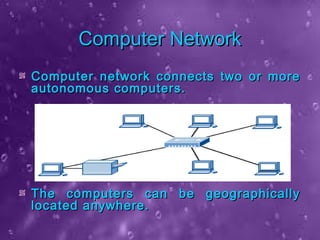
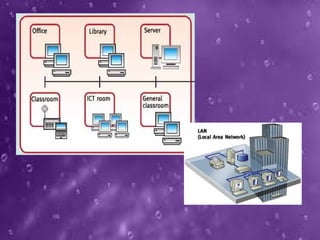
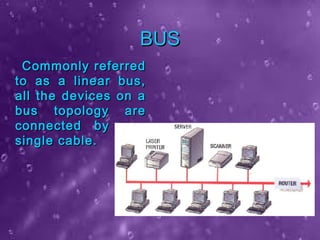
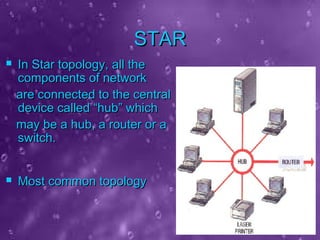
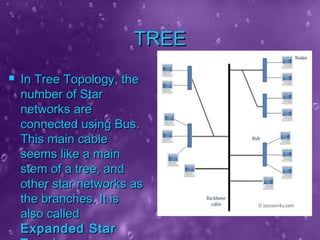
The seminar presented by Priyanka Nain at B.P.S. Women University covers types of computer networks and their topologies, focusing on LAN, MAN, and WAN classifications. It describes the features and geographical scope of each network type, detailing their connection methods and organizational uses. Additionally, it outlines various network topologies, including bus, star, ring, mesh, and tree topologies, explaining how devices are interconnected within each configuration.