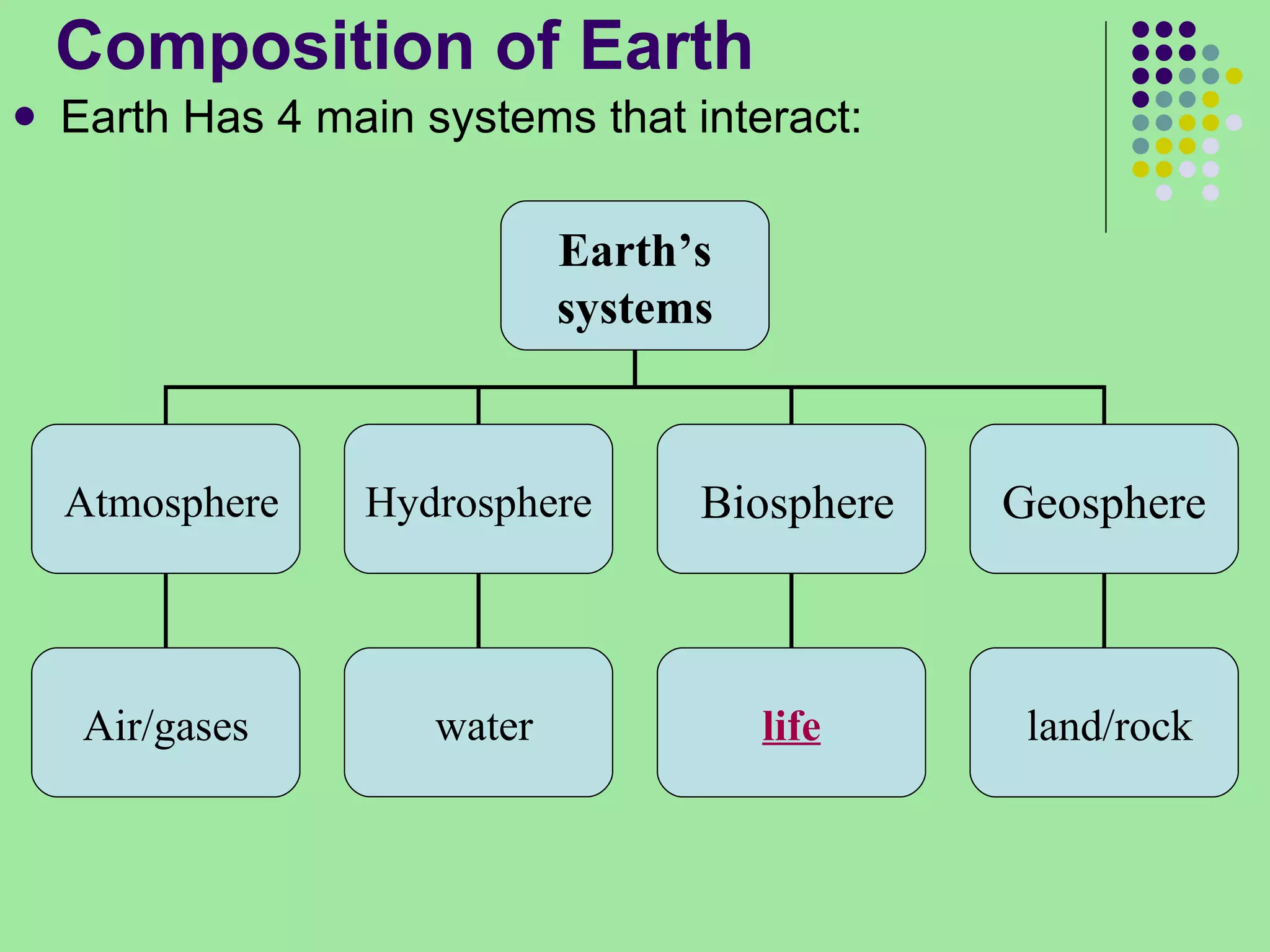
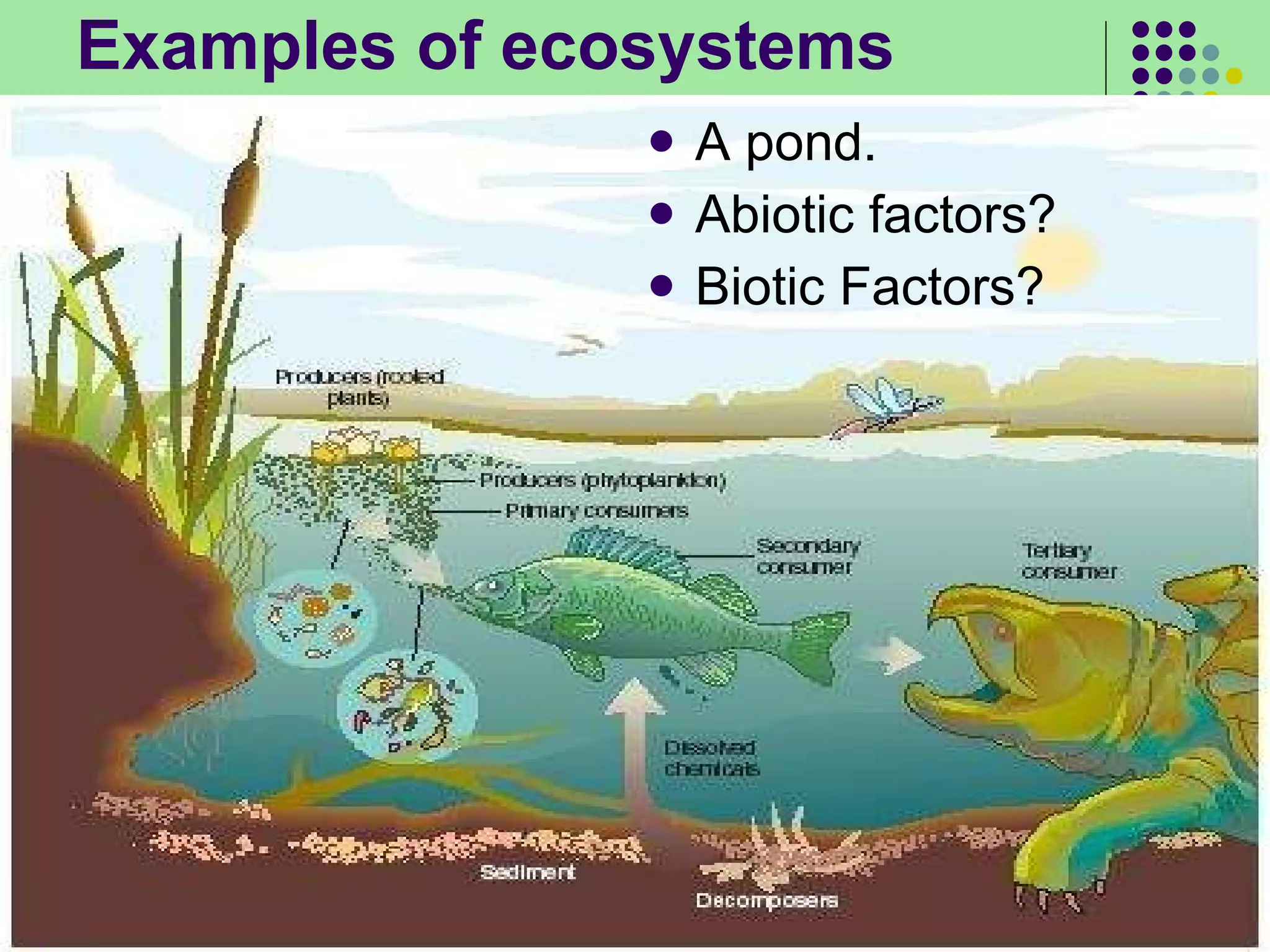
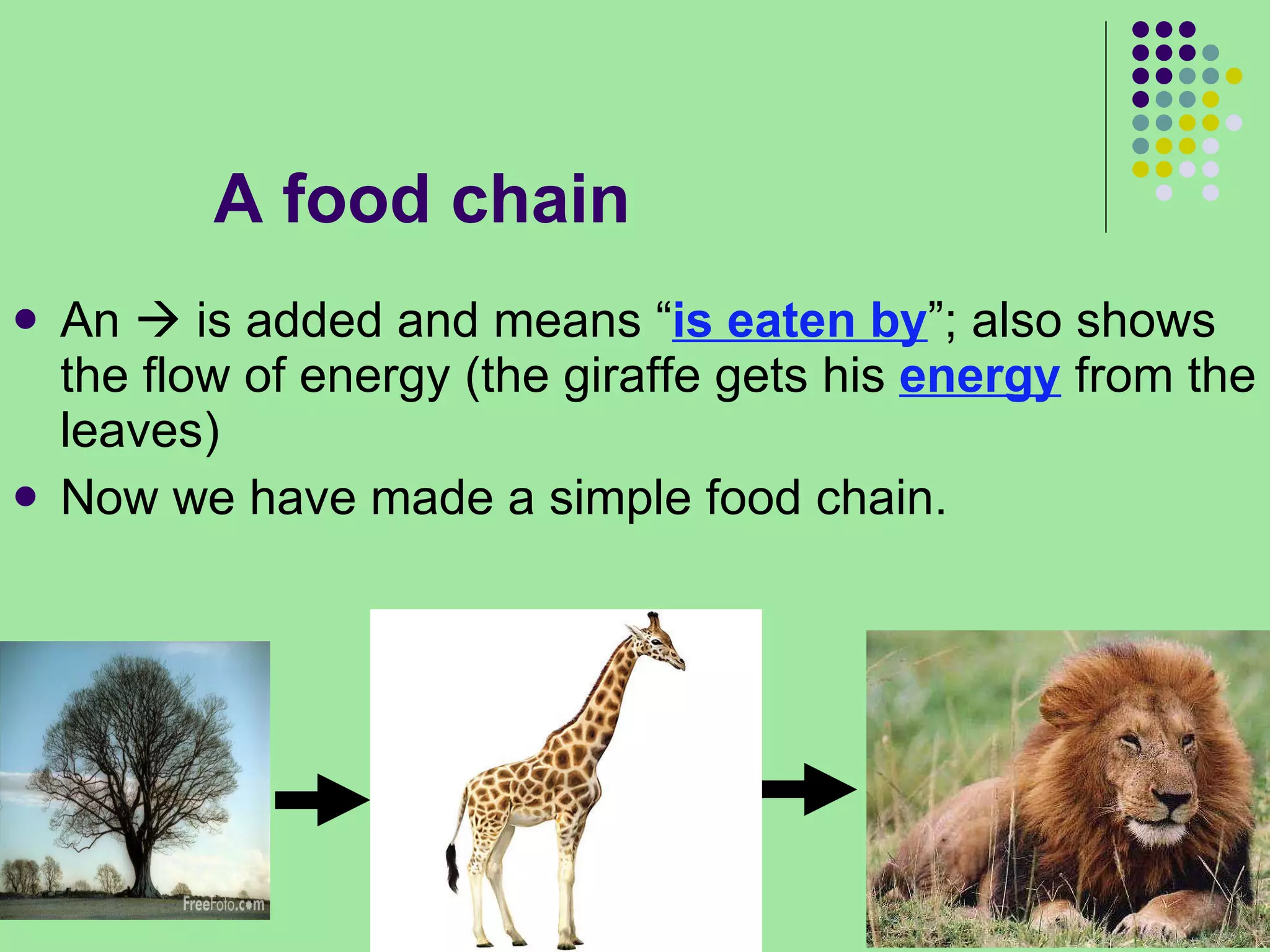
