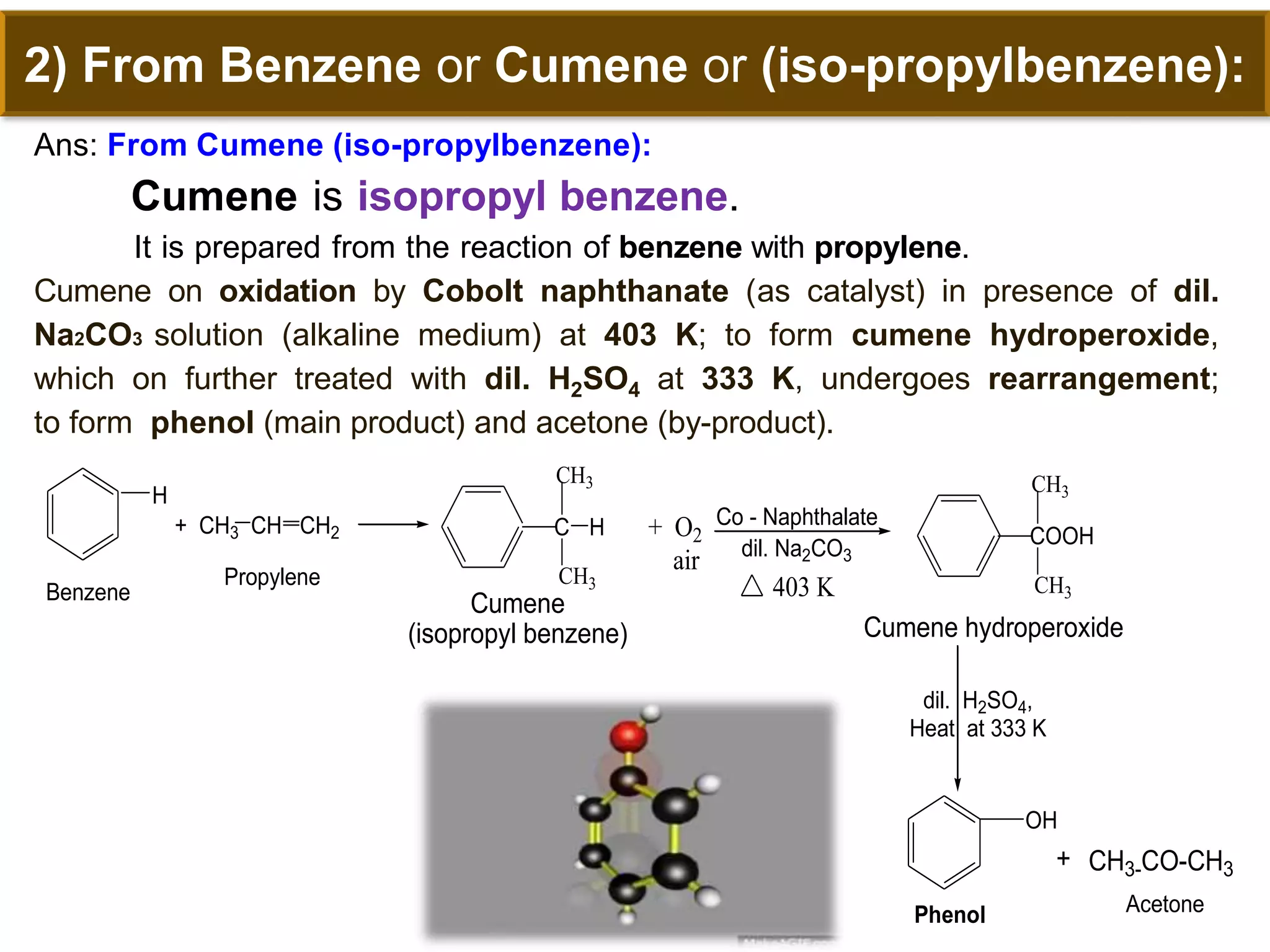
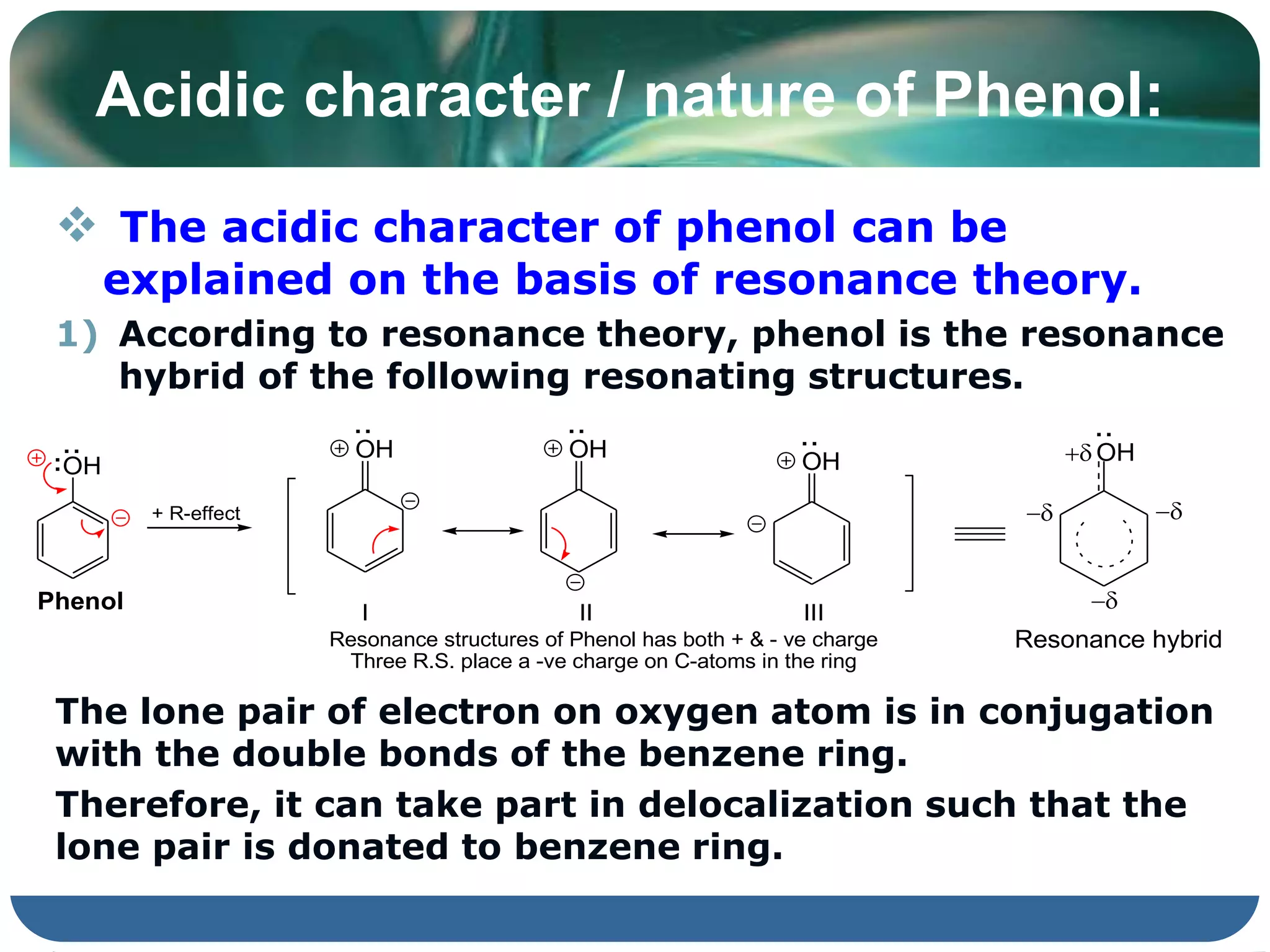
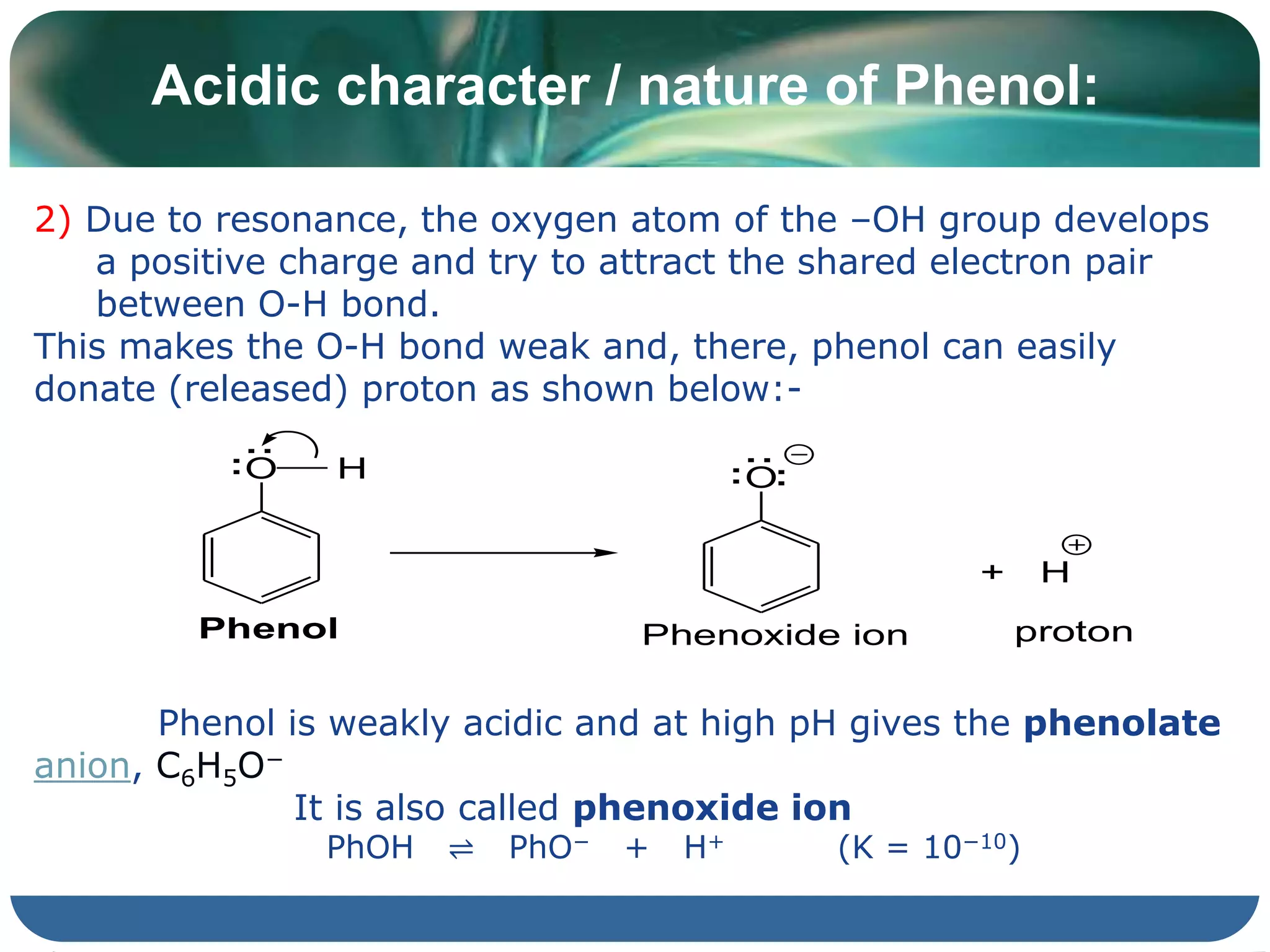
