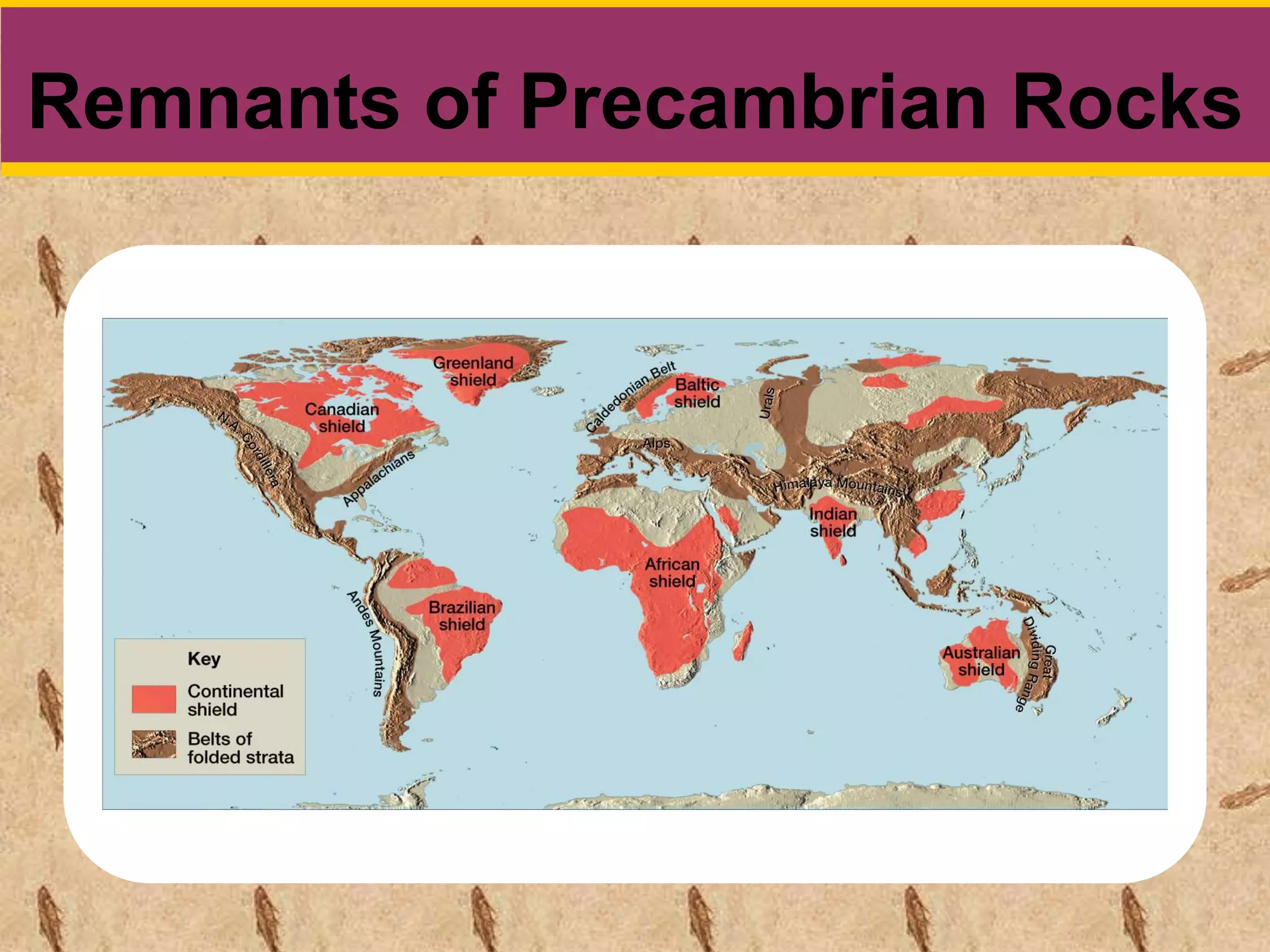
This document provides information about Earth's prehistory and geologic timeline. It discusses how Earth is approximately 4.5 billion years old, and life has changed the planet's chemistry over the past 3/4 of geologic time. Five major extinctions have occurred, including the K-Pg extinction that killed the dinosaurs 65 million years ago. Mass extinctions are caused by long-term stresses combined with short term catastrophic events. Recovery of biodiversity after extinctions can take 5-10 million years as weedy species repopulate the planet. The eras of geologic time - Precambrian, Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic - are summarized along with significant developments in life during each period