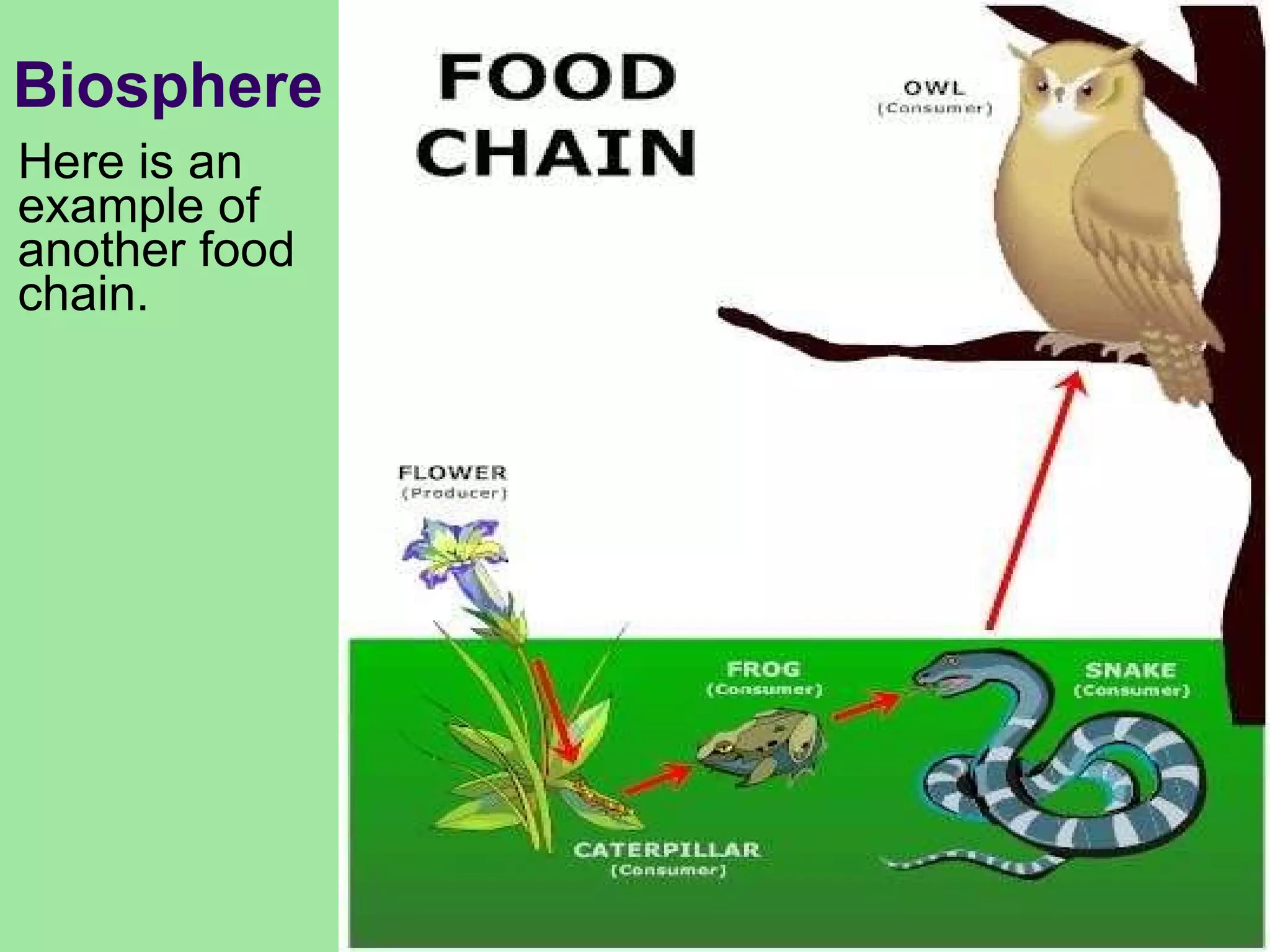
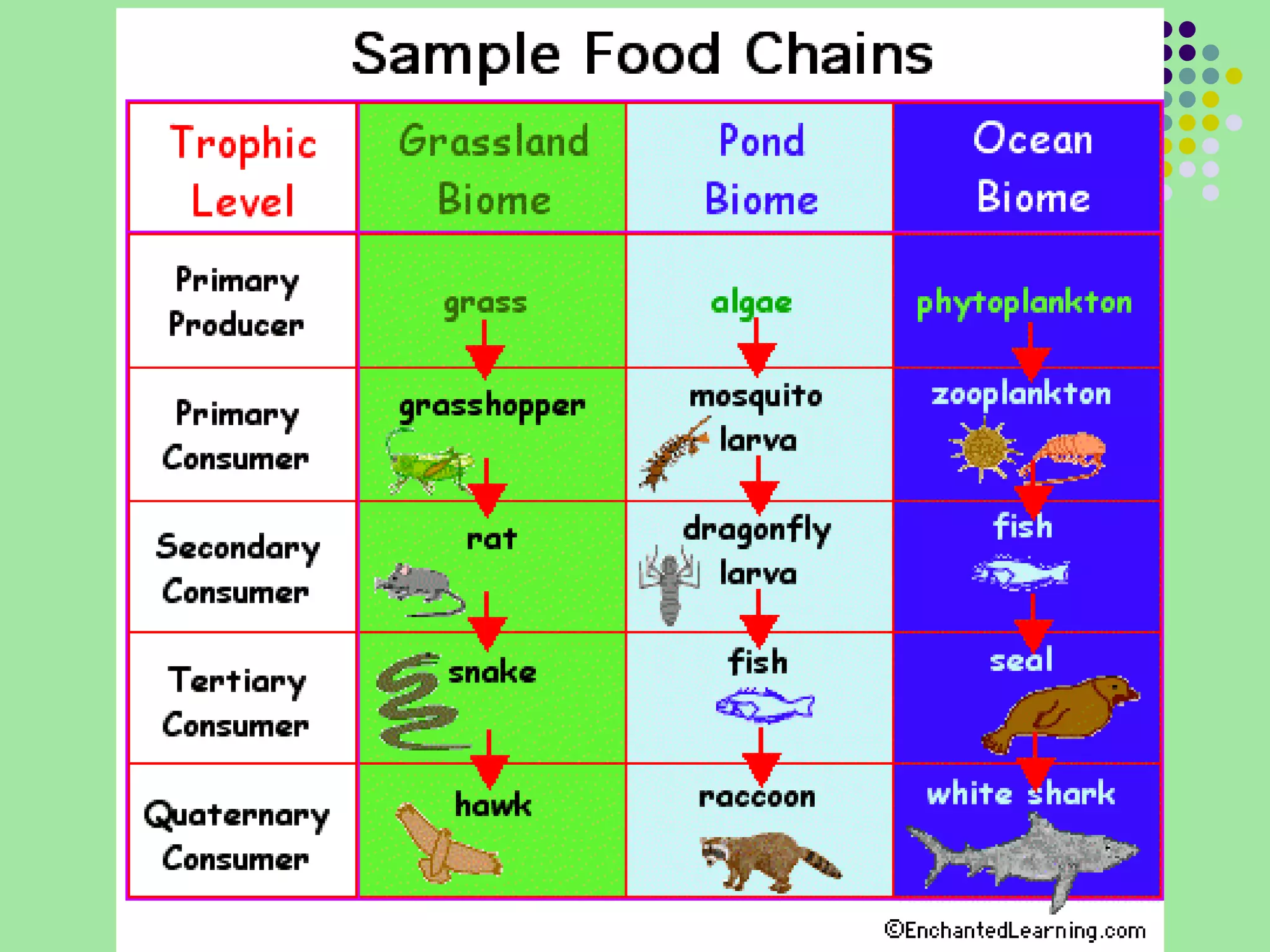
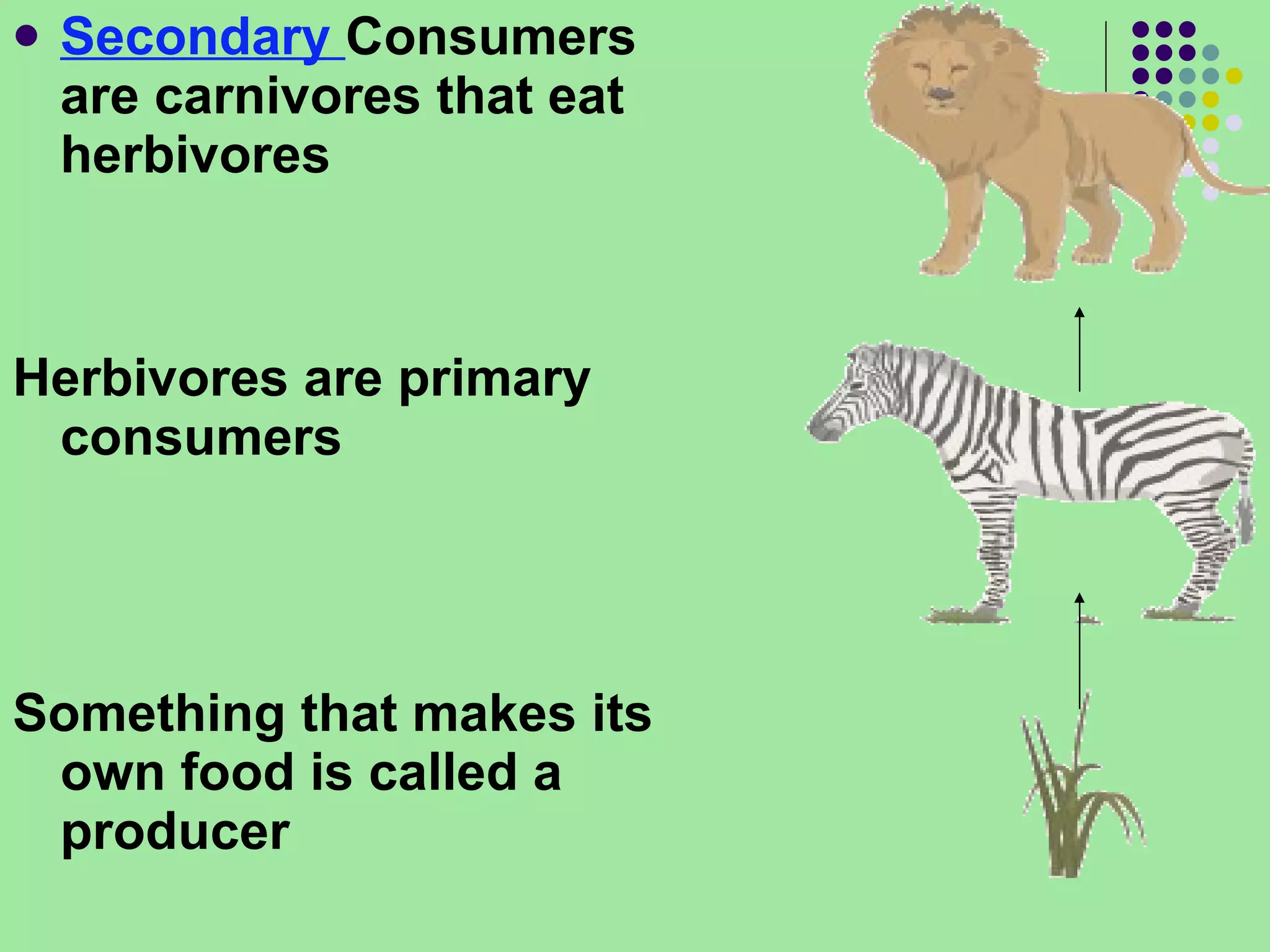
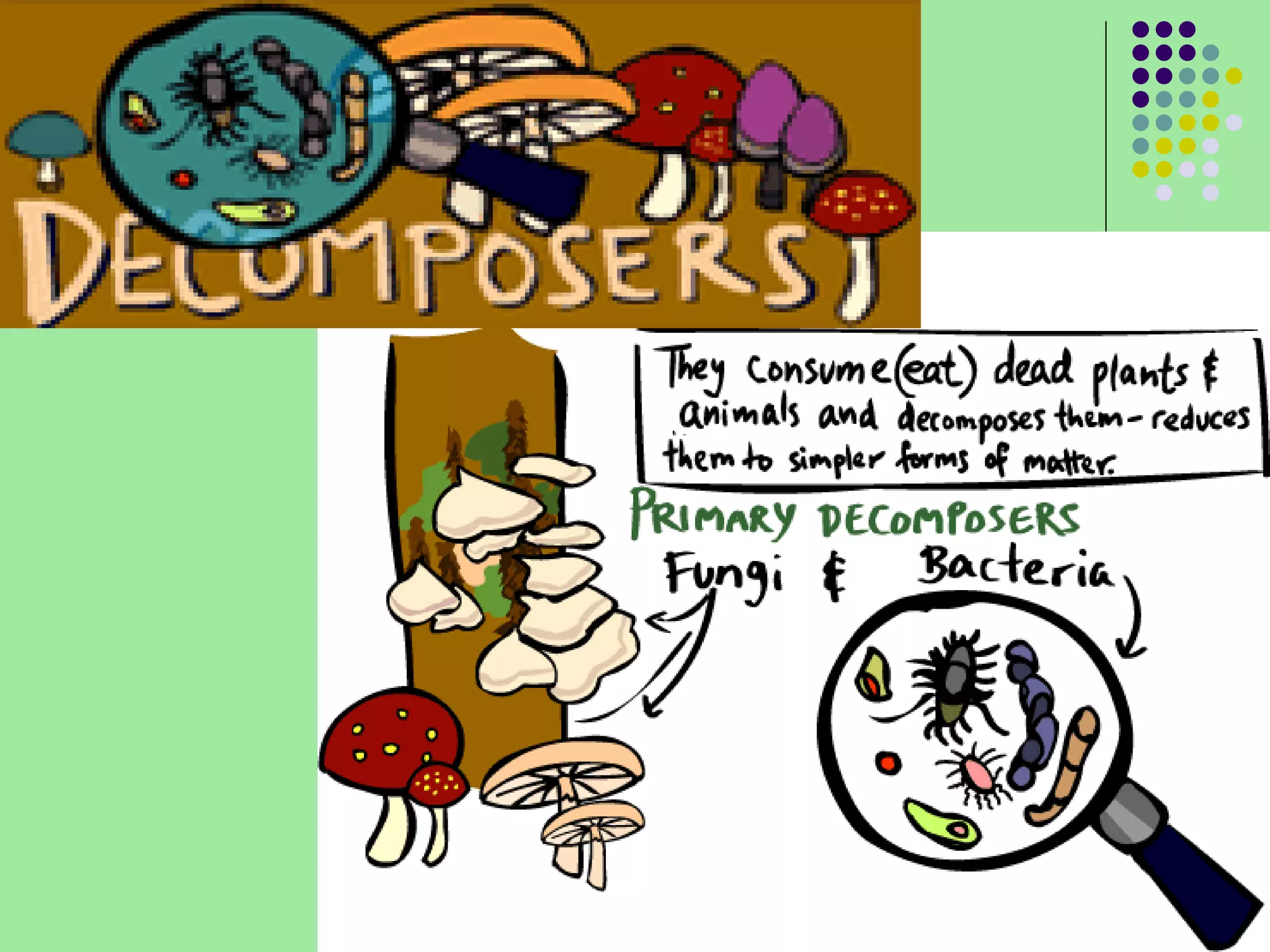
