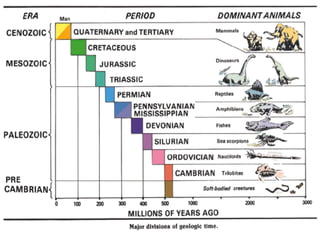
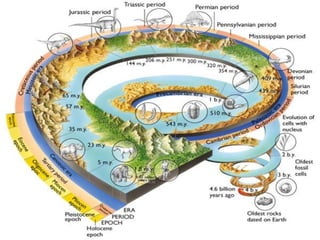
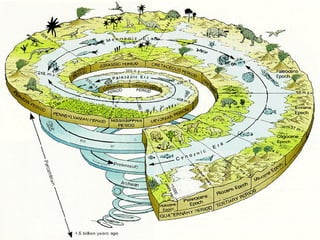
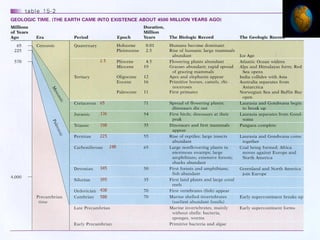
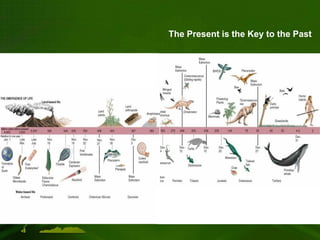
The document summarizes the geological timescale used to divide Earth's history into standardized periods of time. It describes how the timescale is broken down into eons, eras, periods, and epochs. The two main divisions are the Precambrian super eon prior to the Cambrian period and the Phanerozoic eon from the Cambrian period to present day. Precambrian time included the Hadean, Archean, and Proterozoic eons, while the Phanerozoic included the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic eras. The geological timescale provides a standardized framework for correlating and dating rock formations across periods of Earth's history.