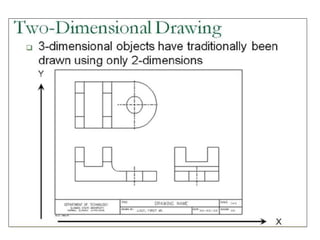
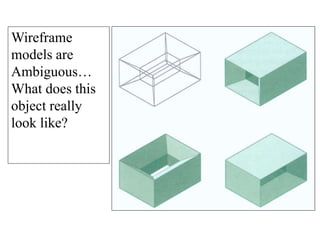
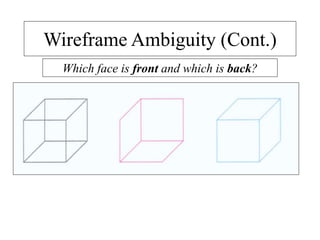
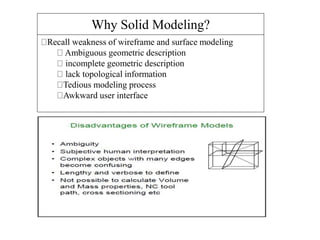
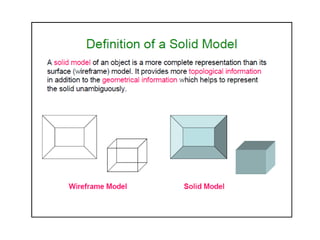
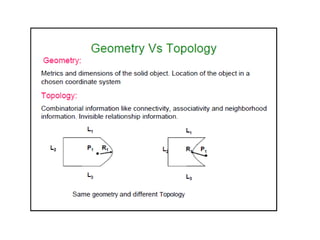
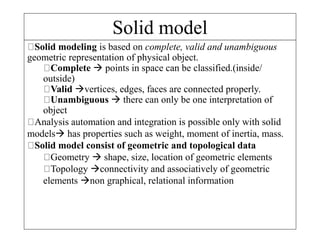
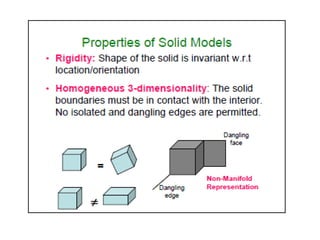
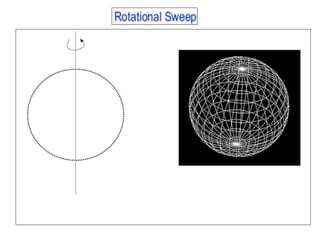
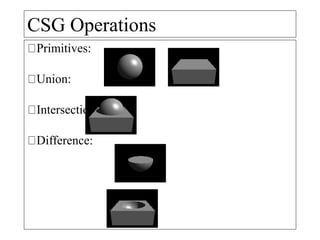
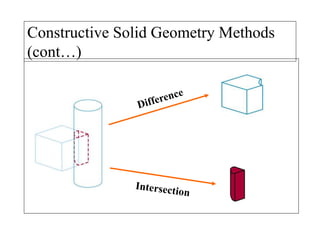
This document discusses different types of 3D modeling including wireframe models, surface models, and solid models. It focuses on solid modeling which provides a complete, valid, and unambiguous geometric representation of physical objects. Solid models contain geometric and topological data and can be represented using constructive solid geometry (CSG) which constructs objects by combining simpler solid objects called primitives using Boolean set operations like union, intersection, and difference. CSG starts with basic primitives that are combined and recombined to model complex objects.