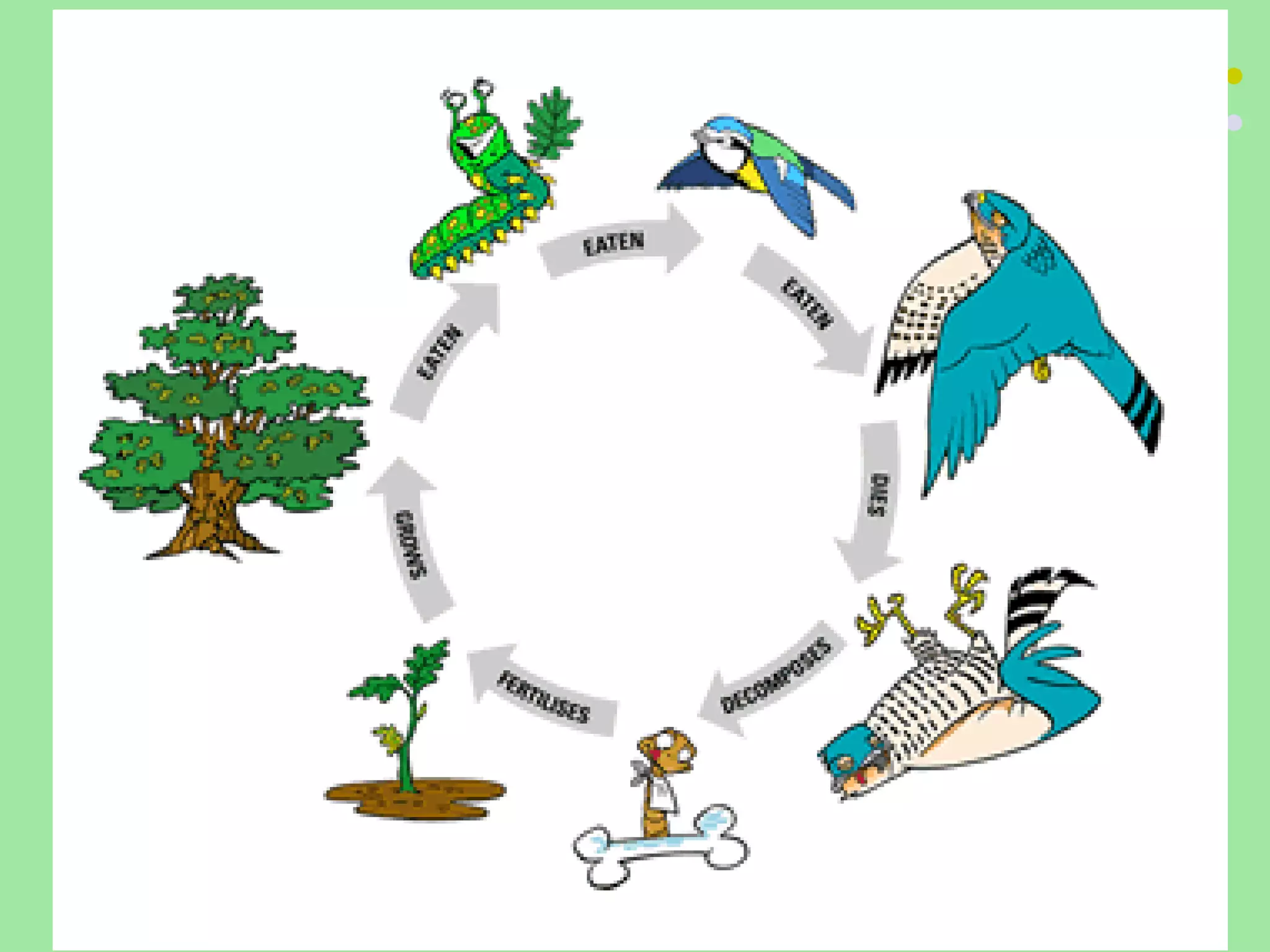
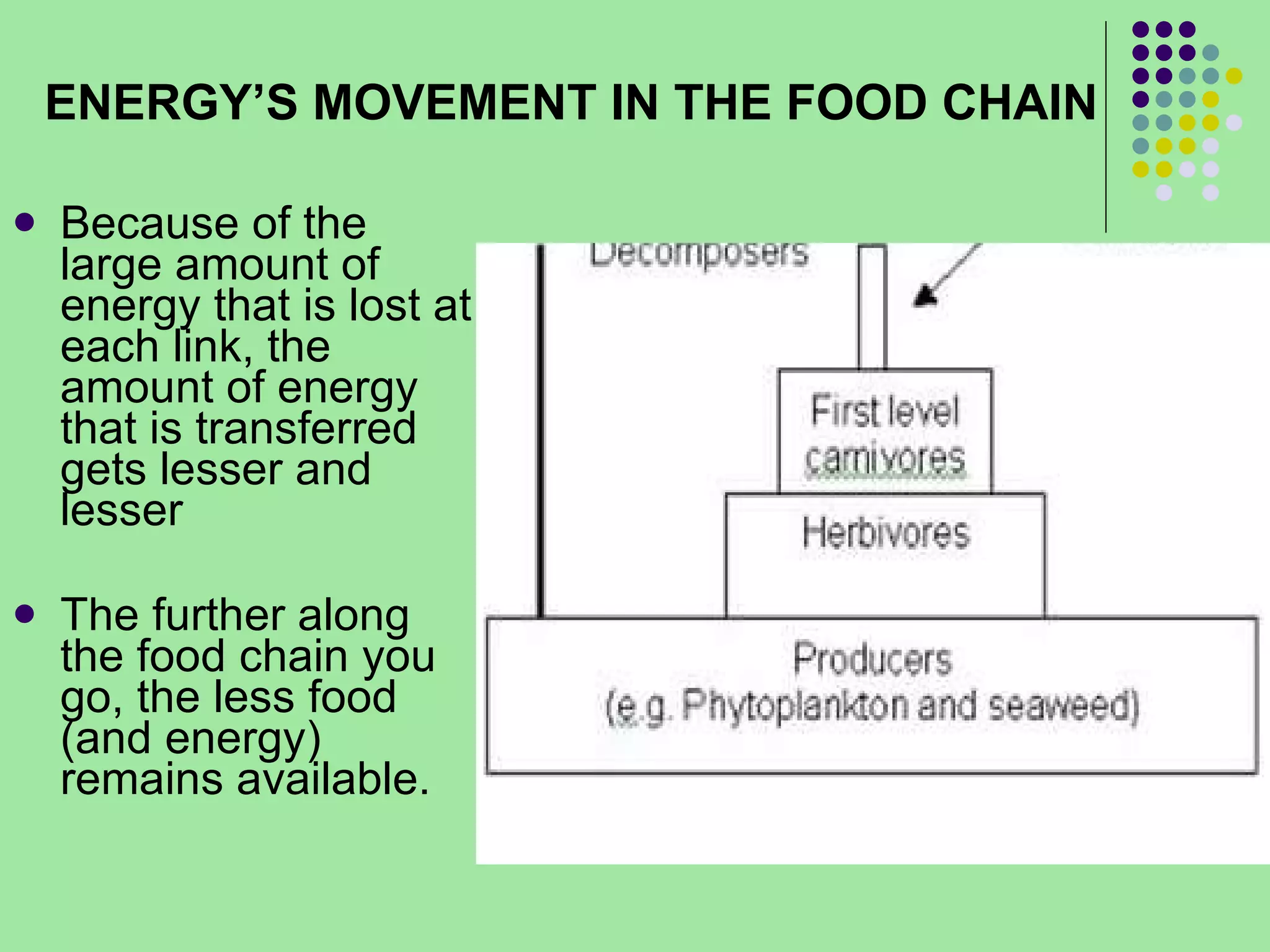
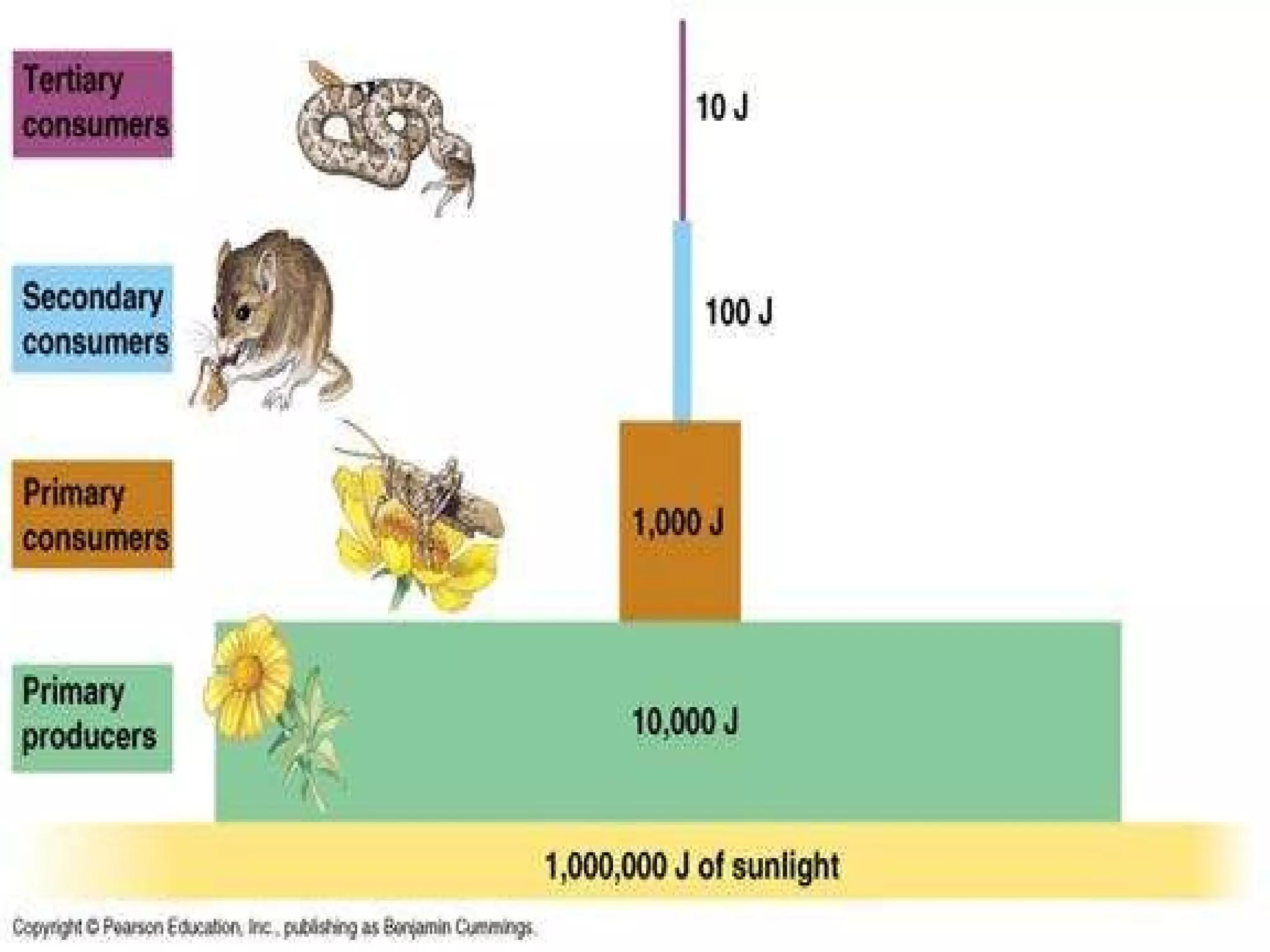