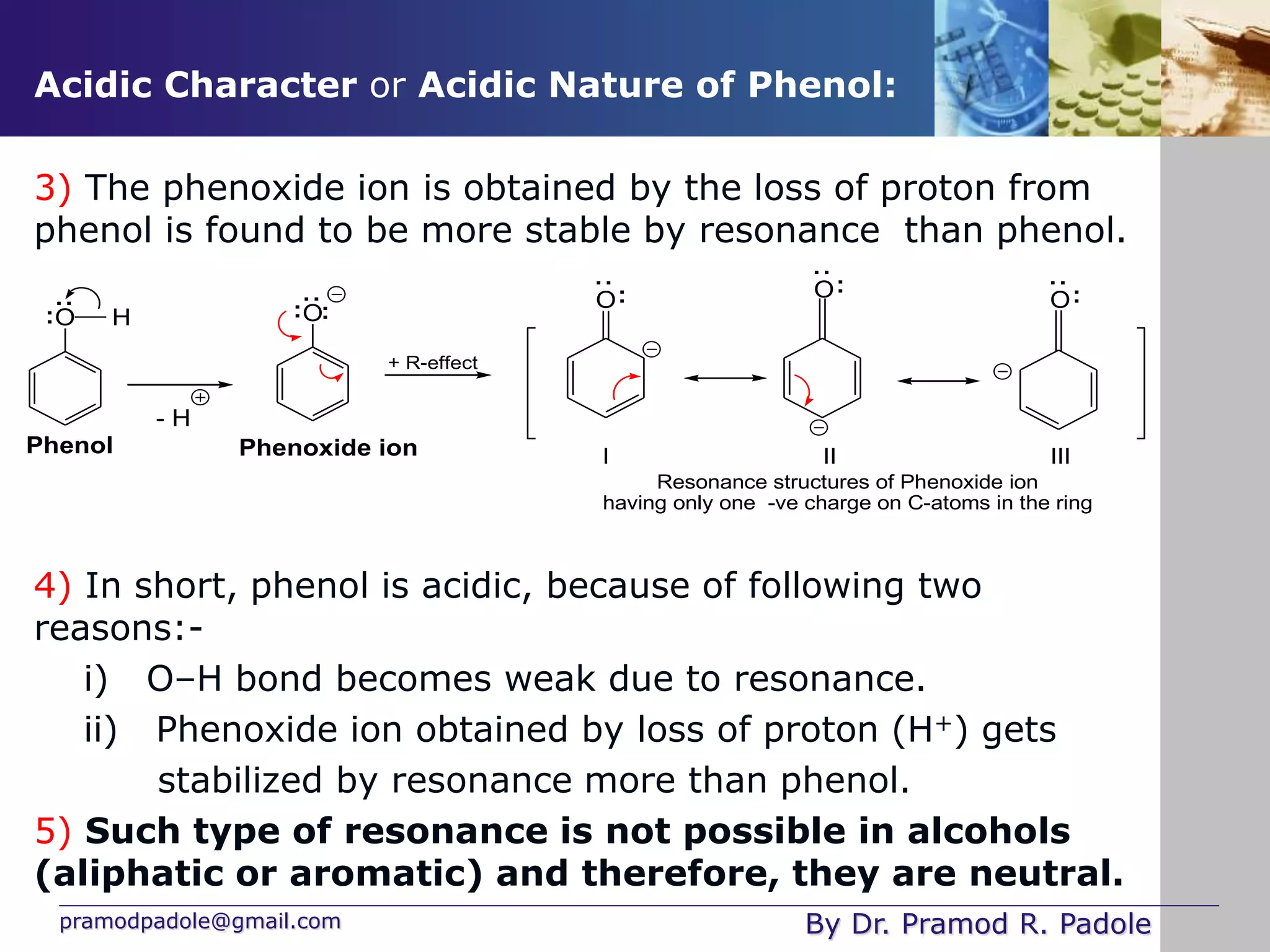
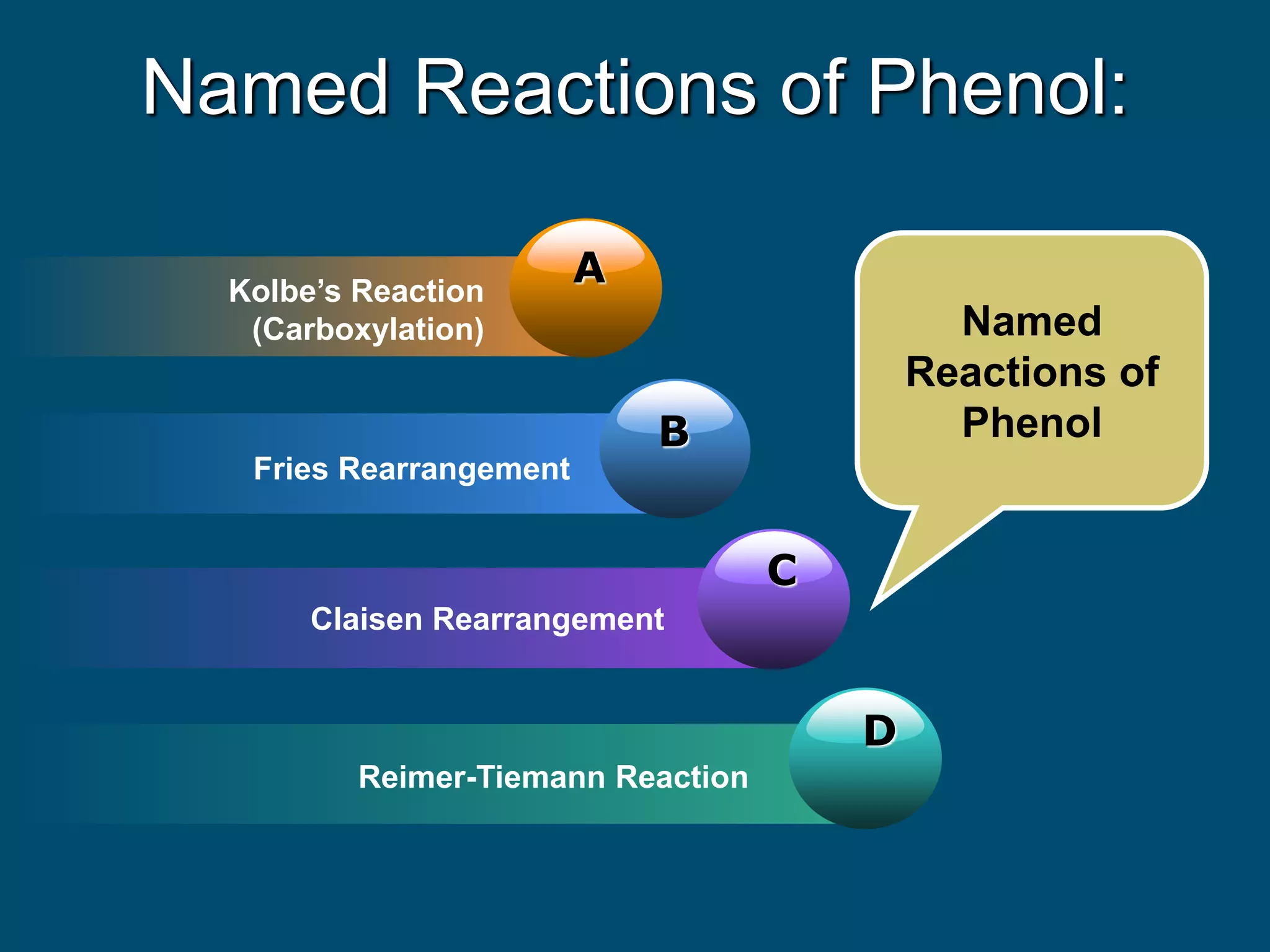
