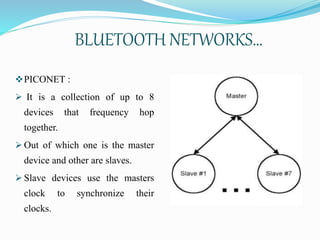
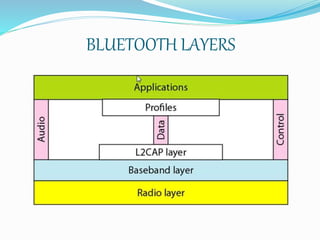
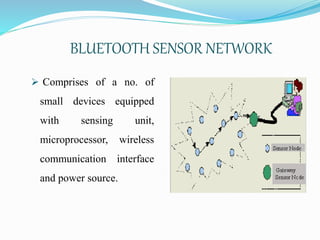
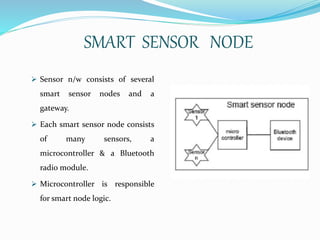
This document provides an overview of Bluetooth technology, including its history, specifications, networks, layers, applications, and issues. Bluetooth was developed in the late 1990s to facilitate short-range wireless connectivity between devices. It uses radio waves and frequency hopping to transmit data between devices within a personal area network. Common applications of Bluetooth technology include connecting headphones, printers, and automobiles. While scalability and throughput are limitations, Bluetooth provides a simple, inexpensive way to connect electronic devices without wires.