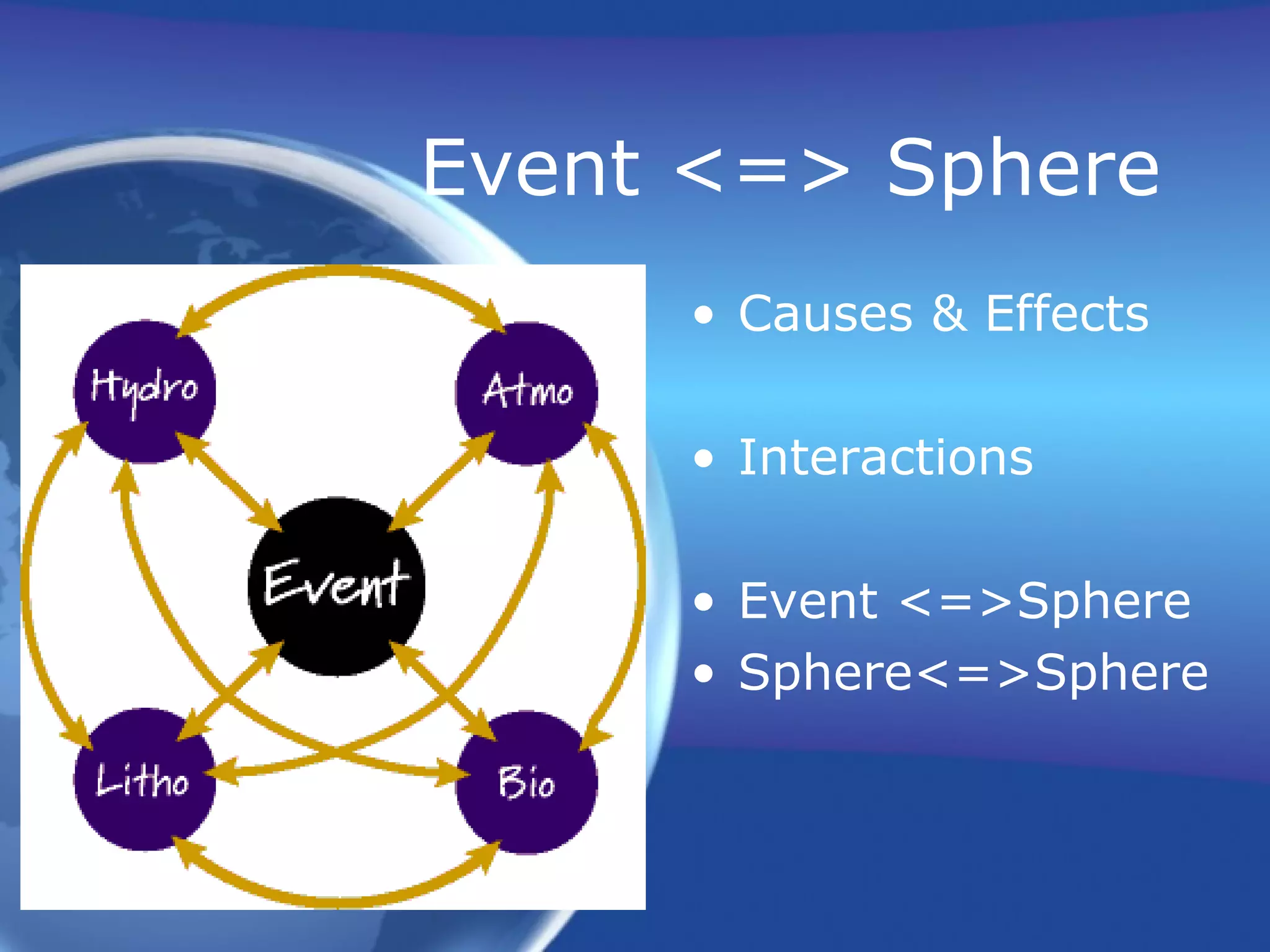
This document discusses Earth System Science (ESS), which studies the interactions between Earth's spheres. It identifies the six main spheres - atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, biosphere, cryosphere, and anthrosphere. The spheres are closely interconnected, so a change in one sphere can trigger changes in others through events and interactions. Understanding these interactions is important for predicting outcomes, preparing for disasters, and assessing human impacts on the environment. ESS analyzes both natural and human-caused events to understand the connections between events and Earth's spheres.