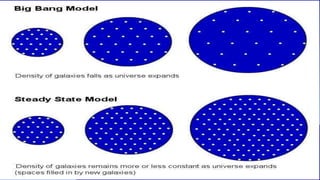
The Steady State Theory proposed that the universe has no beginning or end in time and appears the same from any point. It suggests new stars are continually created to replace those that have died, maintaining a steady state. The theory was proposed as an alternative to the Big Bang Theory. However, evidence emerged in the 1960s that contradicted Steady State Theory, including more distant radio sources in the early universe, discovery of quasars only in the early universe, and detection of the cosmic microwave background radiation, which is difficult to explain under Steady State Theory. The theory has since been discarded.