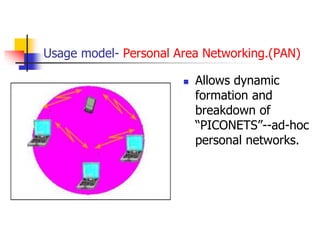
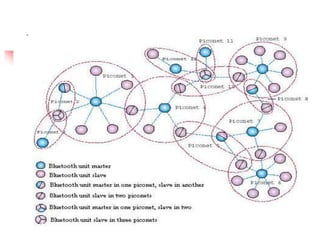
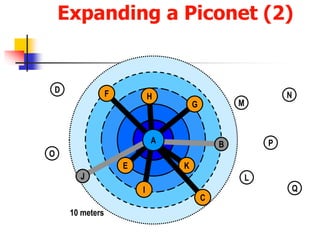
Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard that allows short-range wireless connections between electronic devices like mobile phones, headphones, printers, etc. It was developed by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group to replace wired connections like cables. Bluetooth uses radio waves in the 2.4 GHz spectrum to connect devices within a 10 meter range through ad-hoc networks called piconets. Each piconet can have one master device and up to seven active slave devices connected at once.