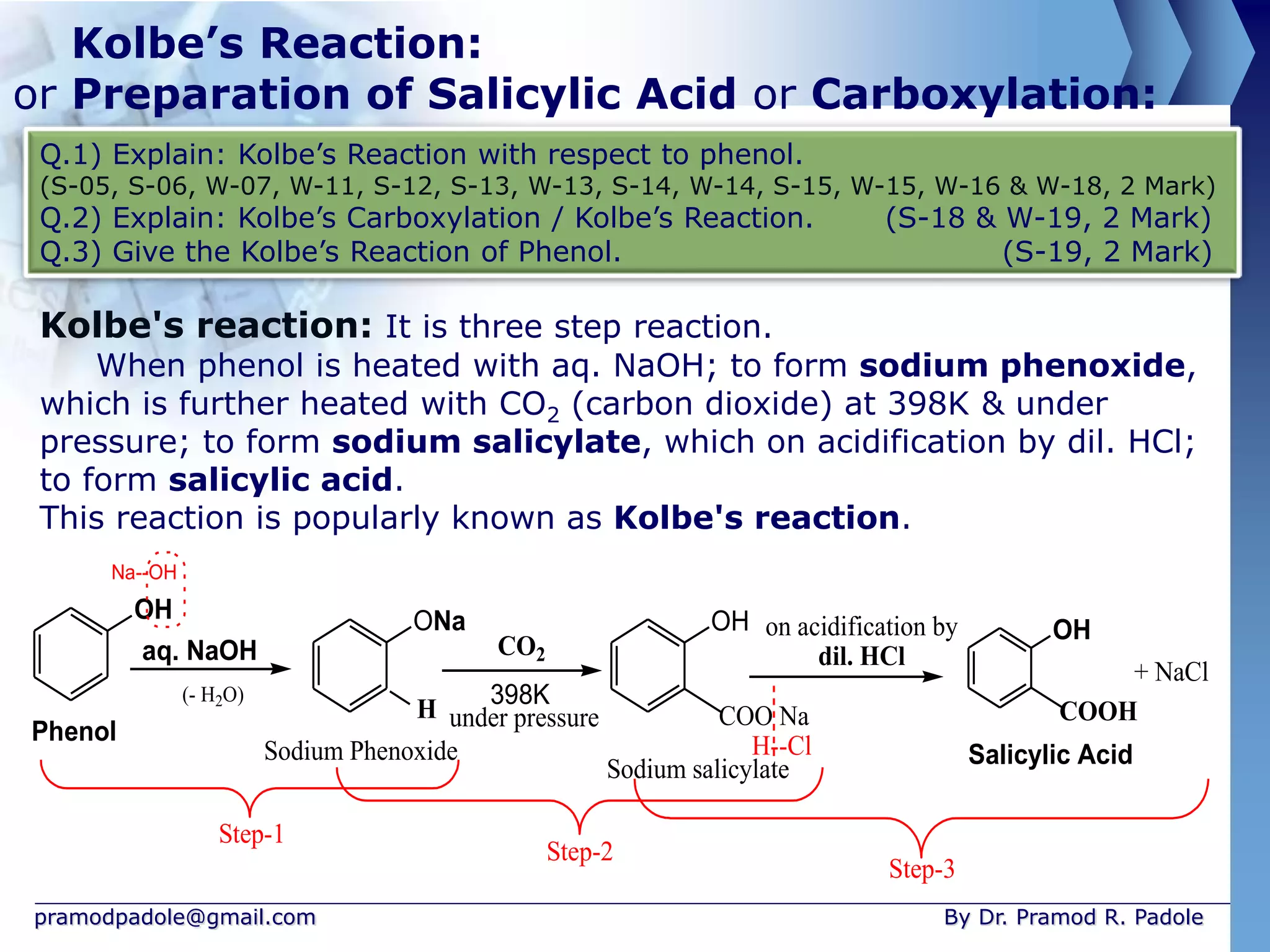
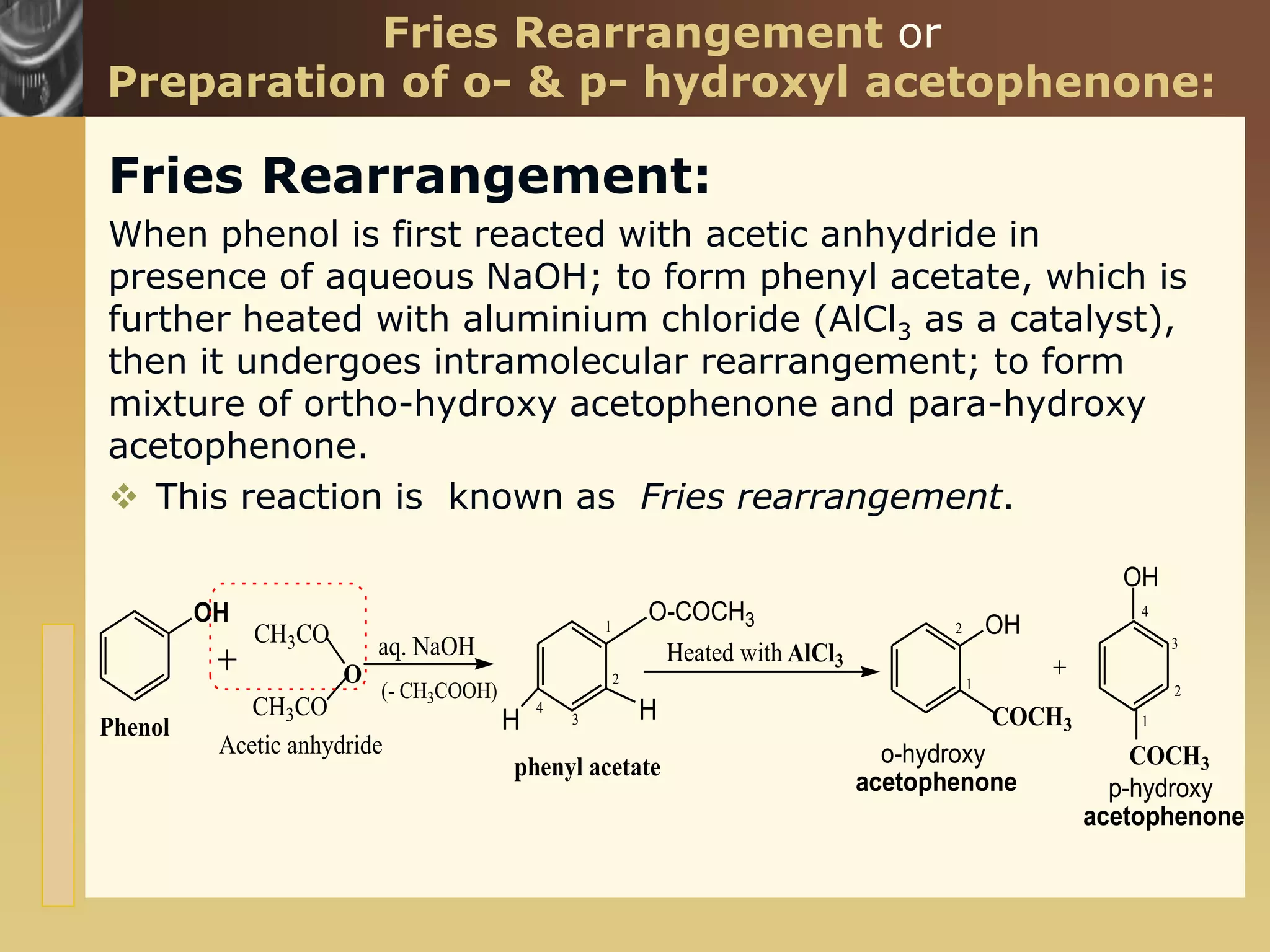
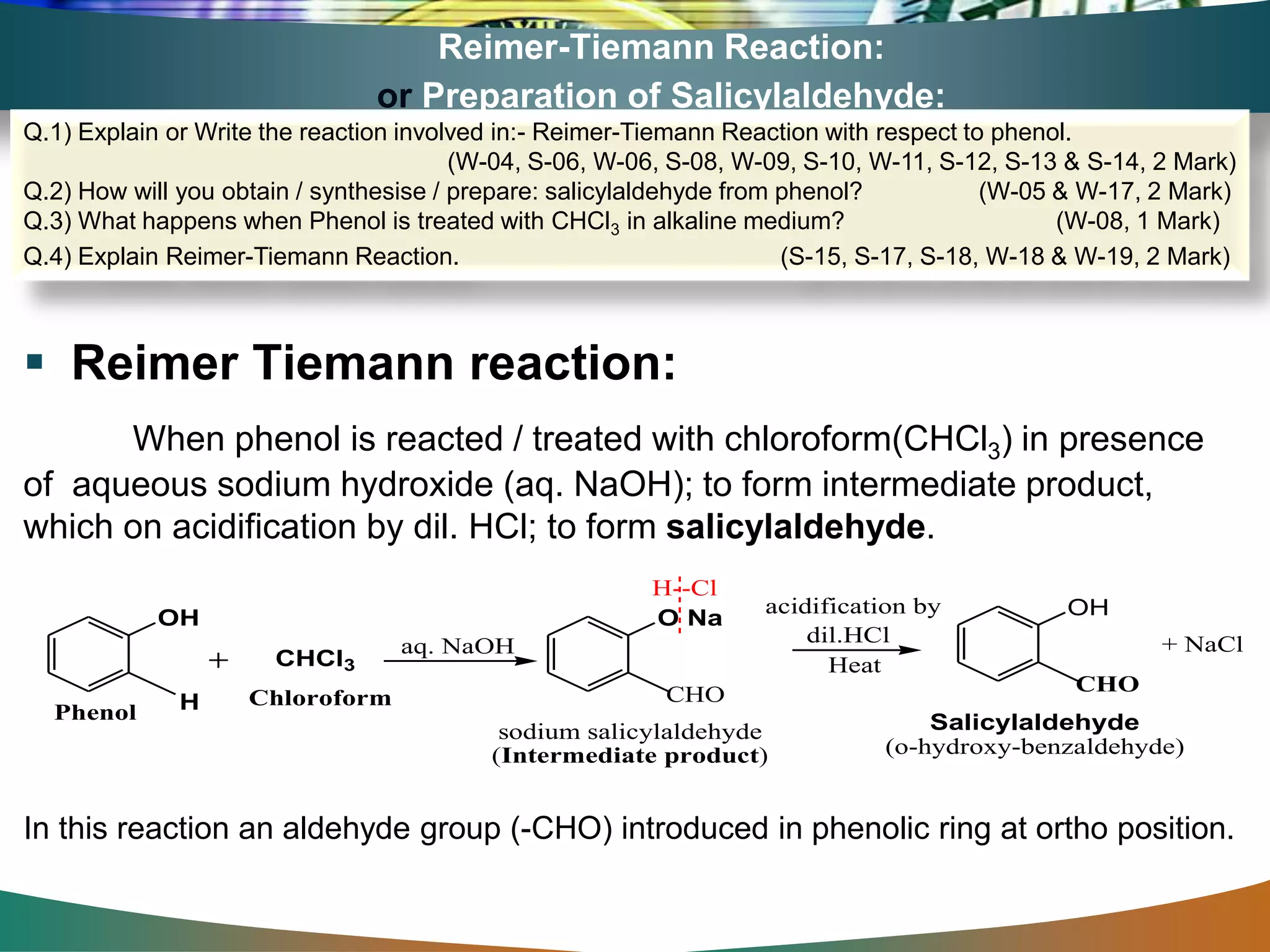
