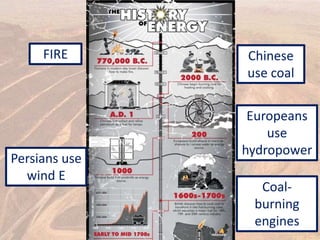
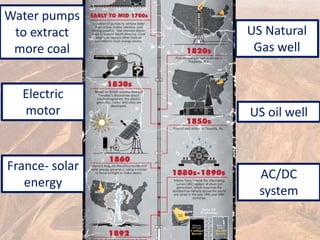
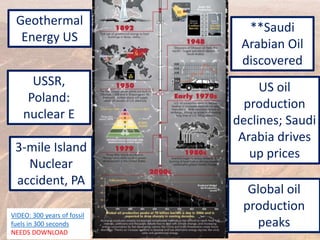
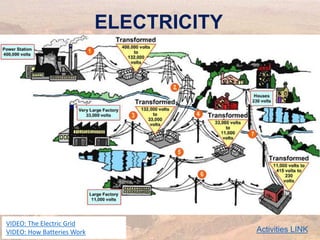
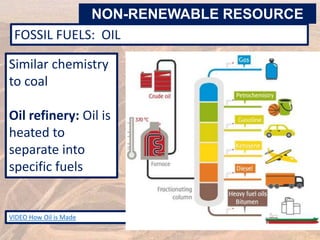
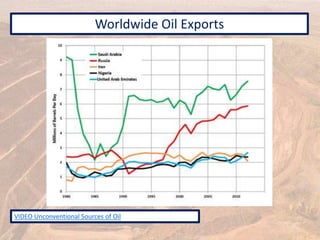
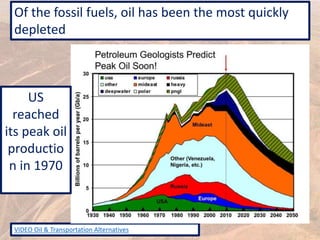
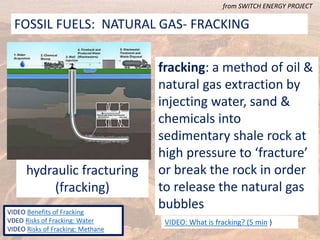
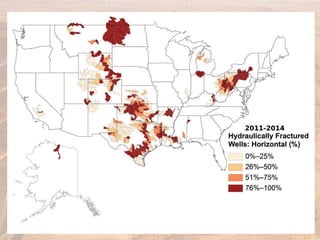
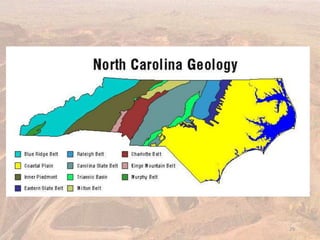
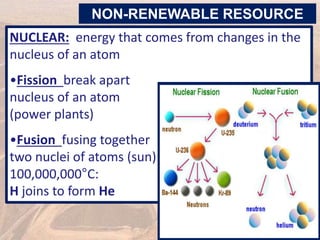
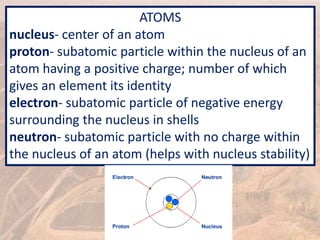
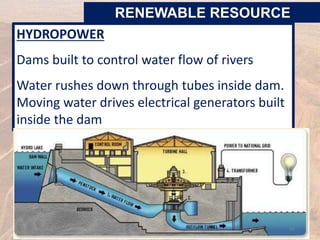
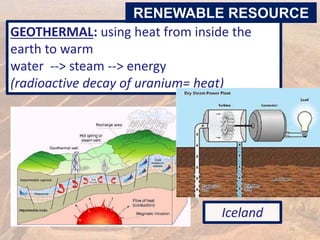
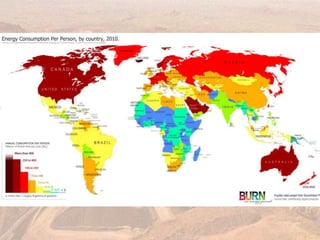
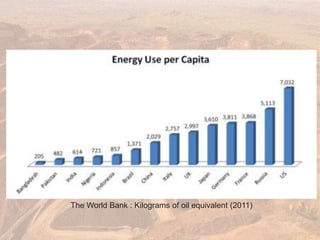
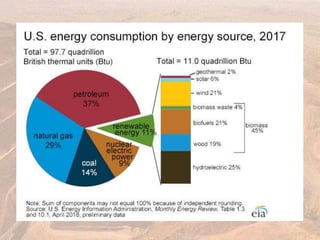
This document provides an overview of different types of energy resources including fossil fuels, nuclear energy, and renewable resources. It discusses the science behind various energy production methods and summarizes pros and cons of each resource. Key points covered include how fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas are non-renewable but currently provide most global energy, as well as safety and environmental issues associated with nuclear power and renewable alternatives like solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal and biomass energy. The document emphasizes the importance of sustainability and moving toward renewable resources.