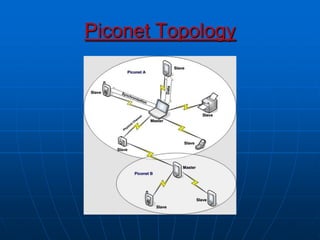
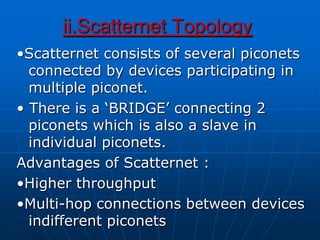
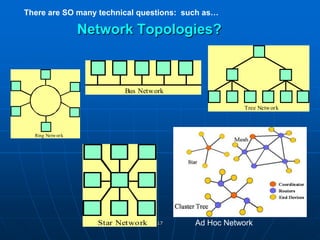
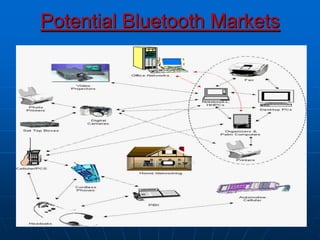
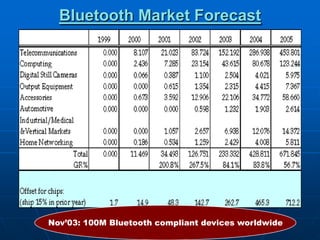
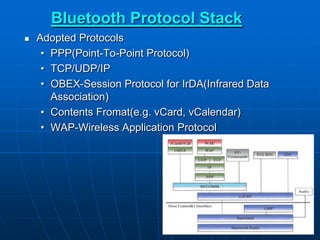
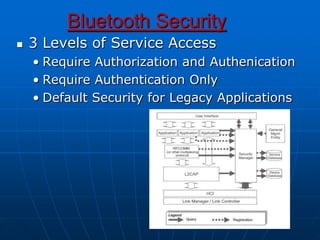
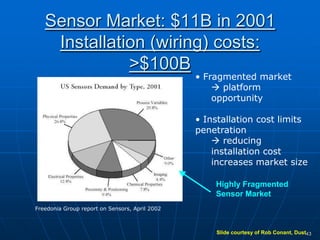
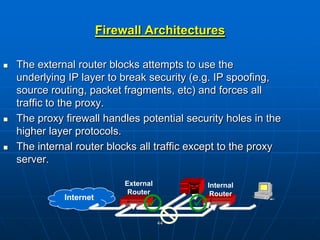
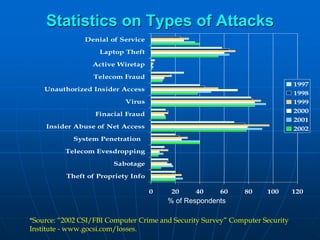
Bluetooth wireless sensor networks can be implemented using Bluetooth technology. Smart sensor nodes equipped with sensors, microprocessors and Bluetooth communication interface can collect data and transmit it to a gateway node. The network involves discovering Bluetooth devices, establishing connections and exchanging data. Algorithms are used for initialization, discovery, parameter setting and data transfer between nodes. While Bluetooth provides benefits like being wireless and inexpensive, it also has limitations such as average data rates and security risks.