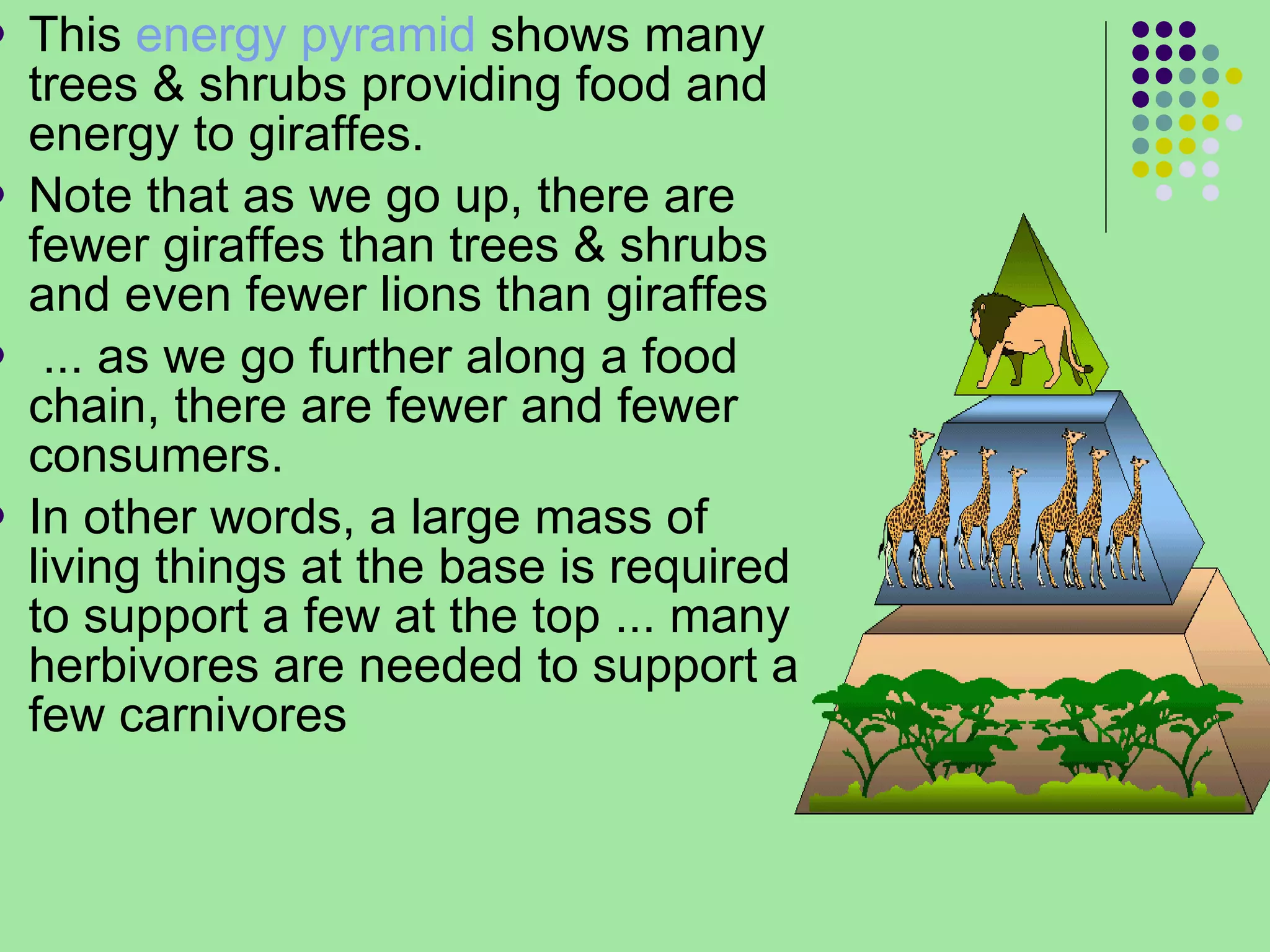
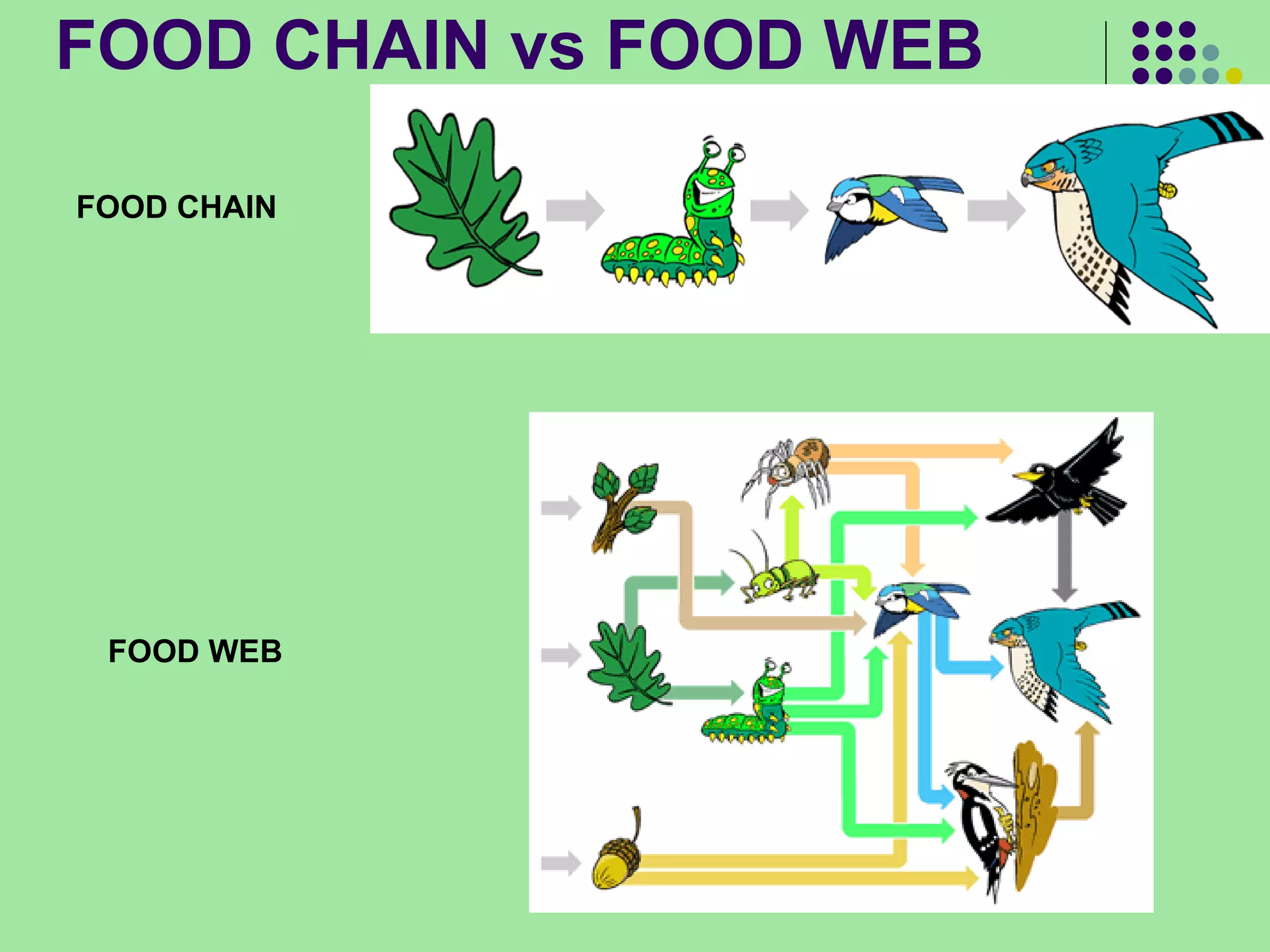
The document discusses the four main systems that make up Earth: the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and geosphere. It focuses on explaining the biosphere and related concepts like ecology, biotic and abiotic factors, food chains, and food webs. The biosphere is made up of all living things that interact with each other and non-living things. Energy from the sun is passed between organisms through food, starting with producers and moving up through herbivores, carnivores, and decomposers. Food chains connect to form more complex food webs in ecosystems.