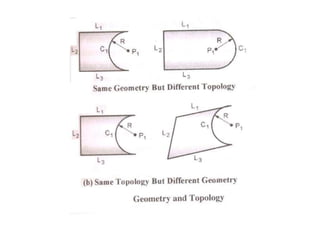
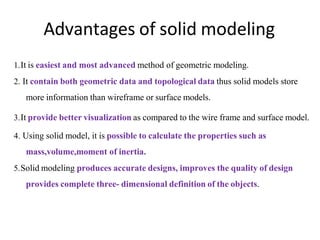
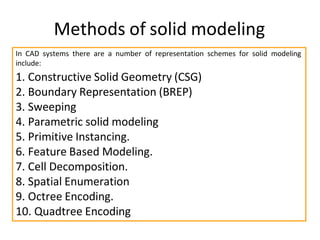
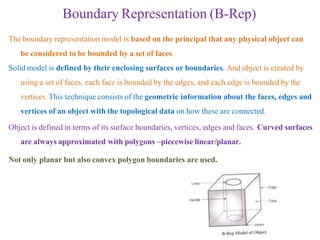
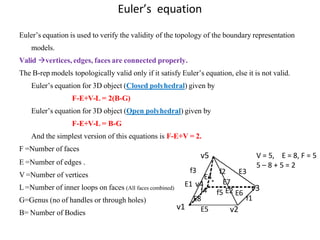
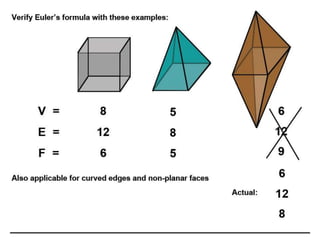
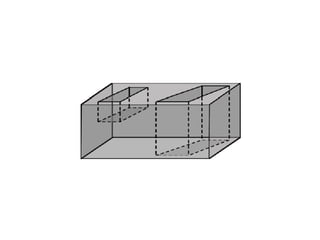
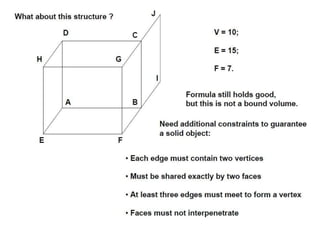
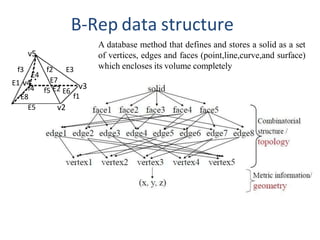
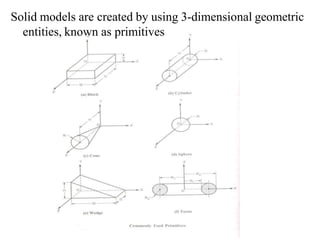
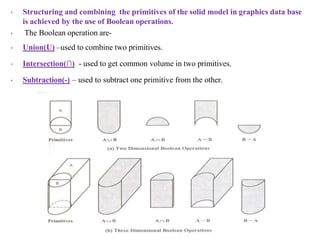
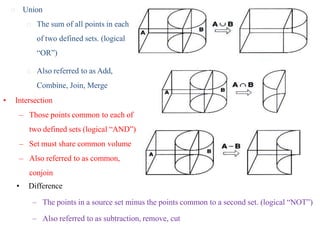
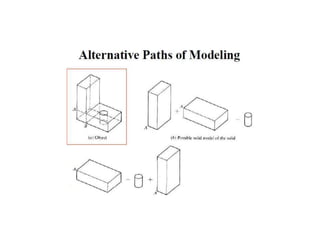
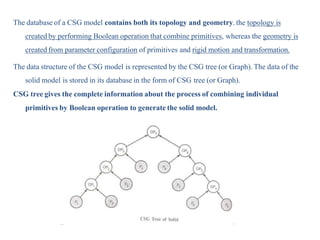
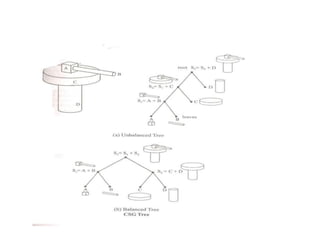
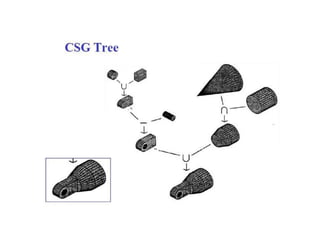
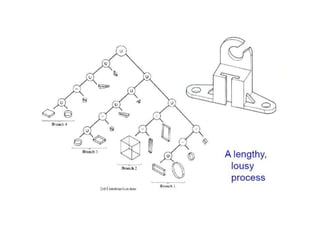
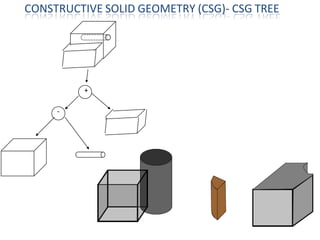
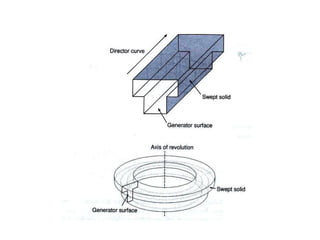
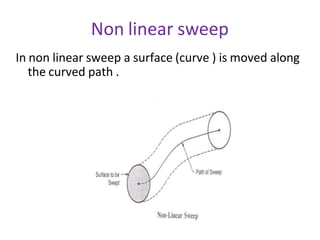
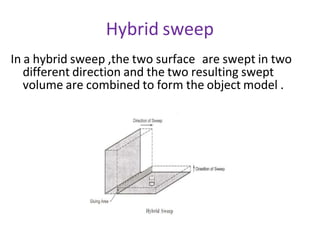
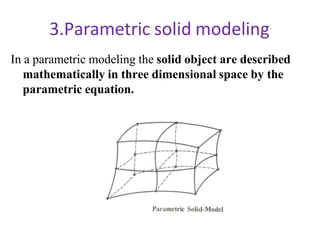
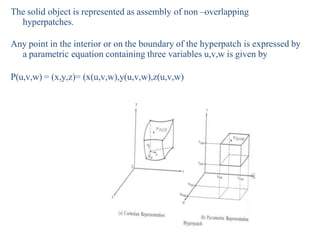
