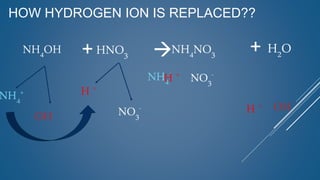
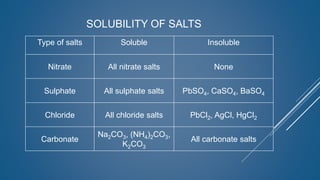
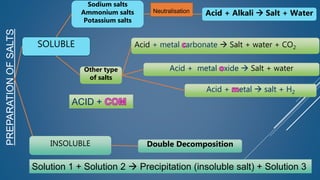
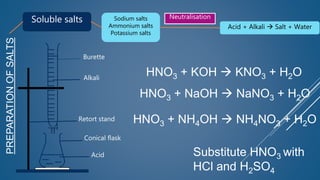
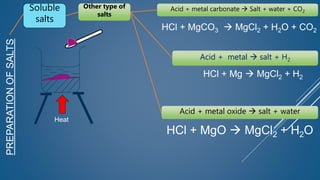
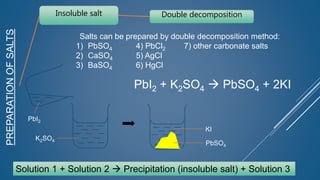
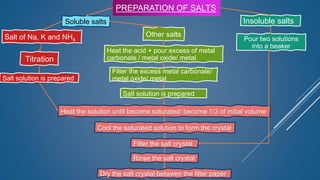
The document discusses the definition, solubility, and preparation methods of salts. It explains how salts are formed through the replacement of hydrogen ions from acids with metal or ammonium ions, and details various types of soluble and insoluble salts. Additionally, it describes different methods for preparing salts, including neutralization reactions and double decomposition.