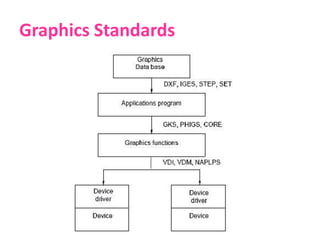
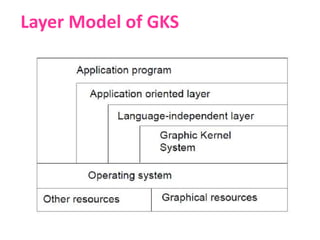
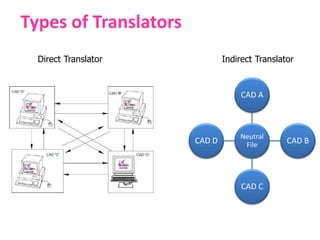
This document discusses various standards used in computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM). It outlines the need for graphics standards to enable portability and device independence. It then describes several key CAD standards, including those for graphics (GKS, PHIGS), data exchange (IGES, STEP, DXF), and communication (LAN, WAN). It provides more detail on specific standards like IGES, STEP, DXF, and VRML. The document emphasizes that standards are crucial to integrating design and manufacturing processes for maximum efficiency.



![Various Interface Standards Exchange Format
• GKS ( Graphical Kernel System)
• PHIGS (Programmer’s Hierarchical Interface for GraphicS)
• GKS -3D
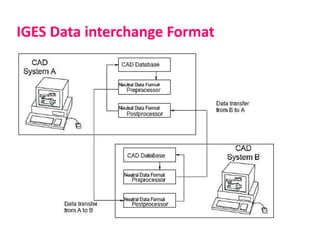
• IGES (Initial Graphics Exchange Specification)
• DXF (Drawing eXchange Format)
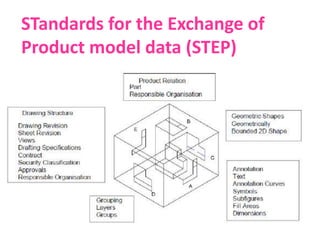
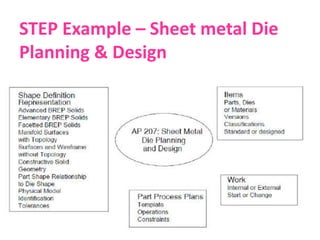
• STEP (STandard for the Exchange of Product Model Data)
• CALS (Continuous Acquisition and Life cycle Support)
• ACIS ( *.sat ) [Alan, Charles, Ian's System]
• OpenGL – Open Graphics Laboratory
• DMIS (Dimensional Measurement Interface Specification)
• VDI (Virtual Device Interface)
• CGI (Computer Graphics Interface)
• VDM (Virtual Device Metafile)
• CGM (Computer Graphics Metafile)
• GKSM (GKS Metafile)
• PDES (Product Data Exchange Standards)
• VRML (Virtual Reality Modelling Language)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cadstandards-190131164024/85/Cad-standards-4-320.jpg)