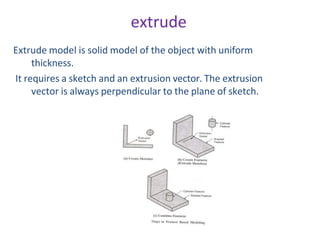
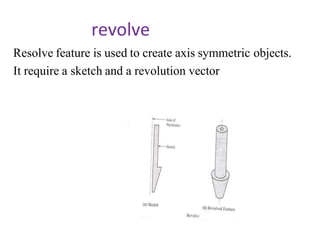
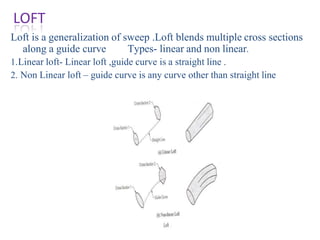
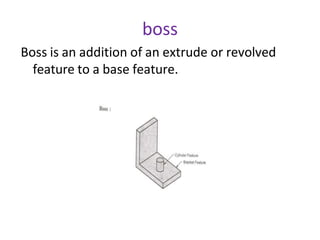
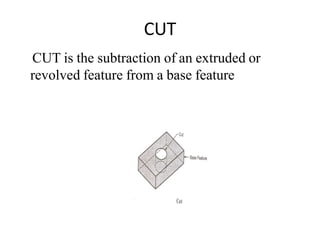
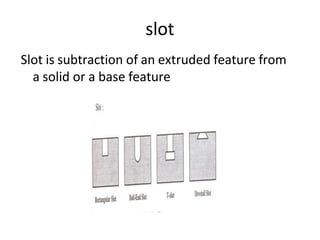
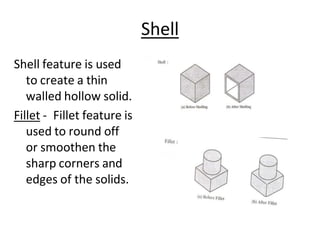
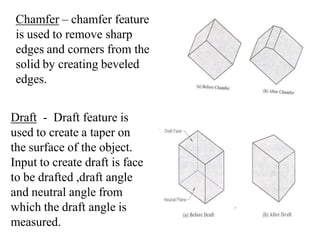
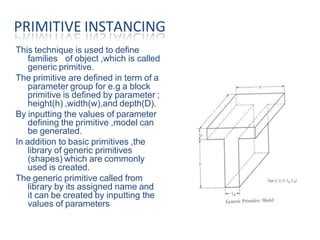
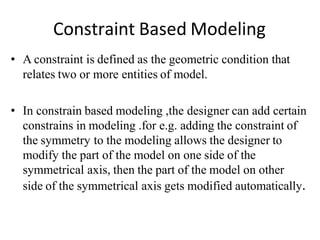
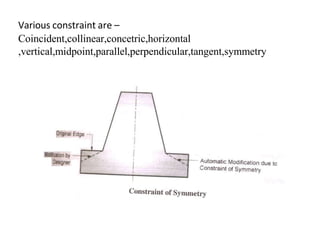
The document discusses solid modeling, emphasizing its advantages over wireframe and surface modeling by providing complete geometric and topological representations of objects. It highlights various methods of solid modeling, including boundary representation (b-rep) and constructive solid geometry (csg), along with their respective strengths and limitations. Solid modeling is integral to design and analysis, offering tools for visualization, property calculations, and effective manufacturing applications.