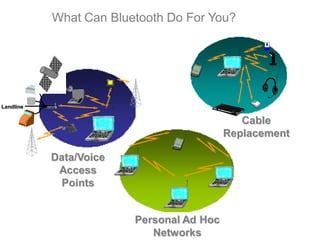
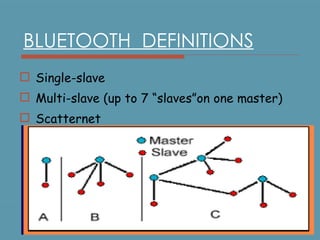
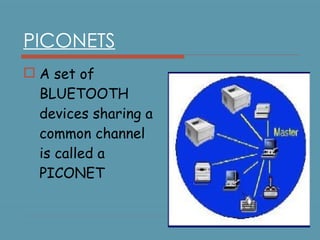
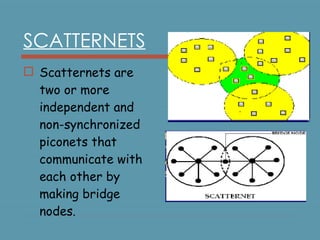
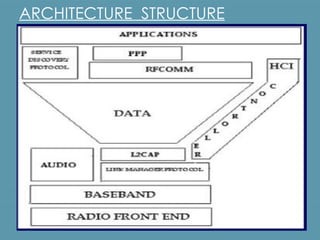
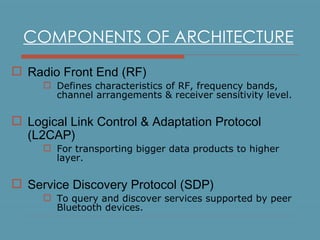
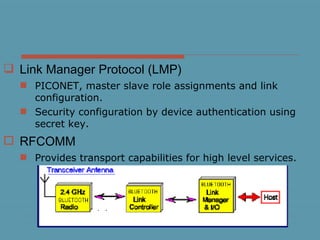
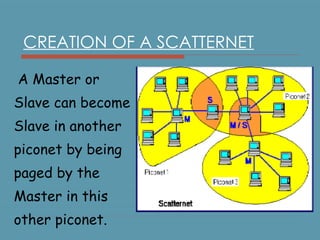
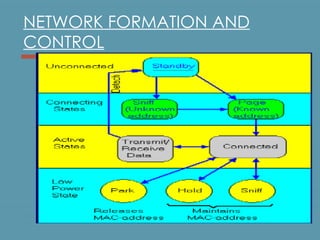
Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances using short-wavelength UHF radio waves in the industrial, scientific and medical radio bands. It allows for connection between devices like computers, phones, keyboards, printers, headsets within a range of about 10 meters. Bluetooth operates using a frequency-hopping spread spectrum in the 2.4 GHz band to avoid interference and jamming. Up to eight devices can be connected in a piconet, with one device acting as the master and up to seven acting as slaves. Multiple piconets can be further connected to form a scatternet, allowing for many more than eight devices to be connected together. Bluetooth is commonly used for hands-free calling, file