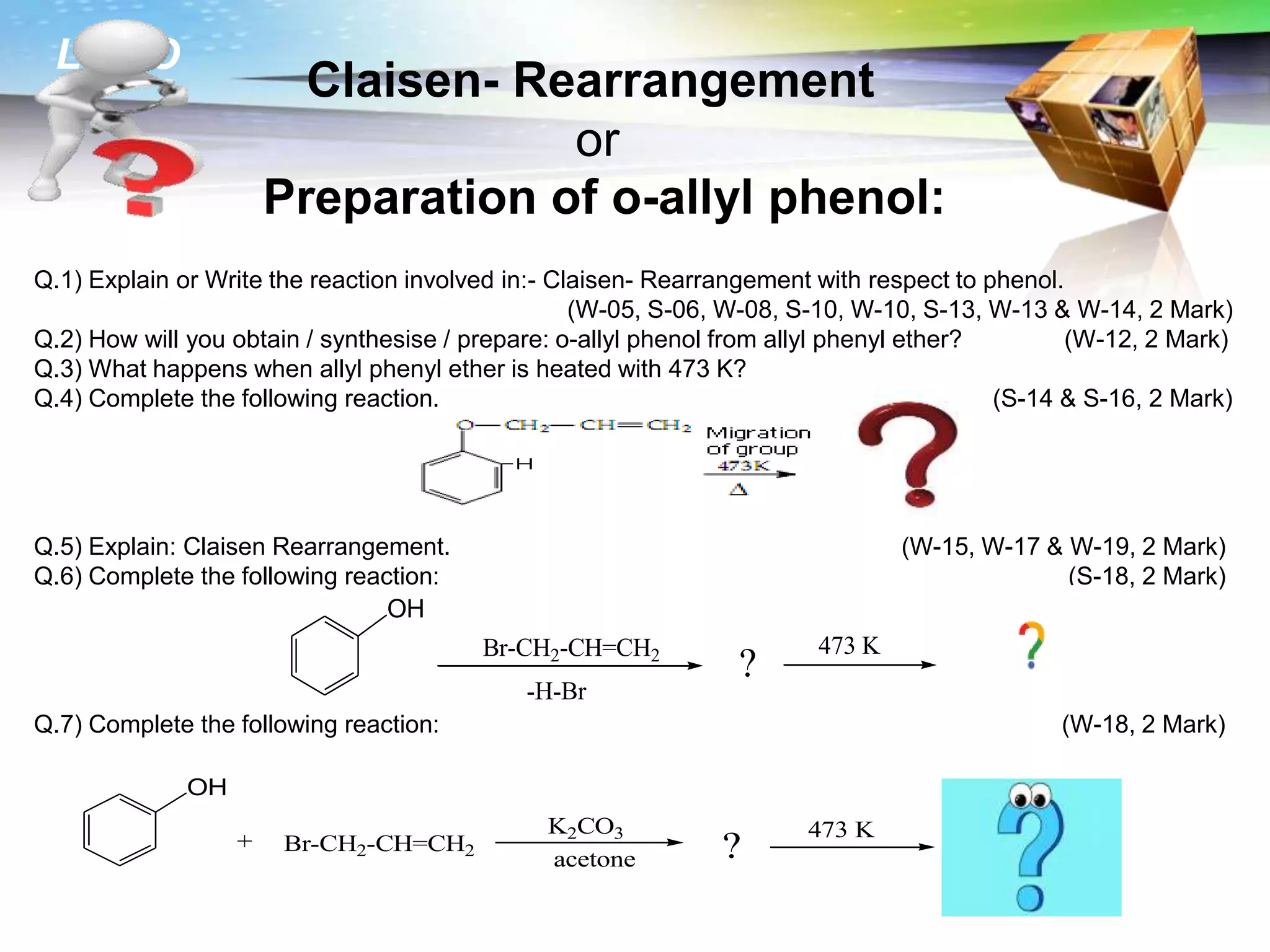
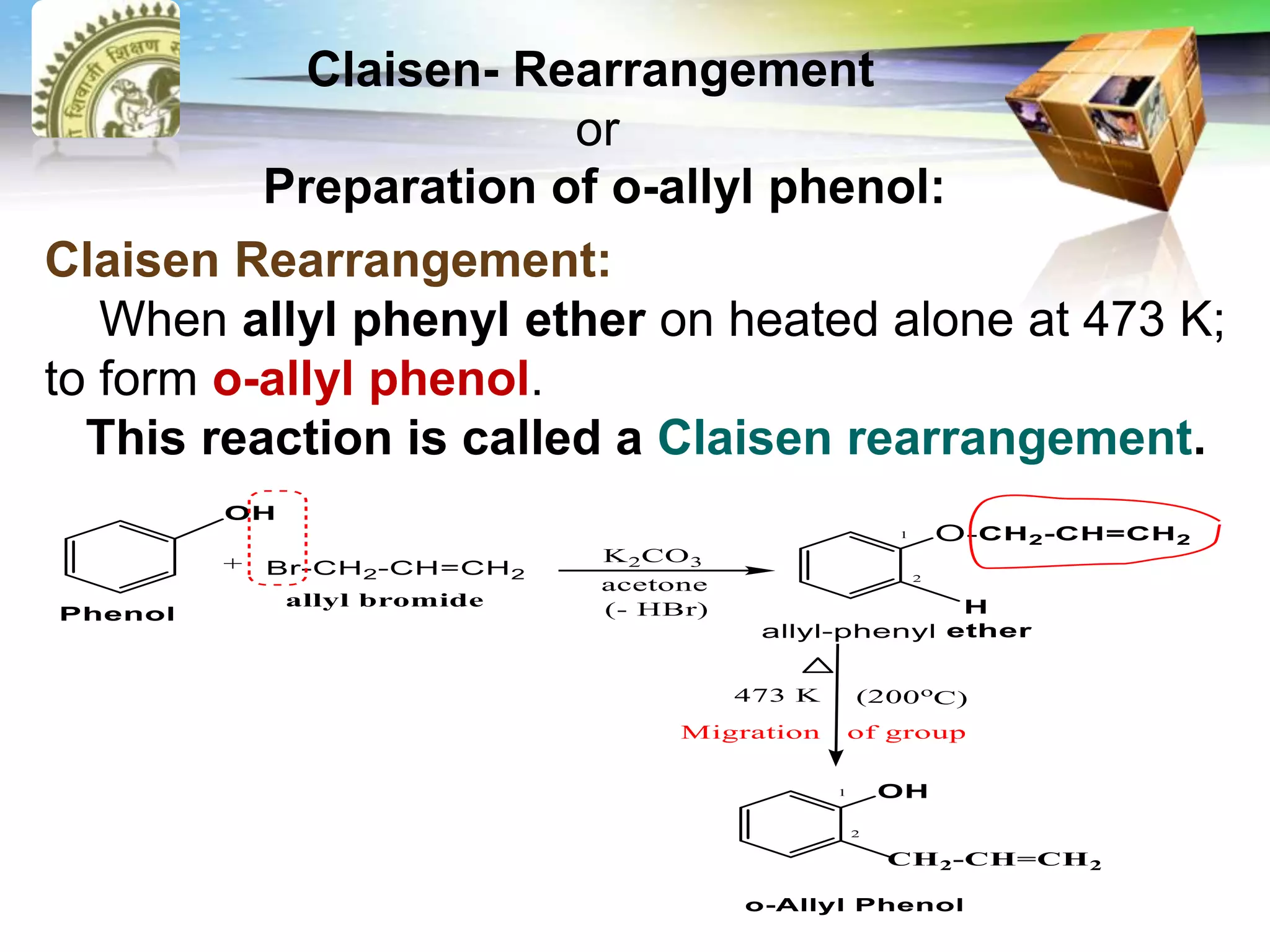
The document is focused on the chemistry of phenols, ethers, and epoxides, detailing their methods of formation, chemical reactions, and classifications. It covers the synthesis of phenols from various sources like aniline and cumene, as well as their acidic character and named reactions such as Kolbe's reaction and Fries rearrangement. Additionally, it touches on the medical uses of phenol and offers insight into different phenolic compounds.