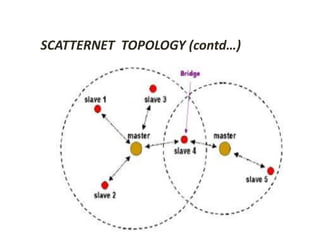
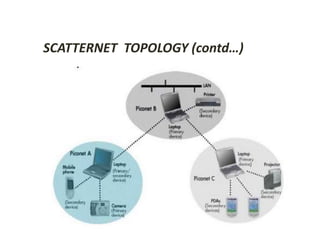
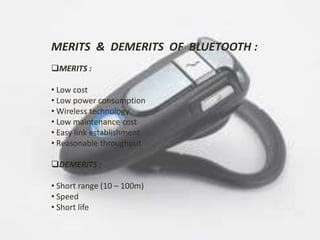
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on Bluetooth technology. It begins by explaining the origin of the name Bluetooth, which comes from a 10th century Viking king known for uniting territories. It then defines Bluetooth as a wireless technology standard for data transfer over short ranges using radio waves. The document outlines the history and development of Bluetooth, describes its specifications and topology including piconets and scatternets. It discusses Bluetooth hardware architecture and lists applications for Bluetooth in electronics and medical devices. It concludes by providing references for further information.