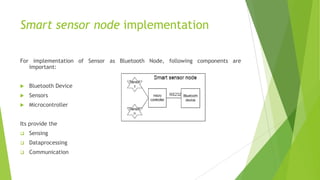
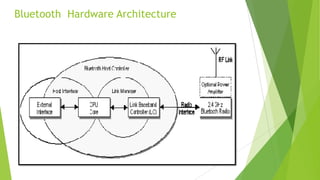
This document discusses a Bluetooth-based smart sensor network, detailing its components, functionalities, and applications across military, environmental, and healthcare sectors. It highlights the advantages of Bluetooth in wireless sensor networks, such as low cost and existing protocols, while also addressing interoperability challenges. Key focuses include the implementation of gateways for communication, discovery of smart sensor nodes, and ongoing research issues related to hardware and software development.